SBAS649B June 2021 – June 2022 DAC12DL3200
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics - DC Specifications
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics - Power Consumption
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics - AC Specifications
- 6.8 Timing Requirements
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 DAC Output Modes
- 7.3.2 DAC Output Interface
- 7.3.3 LVDS Interface
- 7.3.4 Multi-Device Synchronization (SYSREF+/-)
- 7.3.5 Alarms
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.3.5.4 FIFO Over/Under Flow Alarming
Each of the capture flops on the read side of the FIFO is actually constructed of 3 flops (see Figure 7-20). This allows detection of close timing violations that could corrupt the data flop and is used for detecting under and overflow alarms. This will only detect slow drifts. It will not detect sudden jumps in the operation that might jump over the alarm detection. This will also only detect alarms if the violation occurs when the data is changing. Constant input data will not produce alarms.
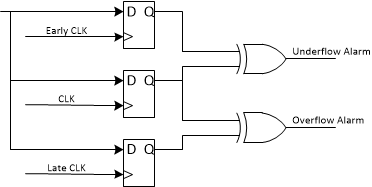 Figure 7-20 Datapath Showing FIFO
Over/Under Flow Alarming
Figure 7-20 Datapath Showing FIFO
Over/Under Flow Alarming