SLLU335A August 2021 – January 2022 MCF8316A
- 1Revision History
- 2Introduction
- 3Essential Controls
-
4Basic Controls
- 4.1 Device and Pin Configuration
- 4.2 System Level Configuration
- 4.3
Control Configurations
- 4.3.1 Motor Parameter Estimation to Minimize Motor Parameter Variation Effects
- 4.3.2 Initial Speed Detection of the Motor for Reliable Motor Resynchronization
- 4.3.3 Unidirectional Motor Drive Detecting Backward Spin
- 4.3.4 Preventing Back Spin of Rotor During Startup
- 4.3.5 Faster Startup Timing
- 4.3.6 Gradual and Smooth Start up Motion
- 4.3.7 Improving Speed Regulation
- 4.3.8 Stopping Motor Quickly
- 4.3.9 Preventing Supply Voltage Overshoot During Motor Stop.
- 4.3.10 Protecting Against Rotor Lock or Stall Condition
- 4.3.11 Maximizing Thermal Efficiency and Increasing Thermal Performance
- 4.3.12 Mitigating Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
- 4.3.13 Faster deceleration
3.5 Testing for Successful Startup into Closed Loop
Apply a nonzero speed command
If the Speed input mode is I2C, change the “I2C Speed Command Percentage” to a non-zero value. Once the speed command is issued, the device will start commutating and the motor should start spinning that is proportional to the I2C Speed Command Percentage.
If the speed input mode is Analog, rotate the Speed Control potentiometer (R4) clockwise to control the motor speed. Once the speed command is issued, the device will start commutating and the motor should start spinning that is proportional to the voltage on the Speed Pin.
If the speed input mode is PWM, apply PWM signal to the speed pin with a given duty cycle with a low of 0 V to a high of 2.2 V (min). Once the speed command is issued, the device will start commutating and the motor should start spinning that is proportional to the duty cycle.
Wait for MPET to estimate motor electrical parameters.
The Motor Parameter Extraction Tool (MPET) will attempt to measure the motor resistance, inductance, and Motor BEMF constant (Ke) and populate these parameters automatically during the initial position detect (IPD) and open loop stage as the rotor speed attempts to accelerate. It usually takes around 10-15 seconds to estimate motor resistance, inductance and Motor BEMF constant Ke.
Check if motor spins in closed loop at commanded speed.
In closed loop, the motor should spin at the commanded speed and there should not be any faults triggered.
Enable the “Auto read fault status” toggle button towards the top right corner of the GUI. Then monitor the Fault Status in the side panel to the right.
If no fault gets triggered, skip Section 3.6 and proceed to Section 4.
Prepare device for fault handling if any fault gets triggered.
If the motor failed to spin successfully in closed loop, check the fault status.
Set zero speed command by turning off the PWM, turning the potentiometer completely counterclockwise, or setting the I2C command percentage to 0%.
Clear the fault status registers by clicking on the “Clear” button in the Fault Status side panel to the right as shown in Figure 3-1
This completes the essential controls section. At the end of this section, user should be able to spin the motor in closed loop. Save the register settings by clicking File->Save Registers in the GUI. If there were no faults, skip to Section 4.
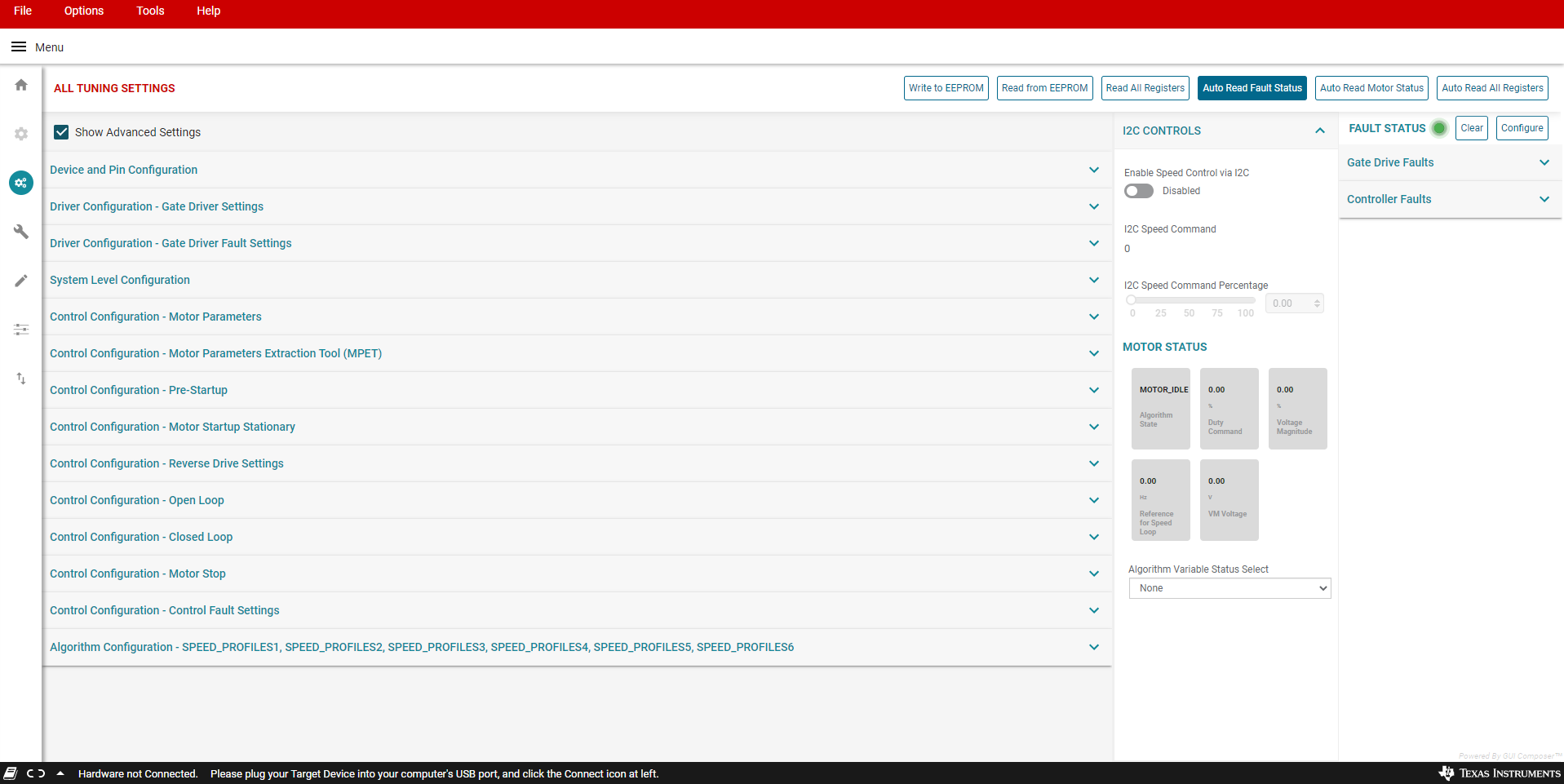 Figure 3-1 Fault Status
Figure 3-1 Fault Status