SLAAEG4 October 2023 MSPM0C1104 , MSPM0L1306
7.2 UART and LIN Resources and Design Considerations
The MSPM0C series MCU includes Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter (UART). As seen in Table 7-2, UART0 supports LIN, DALI, IrDA, ISO7816 Manchester Coding function.
| UART Features | UART0 (Extend) |
|---|---|
| Active in Stop and Standby Mode | Yes |
| Separate transmit and receive FIFOs | Yes |
| Support hardware flow control | Yes |
| Support 9-bit configuration | Yes |
| Support LIN mode | Yes |
| Support DALI | Yes |
| Support IrDA | Yes |
| Support ISO7816 Smart Card | Yes |
| Support Manchester coding | Yes |
| PARAMETERS | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fUART | UART input clock frequency | 24 | MHz | |||
| fBITCLK | BITCLK clock frequency(equals baud rate in MBaud) | 3 | MHz | |||
| tSP | Pulse duration of spikes suppressed by input filter | AGFSELx = 0 | 6 | TODO | ns | |
| AGFSELx = 1 | 14 | 35 | ns | |||
| AGFSELx = 2 | 22 | 60 | ns | |||
| AGFSELx = 3 | 35 | 90 | ns | |||
The MSPM0C UART module can support up to 3-MHz baud date, this can support almost all UART applications.
Local Interconnect Network (LIN) is a commonly used low-speed network interface that consists of a commander node communicating with multiple remote responder nodes. Only a single wire is required for communication and is commonly included in the vehicle wiring harness.
The TLIN1021A-Q1 transmitter supports data rates up to 20 kbps. The transceiver controls the state of the LIN bus through the TXD pin and reports the state of the bus on its open-drain RXD output pin. The device has a current-limited wave-shaping driver to reduce electromagnetic emissions (EME).
The TLIN1021A-Q1 is designed to support 12-V applications with a wide input voltage operating range. The device supports low-power sleep mode, as well as wake-up from low-power mode via wake over LIN, the WAKE pin, or the EN pin. The device allows for system-level reductions in battery current consumption by selectively enabling the various power supplies that can be present on a node through the TLIN1021A-Q1 INH output pin. Figure 7-1 shows a typical interface implemented using the TI TLIN1021A LIN transceiver.
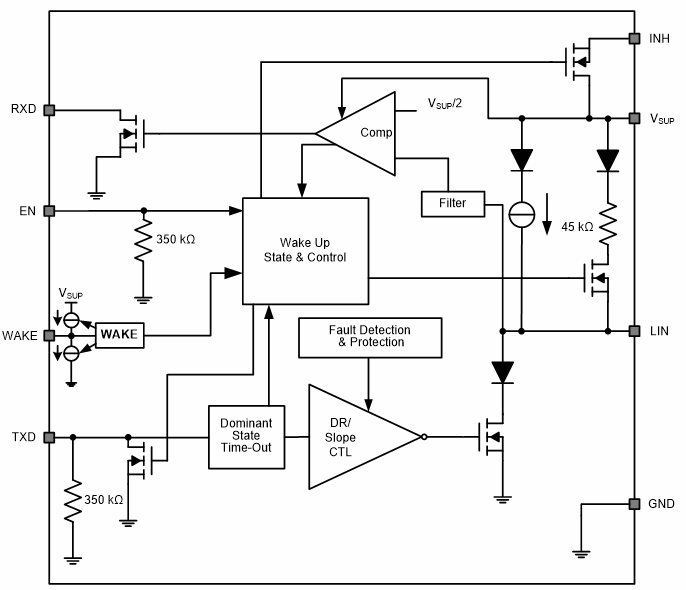 Figure 7-1 Typical LIN TLIN1021A
Transceiver
Figure 7-1 Typical LIN TLIN1021A
TransceiverOnly a single wire is required for communication and is commonly included in the vehicle wiring harness. Figure 7-2 and Figure 7-3 shows a typical interface implemented using the TI TLIN1021A LIN transceiver. For more details, see the device-specific TLIN1021 data sheet.
