SCPA070 june 2023 TCAL6408 , TCAL6416 , TCAL9538 , TCAL9539 , TCAL9539-Q1
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Programmable Output Drive Strength
- 3 Programmable Pull-Up or Pull-Down Resistors
- 4 Latchable Inputs
- 5 Maskable Interrupt
- 6 Interrupt Status Register
- 7 Programmable Open-Drain and Push-Pull Outputs
- 8 Benefits of Using TCAL I/O Expanders Versus TCA I/O Expanders
- 9 Summary
- 10References
7 Programmable Open-Drain and Push-Pull Outputs
TI’s TCA and TCAL family of devices allow the GPIO pins to be configured for open-drain or push-pull outputs. TCA devices can configure open-drain I/O’s by writing to the configuration and output port registers in a specific sequence.
TCAL devices have a built-in output port configuration register from register address 0x4F. The output port configuration register selects port-wise, push-pull, or open-drain I/O stage. A logic 0 configures the I/O as push-pull. A logic 1 configures the I/O as open-drain. ODEN0 configures the Port 0x and ODEN1 configures Port 1x. This information is defined in Table 7-1.
| BIT | Reserved | ODEN-1 | ODEN-0 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
The affects of using push-pull or open-drain GPIO configurations can be observed by the scope captures taken in Figure 7-1 and Figure 7-2.
The open-drain configuration requires a pull-up resistor on the p-port pin since the drain of the internal FET on the p-port is left floating. This configuration results in a slower rising edge due to the RC time constant caused by the combination of parasitic capacitance and pull-up resistance on the p-port.
The push-pull configuration differs from the open-drain as the push-pull configuration does not require an external pull-up resistor. Internal to the device exists two driving FETS, one to VCC and the other to GND in the push-pull architecture. This configuration results in very fast rise and fall times with steep slew rates, but also introduces larger overshoots and undershoots.
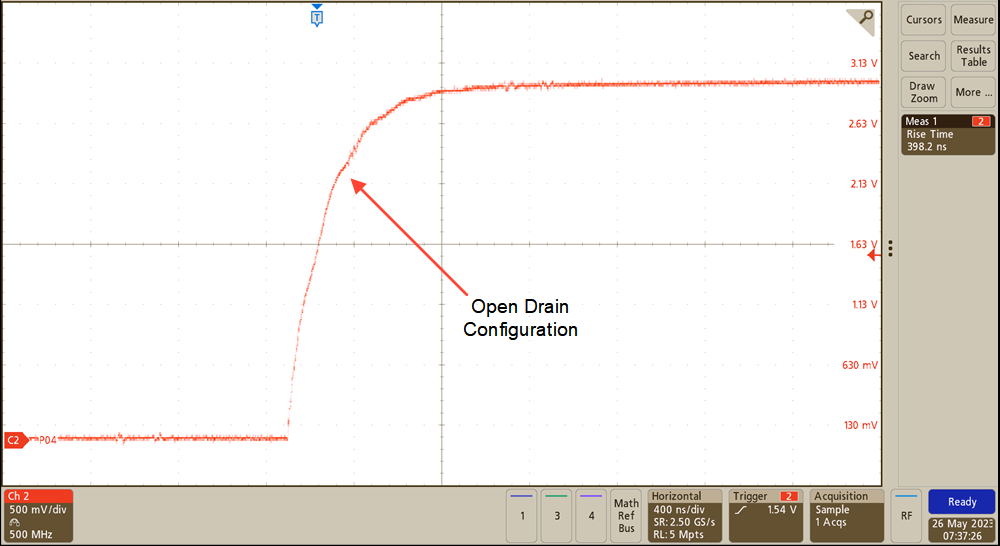 Figure 7-1 Open-Drain
Configuration
Figure 7-1 Open-Drain
Configuration Figure 7-2 Push-Pull
Configuration
Figure 7-2 Push-Pull
Configuration