-
Optimizing Micro Inverter Systems Using Logicand Translation
Optimizing Micro Inverter Systems Using Logicand Translation
1
Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 shows a simplified micro inverter block diagram to illustrate the logic and translation use cases. Each red block has an associated use-case document. Links are provided in Table 1-1 and Table 1-2. For a more complete block diagram, see the interactive online end equipment reference diagram for micro inverters.
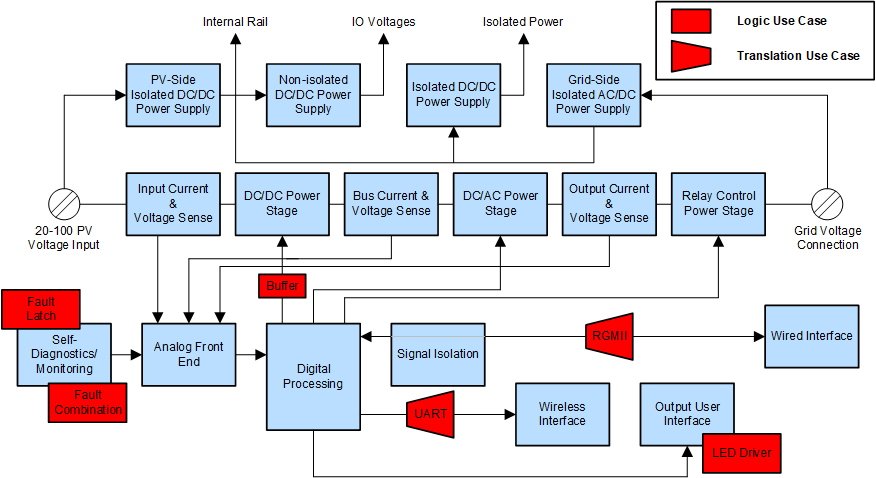 Figure 1-1 Simplified Block Diagram for
Micro Inverters
Figure 1-1 Simplified Block Diagram for
Micro InvertersLogic and Translation Use Cases
Each use case links to a separate document that provides additional details including a block diagram, design tips, and part recommendations. The nearest block and use-case identifiers are listed to match up exactly to the use cases shown in the provided simplified block diagram.
| Nearest Block | Use-Case Identifier | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Diagnostics/Monitoring | Fault Latch | |
| Fault Combination | Use Fewer Inputs to Monitor Error Signals | |
| Digital Processing | Buffer | Redrive Digital Signals |
| Output User Interface | LED Driver | Drive Indicator LEDs |
| Nearest Block | Use-Case Identifier | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Wireless Interface | UART | Voltage Translation for Wireless Interface Modules |
| Wired Interface | RGMII | Translate Voltages for RGMII |
Voltage Translation for Wireless Interface Modules
It is common to see micro inverters utilizing wireless interface modules to communicate due to their distributed nature. These modules often use UART for internal communication, and commonly are operating at a different logic voltage level from the primary system controller. The addition of a voltage level translator protects low-power system controllers and ensures accurate communication to the peripheral module.
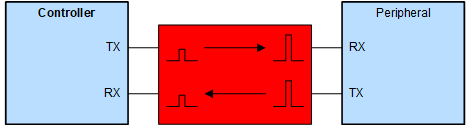 Figure 1-2 Example Two-Wire UART Voltage
Translation Block Diagram
Figure 1-2 Example Two-Wire UART Voltage
Translation Block DiagramSee more about this use case in the Logic Minute video Voltage Level Translation for UART Interface
- Some devices support up to 5 Mbps UART communication; most are limited to 115 kbps or less
- Translators enable communication when devices have mismatched logic voltage levels
- Prevent damage to devices that cannot support higher voltage inputs
- Improve data rates over discrete translation solutions
- Protect controller while peripheral is not connected
- [FAQ] How does a slow or floating input affect a CMOS device?
- Need additional assistance? Ask our engineers a question on the TI E2E™ Logic Support Forum
| Part Number | Automotive Qualified | Voltage Translation Range | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| SN74AXC2T245-Q1 | ✓ | 0.65 V to 3.6 V | Glitch-free power supply sequencing Outputs are disabled when either supply is 0 V Active translation architecture |
| SN74AXC2T245 | |||
| TXB0102 | 1.2 V to 3.6 V to 1.65 V to 5.5 V |
Auto-bidirectional Active translation architecture |
|
| TXS0102-Q1 | ✓ | 1.2 V to 3.6 V to 1.65 V to 5.5 V |
Auto-bidirectional Internal pull-up resistors Passive translation architecture |
For more devices, browse through the online parametric tool where you can sort by desired voltage, channel numbers, and other features.
IMPORTANT NOTICE AND DISCLAIMER
| TI PROVIDES TECHNICAL AND RELIABILITY DATA (INCLUDING DATASHEETS), DESIGN RESOURCES (INCLUDING REFERENCE DESIGNS), APPLICATION OR OTHER DESIGN ADVICE, WEB TOOLS, SAFETY INFORMATION, AND OTHER RESOURCES “AS IS” AND WITH ALL FAULTS, AND DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS AND IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF THIRD PARTY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS. |
| These resources are intended for skilled developers designing with TI products. You are solely responsible for (1) selecting the appropriate TI products for your application, (2) designing, validating and testing your application, and (3) ensuring your application meets applicable standards, and any other safety, security, or other requirements. These resources are subject to change without notice. TI grants you permission to use these resources only for development of an application that uses the TI products described in the resource. Other reproduction and display of these resources is prohibited. No license is granted to any other TI intellectual property right or to any third party intellectual property right. TI disclaims responsibility for, and you will fully indemnify TI and its representatives against, any claims, damages, costs, losses, and liabilities arising out of your use of these resources. |
| TI’s products are provided subject to TI’s Terms of Sale (www.ti.com/legal/termsofsale.html) or other applicable terms available either on ti.com or provided in conjunction with such TI products. TI’s provision of these resources does not expand or otherwise alter TI’s applicable warranties or warranty disclaimers for TI products. |
| Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2021, Texas Instruments Incorporated |