SLAAE76B march 2023 – june 2023 MSPM0G1105 , MSPM0G1106 , MSPM0G1107 , MSPM0G1505 , MSPM0G1506 , MSPM0G1507 , MSPM0G3105 , MSPM0G3106 , MSPM0G3107 , MSPM0G3505 , MSPM0G3506 , MSPM0G3507
2.1 Digital Power Supply
An internal low-dropout linear voltage regulator generates a 1.35-V supply rail to power the device core. In general, the core regulator output (VCORE) supplies power to the core logic, which includes the CPU, digital peripherals and the device memory. The core regulator requires an external capacitor (CVCORE) which is connected between the device VCORE pin and VSS (ground) (see Figure 2-1). See the device-specific data sheet for the correct value and tolerance of CVCORE. CVCORE should be placed close to the VCORE pin.
The core regulator is active in all power modes except for SHUTDOWN. In all other power modes (RUN, SLEEP, STOP, and STANDBY) the drive strength of the regulator is configured automatically to support the max load current of each mode. This reduces the quiescent current of the regulator when using low power modes, improving low power performance.
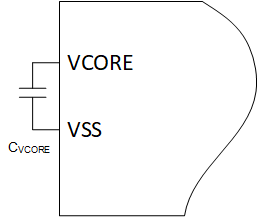 Figure 2-1 VCORE Regulator Circuit
Figure 2-1 VCORE Regulator Circuit