SLAU846A June 2023 – October 2023 MSPM0G1105 , MSPM0G1106 , MSPM0G1107 , MSPM0G1505 , MSPM0G1506 , MSPM0G1507 , MSPM0G3105 , MSPM0G3105-Q1 , MSPM0G3106 , MSPM0G3106-Q1 , MSPM0G3107 , MSPM0G3107-Q1 , MSPM0G3505 , MSPM0G3505-Q1 , MSPM0G3506 , MSPM0G3506-Q1 , MSPM0G3507 , MSPM0G3507-Q1
- 1
- Read This First
-
1 Architecture
- 1.1 Architecture Overview
- 1.2 Bus Organization
- 1.3 Platform Memory Map
- 1.4
Boot Configuration
- 1.4.1 Configuration Memory (NONMAIN)
- 1.4.2 Boot Configuration Routine (BCR)
- 1.4.3 Bootstrap Loader (BSL)
- 1.5 NONMAIN Registers
- 1.6 Factory Constants
-
2 PMCU
- 2.1 PMCU Overview
- 2.2 Power Management (PMU)
- 2.3
Clock Module (CKM)
- 2.3.1 Oscillators
- 2.3.2
Clocks
- 2.3.2.1 MCLK (Main Clock) Tree
- 2.3.2.2 CPUCLK (Processor Clock)
- 2.3.2.3 ULPCLK (Low-Power Clock)
- 2.3.2.4 MFCLK (Middle Frequency Clock)
- 2.3.2.5 MFPCLK (Middle Frequency Precision Clock)
- 2.3.2.6 LFCLK (Low-Frequency Clock)
- 2.3.2.7 HFCLK (High-Frequency External Clock)
- 2.3.2.8 HSCLK (High Speed Clock)
- 2.3.2.9 ADCCLK (ADC Sample Period Clock)
- 2.3.2.10 CANCLK (CAN-FD Functional Clock)
- 2.3.2.11 RTCCLK (RTC Clock)
- 2.3.2.12 External Clock Output (CLK_OUT)
- 2.3.2.13 Direct Clock Connections for Infrastructure
- 2.3.3 Clock Tree
- 2.3.4 Clock Monitors
- 2.3.5 Frequency Clock Counter (FCC)
- 2.4
System Controller (SYSCTL)
- 2.4.1 Resets and Device Initialization
- 2.4.2 Operating Mode Selection
- 2.4.3 Asynchronous Fast Clock Requests
- 2.4.4 SRAM Write Protection
- 2.4.5 Flash Wait States
- 2.4.6 Flash Bank Address Swap
- 2.4.7 Shutdown Mode Handling
- 2.4.8 Configuration Lockout
- 2.4.9 System Status
- 2.4.10 Error Handling
- 2.4.11 SYSCTL Events
- 2.5
Quick Start Reference
- 2.5.1 Default Device Configuration
- 2.5.2 Leveraging MFCLK
- 2.5.3 Optimizing Power Consumption in STOP Mode
- 2.5.4 Optimizing Power Consumption in STANDBY Mode
- 2.5.5 Increasing MCLK and ULPCLK Precision
- 2.5.6 Configuring MCLK for Maximum Speed
- 2.5.7 High Speed Clock (SYSPLL, HFCLK) Handling in Low-Power Modes
- 2.5.8 Optimizing for Lowest Wakeup Latency
- 2.5.9 Optimizing for Lowest Peak Current in RUN/SLEEP Mode
- 2.6 SYSCTL Registers
- 3 CPU
-
4 DMA
- 4.1 DMA Overview
- 4.2
DMA Operation
- 4.2.1 Addressing Modes
- 4.2.2 Channel Types
- 4.2.3 Transfer Modes
- 4.2.4 Extended Modes
- 4.2.5 Initiating DMA Transfers
- 4.2.6 Stopping DMA Transfers
- 4.2.7 Channel Priorities
- 4.2.8 Burst Block Mode
- 4.2.9 Using DMA with System Interrupts
- 4.2.10 DMA Controller Interrupts
- 4.2.11 DMA Trigger Event Status
- 4.2.12 DMA Operating Mode Support
- 4.2.13 DMA Address and Data Errors
- 4.2.14 Interrupt and Event Support
- 4.3 DMA Registers
- 5 MATHACL
-
6 NVM (Flash)
- 6.1 NVM Overview
- 6.2 Flash Memory Bank Organization
- 6.3 Flash Controller
- 6.4 Write Protection
- 6.5 Read Interface
- 6.6 FLASHCTL Registers
- 7 Events
- 8 IOMUX
- 9 GPIO
-
10ADC
- 10.1 ADC Overview
- 10.2
ADC Operation
- 10.2.1 ADC Core
- 10.2.2 Voltage Reference Options
- 10.2.3 Generic Resolution Modes
- 10.2.4 Hardware Averaging
- 10.2.5 ADC Clocking
- 10.2.6 Common ADC Use Cases
- 10.2.7 Power Down Behavior
- 10.2.8 Sampling Trigger Sources and Sampling Modes
- 10.2.9 Sampling Period
- 10.2.10 Conversion Modes
- 10.2.11 Data Format
- 10.2.12 Advanced Features
- 10.2.13 Status Register
- 10.2.14 ADC Events
