SLAAE76B march 2023 – june 2023 MSPM0G1105 , MSPM0G1106 , MSPM0G1107 , MSPM0G1505 , MSPM0G1506 , MSPM0G1507 , MSPM0G3105 , MSPM0G3106 , MSPM0G3107 , MSPM0G3505 , MSPM0G3506 , MSPM0G3507
6.1 ADC Design Considerations
MSPM0G devices have a 12-bit, up to 4 Msps, analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The ADC supports fast 12-, 10-, and 8-bit analog-to-digital conversions. The ADC implements a 12-bit SAR core, sample/conversion mode control, and up to 12 independent conversion-and-control buffers.
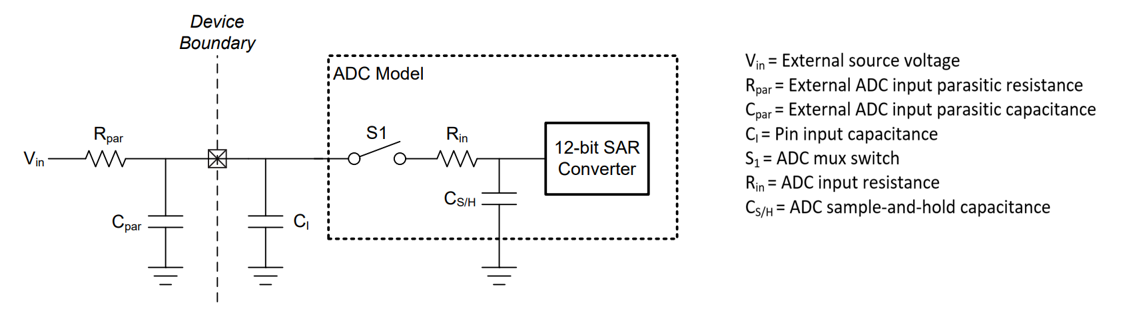 Figure 6-1 ADC Input Network
Figure 6-1 ADC Input NetworkTo achieve the desired conversion speed and keep high accuracy, it is necessary to ensure proper sampling time in hardware design. Sampling (sample-and-hold) time determines how long to sample a signal before digital conversion. During sample time, an internal switch allows the input capacitor to be charged. The required time to fully charge the capacitor is dependent on the external analog front-end (AFE) connected to the ADC input pin. Figure 6-1shows a typical ADC model of an MSPM0G MCU. The Rin and CS/H values can be obtained from the device-specific data sheet. It is critical to understand the AFE drive capability and calculate the minimum sampling time required to sample the signal. The resistance of RPar and Rin affects tsample. Equation 1 can be used to calculate a conservative value of the minimum sample time tsample for an n-bit conversion:
To evaluate continuous high speed (4 Msps) ADC performance, TI recommends adding an external buffer to ensure sufficient signal source drive capability. As a design reference, see the LP-MSPM0G3507 hardware design, which includes a recommended external OPA.