SBAS649B June 2021 – June 2022 DAC12DL3200
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics - DC Specifications
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics - Power Consumption
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics - AC Specifications
- 6.8 Timing Requirements
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 DAC Output Modes
- 7.3.2 DAC Output Interface
- 7.3.3 LVDS Interface
- 7.3.4 Multi-Device Synchronization (SYSREF+/-)
- 7.3.5 Alarms
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.1.3 RF Mode
RF mode adds a mixing function to the DAC output response by inverting the sample halfway through the sample period. The result is a sinc response that peaks and provides maximum flatness in the 2nd Nyquist zone. The timing diagram for RF mode is given in Figure 7-5. A plot of the frequency response of RF mode is shown in Figure 7-6.
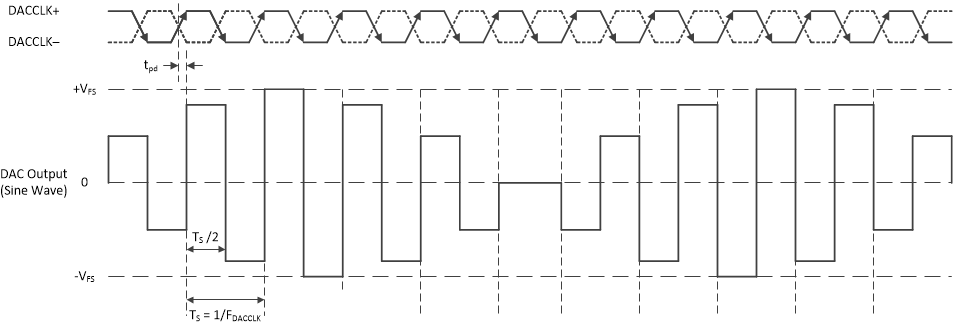 Figure 7-5 RF Mode Timing Diagram
Figure 7-5 RF Mode Timing Diagram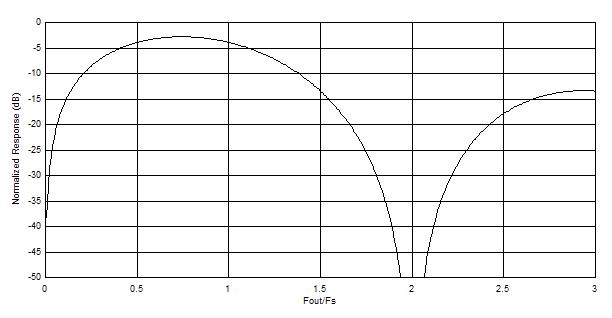 Figure 7-6 RF Mode Output Waveform Response
Figure 7-6 RF Mode Output Waveform Response