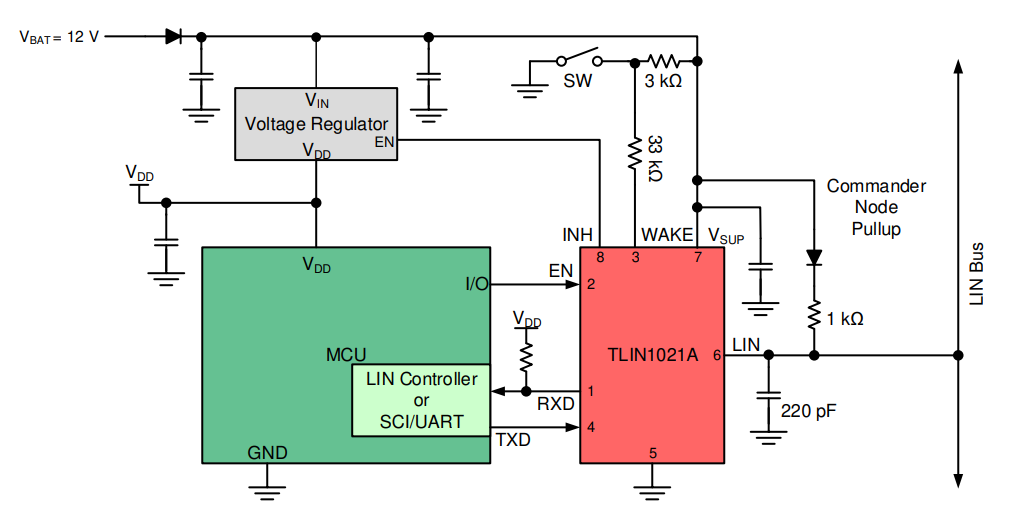 Figure 7-2 Typical LIN
Application(Commander) with MSPM0C
Figure 7-2 Typical LIN
Application(Commander) with MSPM0C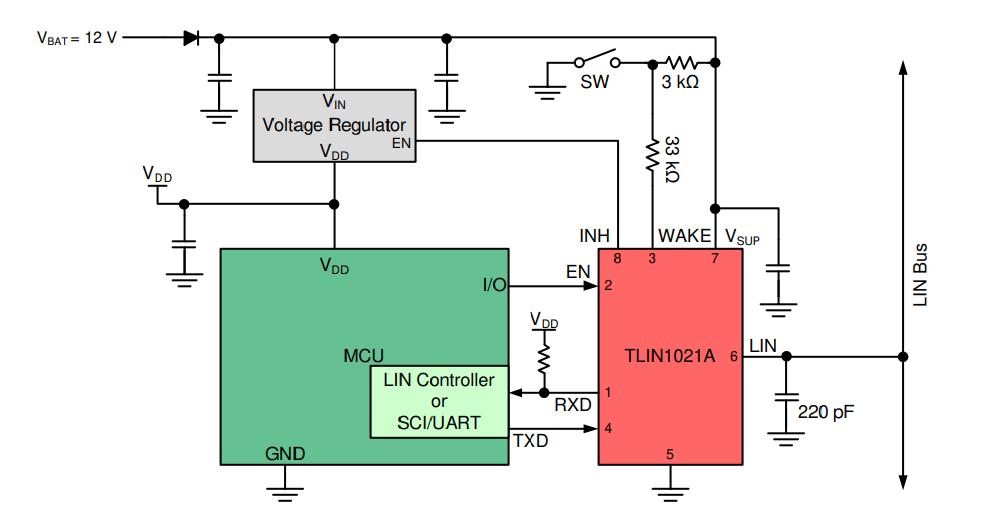 Figure 7-3 Typical LIN
Application(Responder) with MSPM0C
Figure 7-3 Typical LIN
Application(Responder) with MSPM0C