- 10.3 ADC12 Registers
-
11COMP
- 11.1 Comparator Overview
- 11.2
Comparator Operation
- 11.2.1 Comparator Configuration
- 11.2.2 Comparator Channels Selection
- 11.2.3 Comparator Output
- 11.2.4 Output Filter
- 11.2.5 Sampled Output Mode
- 11.2.6 Blanking Mode
- 11.2.7 Reference Voltage Generator
- 11.2.8 Window Comparator Mode
- 11.2.9 Comparator Hysteresis
- 11.2.10 Input SHORT Switch
- 11.2.11 Interrupt and Events Support
- 11.3 COMP Registers
- 12OPA
- 13GPAMP
-
14DAC
- 14.1 DAC Introduction
- 14.2
DAC Operation
- 14.2.1 DAC Core
- 14.2.2 DAC Output
- 14.2.3 DAC Voltage Reference
- 14.2.4 DAC Output Buffers
- 14.2.5 DAC Data Formats
- 14.2.6 Sample Time Generator
- 14.2.7 DAC FIFO Structure
- 14.2.8 DAC Operation With DMA Controller
- 14.2.9 DAC Operation With CPU
- 14.2.10 Data Register Format
- 14.2.11 DAC Output Amplifier Offset Calibration
- 14.2.12 Interrupt and Event Support
- 14.3 DAC12 Registers
- 15VREF
-
16UART
- 16.1 UART Overview
- 16.2
UART Operation
- 16.2.1 Clock Control
- 16.2.2 Signal Descriptions
- 16.2.3
General Architecture and Protocol
- 16.2.3.1 Transmit Receive Logic
- 16.2.3.2 Bit Sampling
- 16.2.3.3 Majority Voting Feature
- 16.2.3.4 Baud Rate Generation
- 16.2.3.5 Data Transmission
- 16.2.3.6 Error and Status
- 16.2.3.7 Local Interconnect Network (LIN) Support
- 16.2.3.8 Flow Control
- 16.2.3.9 Idle-Line Multiprocessor
- 16.2.3.10 9-Bit UART Mode
- 16.2.3.11 RS485 Support
- 16.2.3.12 DALI Protocol
- 16.2.3.13 Manchester Encoding and Decoding
- 16.2.3.14 IrDA Encoding and Decoding
- 16.2.3.15 ISO7816 Smart Card Support
- 16.2.3.16 Address Detection
- 16.2.3.17 FIFO Operation
- 16.2.3.18 Loopback Operation
- 16.2.3.19 Glitch Suppression
- 16.2.4 Low Power Operation
- 16.2.5 Reset Considerations
- 16.2.6 Initialization
- 16.2.7 Interrupt and Events Support
- 16.2.8 Emulation Modes
- 16.3 UART Registers
-
17SPI
- 17.1 SPI Overview
- 17.2
SPI Operation
- 17.2.1 Clock Control
- 17.2.2 General Architecture
- 17.2.3 Protocol Descriptions
- 17.2.4 Reset Considerations
- 17.2.5 Initialization
- 17.2.6 Interrupt and Events Support
- 17.2.7 Emulation Modes
- 17.3 SPI Registers
-
18I2C
- 18.1 I2C Overview
- 18.2
I2C Operation
- 18.2.1 Clock Control
- 18.2.2 Signal Descriptions
- 18.2.3
General Architecture
- 18.2.3.1 I2C Bus Functional Overview
- 18.2.3.2 START and STOP Conditions
- 18.2.3.3 Data Format with 7-Bit Address
- 18.2.3.4 Acknowledge
- 18.2.3.5 Repeated Start
- 18.2.3.6 SCL Clock Low Timeout
- 18.2.3.7 Clock Stretching
- 18.2.3.8 Dual Address
- 18.2.3.9 Arbitration
- 18.2.3.10 Multiple Controller Mode
- 18.2.3.11 Glitch Suppression
- 18.2.3.12 FIFO operation
- 18.2.3.13 Loopback mode
- 18.2.3.14 Burst Mode
- 18.2.3.15 DMA Operation
- 18.2.3.16 Low-Power Operation
- 18.2.4 Protocol Descriptions
- 18.2.5 Reset Considerations
- 18.2.6 Initialization
- 18.2.7 Interrupt and Events Support
- 18.2.8 Emulation Modes
- 19I2C Registers
-
20CAN-FD
- 20.1 MCAN Overview
- 20.2 MCAN Environment
- 20.3 CAN Network Basics
- 20.4
MCAN Functional Description
- 20.4.1 Clock Set up
- 20.4.2 Module Clocking Requirements
- 20.4.3 Interrupt Requests
- 20.4.4 Operating Modes
- 20.4.5 Software Initialization
- 20.4.6 Transmitter Delay Compensation
- 20.4.7 Restricted Operation Mode
- 20.4.8 Bus Monitoring Mode
- 20.4.9 Disabled Automatic Retransmission (DAR) Mode
