SLLU335A August 2021 – January 2022 MCF8316A
- 1Revision History
- 2Introduction
- 3Essential Controls
-
4Basic Controls
- 4.1 Device and Pin Configuration
- 4.2 System Level Configuration
- 4.3
Control Configurations
- 4.3.1 Motor Parameter Estimation to Minimize Motor Parameter Variation Effects
- 4.3.2 Initial Speed Detection of the Motor for Reliable Motor Resynchronization
- 4.3.3 Unidirectional Motor Drive Detecting Backward Spin
- 4.3.4 Preventing Back Spin of Rotor During Startup
- 4.3.5 Faster Startup Timing
- 4.3.6 Gradual and Smooth Start up Motion
- 4.3.7 Improving Speed Regulation
- 4.3.8 Stopping Motor Quickly
- 4.3.9 Preventing Supply Voltage Overshoot During Motor Stop.
- 4.3.10 Protecting Against Rotor Lock or Stall Condition
- 4.3.11 Maximizing Thermal Efficiency and Increasing Thermal Performance
- 4.3.12 Mitigating Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
- 4.3.13 Faster deceleration
3.6.2 MPET BEMF Fault [MPET_BEMF_Fault]
This fault gets triggered when motor stalls while running in open loop for BEMF estimation. If this fault is triggered, then please follow the below suggestions.
Step 1: Increase MPET Open loop current reference [MPET_OPEN_LOOP_CURR_REF]
Step 2: Decrease MPET open loop slew rate [MPET_OPEN_LOOP_SLEW_RATE]
Step 3: If this fault persists, check motor datasheet for motor BEMF constant in mV/Hz and program Motor BEMF Constant [MOTOR_BEMF_CONST] in the “Control configuration – Motor Parameters” tab in All tuning settings section in the GUI.
Equation 3 and Equation 4 can be used to convert Ke in mV/rpm and torque constant to Ke in mV/Hz.
Step 4: If the motor does not have a datasheet, then measure the voltage across any two phases of the motor using an oscilloscope by manually spinning the motor. A sinusoidal or trapezoidal voltage should appear on the oscilloscope. Measure the peak voltage EPH in milli-volts and time period TE in seconds as shown in Figure 3-4. Calculate BEMF constant Ke as shown in Equation 5.
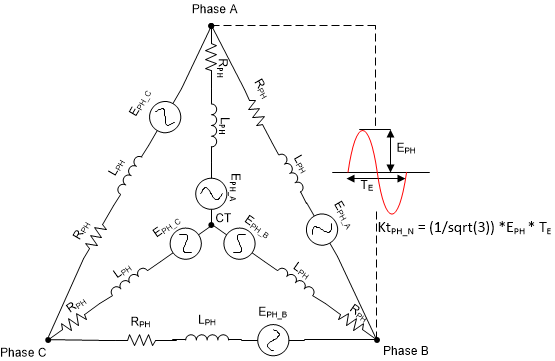 Figure 3-4 Motor BEMF Constant
Figure 3-4 Motor BEMF Constant