SBAU193E June 2011 – May 2021 ADS8568
2.1 ADC Supply, Input, Voltage Reference, and Digital Connections
Figure 2-1 illustrates the decoupling on AVDD, DVDD, HVDD, HVSS, and the reference IO. The capacitors for decoupling match the recommendations in the ADS8568 data sheet. The layout (see Figure 2-1) uses the shortest possible connections to the decoupling capacitors and connections the ground end to the GND plane using vias. The ADS8568 can use an external or internal voltage reference. This can be selected by changing the position of JP9 to “INT” for internal, or “EXT” for external. Figure 2-1 also illustrates the analog input signal and digital signal connections.
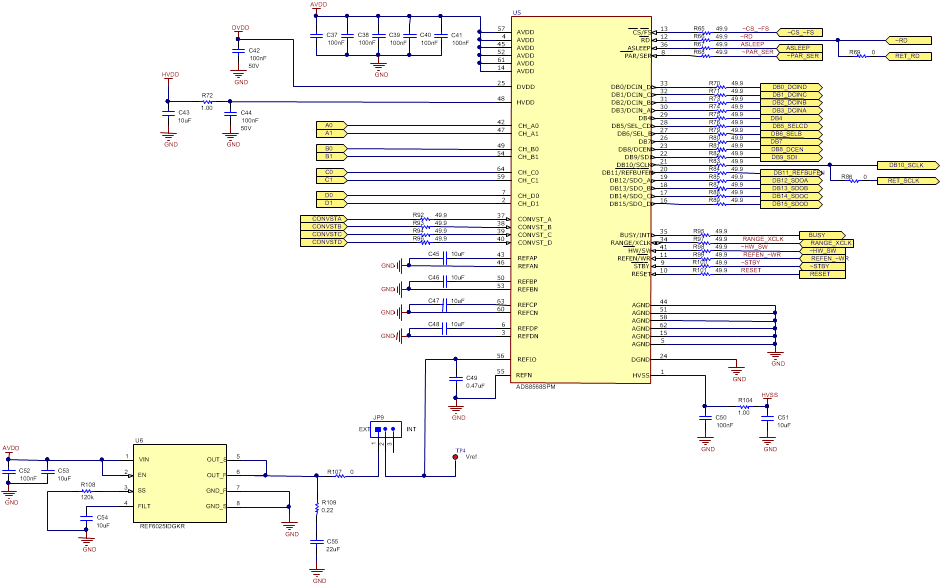 Figure 2-1 ADC Signal and Supply
Connection
Figure 2-1 ADC Signal and Supply
Connection