- 20.4.10 Clock Stop Mode
- 20.4.11 Test Modes
- 20.4.12 Timestamp Generation
- 20.4.13 Timeout Counter
- 20.4.14 Safety
- 20.4.15 Tx Handling
- 20.4.16 Rx Handling
- 20.4.17 Rx FIFOs
- 20.4.18 Dedicated Rx Buffers
- 20.4.19 Message RAM
- 20.5 MCAN Integration
- 20.6 Interrupt and Event Support
- 20.7 MCAN Registers
- 21MCAN Registers
- 22CRC
-
23AES
- 23.1 AES Overview
- 23.2
AES Operation
- 23.2.1 AES Register Access Rules
- 23.2.2 Loading the Key
- 23.2.3 Loading Data
- 23.2.4 Reading Data
- 23.2.5 Triggering an Encryption or Decryption
- 23.2.6 Single Block Operations
- 23.2.7 Block Cipher Mode Operations
- 23.2.8 AES Events
- 23.3 AES Registers
- 24TRNG
-
25Timers (TIMx)
- 25.1 TIMx Overview
- 25.2
TIMx Operation
- 25.2.1 Timer Counter
- 25.2.2 Counting Mode Control
- 25.2.3 Capture/Compare Module
- 25.2.4 Shadow Load and Shadow Compare
- 25.2.5 Output Generator
- 25.2.6 Fault Handler (TIMA only)
- 25.2.7 Synchronization With Cross Trigger
- 25.2.8 Low Power Operation
- 25.2.9 Interrupt and Event Support
- 25.2.10 Debug Handler (TIMA only)
- 25.3 Timers (TIMx) Registers
-
26RTC
- 26.1 Overview
- 26.2 Basic Operation
- 26.3 Configuration
- 26.4 RTC Registers
- 27WWDT
- 28Debug
- 29Revision History
20.4.4.3 CAN FD Operation
The CAN FD standard allows extended frames to be sent, up to 64 data bytes in a single frame at a higher bit rate for the data phase of a frame, up to 8 Mbps. The CAN FD standard introduces the ability to switch from one bit rate to another. Extended Data Length (EDL), as shown in Figure 20-4 and described in Table 20-2, sets a data length of up to 8 or 64 data bytes. Bit Rate Switching (BRS) indicates whether two bit rates (the data phase is transmitted at a different bit rate compared to the arbitration phase) are enabled.
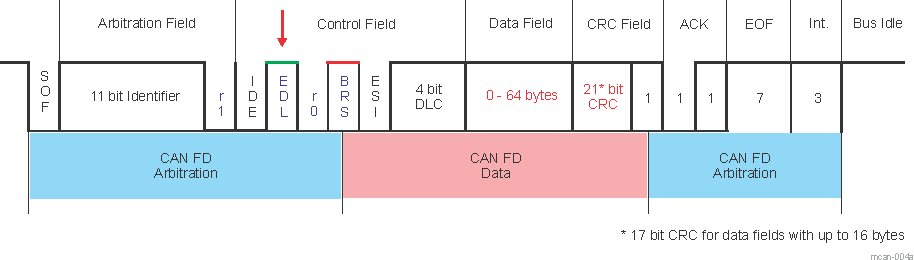 Figure 20-4 CAN FD Frame
Figure 20-4 CAN FD Frame| Bit | Description |
|---|---|
| SOF | Start of Frame |
| IDE | Identifier extension (for 29 bit extended ID) |
| FDF | Flexible Data Format |
| BRS | Bit Rate Switching |
| ESI | Error Status Indicator |
| DLC | Data Length Code |
| CRC | Cyclic Redundancy check |
There are two variants of CAN FD frame transmission:
- CAN FD frame transmission without bit rate switching
- CAN FD frame transmission where control field, data field, and CRC field are transmitted with a higher bit rate than the beginning and the end of the frame
In the CAN frames, FDF = recessive (logical 1) signifies a CAN FD frame, FDF = dominant (logical 0) signifies a Classic CAN frame. In a CAN FD frame, the two bits following FDF - res and BRS, decide whether the bit rate inside of this CAN FD frame is switched. A CAN FD bit rate switch is signified by res = dominant and BRS = recessive. Note that the coding of res = recessive is reserved for future expansion of the protocol. If the MCAN module receives a frame with FDF = recessive and res = recessive, the MCAN signals a Protocol Exception Event by setting the MCAN_PSR.PXE bit. When Protocol Exception Handling is enabled (MCAN_CCCR.PXHD = 0), this causes the operation state to change from Receiver (MCAN_PSR.ACT = 10) to Integrating (MCAN_PSR.ACT = 00) at the next sample point. In case Protocol Exception Handling is disabled (MCAN_CCCR.PXHD = 1), the MCAN treats a recessive bit as an error and responds with an error frame.
