SLOA284A january 2020 – may 2023 AFE5832 , AFE5832LP , ISO7741 , ISOW7841 , LM25037 , LM25180 , LM5180 , LM5181 , LM5181-Q1 , TX7316 , TX7332
4.2 Option 2: Support Input From 1S Li-Ion Battery
1S Li-Ion battery has a typical operating voltage range of 3.0 V to 4.2 V. To generate an output voltage of +/- 80V, the existing SEPIC needs a PWM controller that can achieve high duty cycle > 95%. At these very high duty cycle there are practical limitations such as: parasitics which affect the turn-on and turn-off time of the MOSFET, lower available time for energy transfer from primary to secondary side which limit the achievable maximum output voltage. Hence an intermediate boost stage is required to be added, as shown in Figure 4-3.
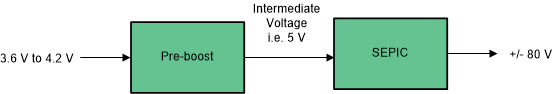 Figure 4-3 Case of 1S Battery
Figure 4-3 Case of 1S Battery