CAN FD operation is enabled by programming the MCAN_CCCR.FDOE bit. If MCAN_CCCR.FDOE = 1, transmission and reception of CAN FD frames is enabled. Transmission and reception of Classic CAN frames is always possible. Whether a CAN FD frame or a Classic CAN frame is transmitted can be configured using the FDF bit in the respective Tx Buffer element.
With MCAN_CCCR.FDOE = 0, received frames are interpreted as Classic CAN frames, which leads to the transmission of an error frame when receiving a CAN FD frame. When CAN FD operation is disabled, no CAN FD frames are transmitted even if the FDF bit of a Tx Buffer element is set. The MCAN_CCCR.FDOE and MCAN_CCCR.BRSE bits can only be changed while the MCAN_CCCR.INIT and MCAN_CCCR.CCE bits are both set. With MCAN_CCCR.FDOE = 0, the setting of bits FDF and BRS is ignored and frames are transmitted in Classic CAN format.
With MCAN_CCCR.FDOE = 1 and MCAN_CCCR.BRSE = 0, only FDF bit of a Tx Buffer element is evaluated. With MCAN_CCCR.FDOE = 1 and MCAN_CCCR.BRSE = 1, transmission of CAN FD frames with bit rate switching is enabled. All Tx Buffer elements with bits FDF and BRS set are transmitted in CAN FD format with bit rate switching.
A mode change during CAN operation is only recommended under the following conditions:
- The failure rate in the CAN FD data phase is significantly higher than in the CAN FD arbitration phase. In this case, disable the CAN FD bit rate switching option for transmissions.
- During system startup, all nodes are transmitting Classic CAN messages until verified that the nodes are able to communicate in CAN FD format. If this is true, all nodes switch to CAN FD operation.
- Wakeup messages in CAN Partial Networking have to be transmitted in Classic CAN format.
- End-of-line programming in case not all nodes are CAN FD capable. Non CAN FD nodes are held in Silent mode until programming has completed. Then all nodes switch back to Classic CAN communication.
The coding of the DLC in the CAN FD format differs from the standard CAN format. The DLC codes 0 to 8 have the same coding as in standard CAN (0 to 8 data bytes), the codes 9 to 15, which in standard CAN all code a data field of 8 bytes, are coded according to Table 20-3.
| DLC | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Data Bytes | 12 | 16 | 20 | 24 | 32 | 48 | 64 |
For CAN FD frames, the bit timing is switched inside the frame after the BRS (Bit Rate Switch) bit in case this bit is recessive. In the CAN FD arbitration phase, before the BRS bit, the nominal CAN bit timing (see Figure 20-5) is used as configured by the Nominal Bit Timing and Prescaler Register (MCAN_NBTP). In the following CAN FD data phase, the data phase bit timing is used as configured by the Data Bit Timing and Prescaler Register (MCAN_DBTP). The bit timing is switched back from the data phase timing at the CRC delimiter or when an error is detected, whichever occurs first.
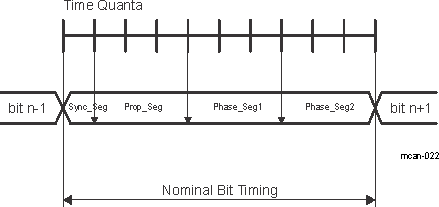 Figure 20-5 CAN Bit Timing
Figure 20-5 CAN Bit TimingThe maximum configurable data phase bit timing depends on the CAN clock frequency (MCAN_FCLK). Example: with MCAN_FCLK = 20 MHz and the shortest configurable bit time of 4 tq (time quanta), the bit rate in the data phase is 5 Mbit/s.
In both data frame formats, CAN FD and CAN FD with bit rate switching, the value of the Error Status Indicator (ESI) bit depends on the transmitter error state (see MCAN_PSR.RESI bit) monitored at the start of the transmission. If the transmitter has an error passive flag, the ESI bit is transmitted recessive; else, the ESI bit is transmitted dominant.