SLOA284A january 2020 – may 2023 AFE5832 , AFE5832LP , ISO7741 , ISOW7841 , LM25037 , LM25180 , LM5180 , LM5181 , LM5181-Q1 , TX7316 , TX7332
3.1 Efficiency and Load Regulation
Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2 shows the efficiency and load regulation of the power supply with symmetrical loads on the positive and the negative rail. The load is varied from 0 to 25 mA on each rail. The peak efficiency observed is ~75 % and worst case load regulation is 1.99 %. The positive and negative outputs are symmetrical within 1% with respect to each other.
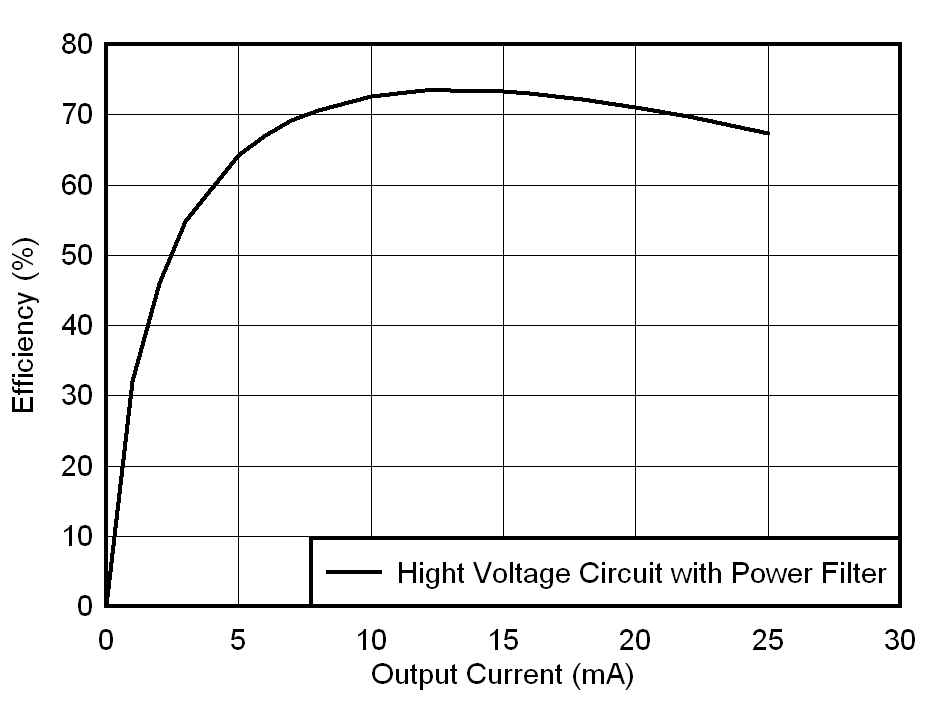 Figure 3-1 Efficiency Curve of SEPIC HV Power Supply
Figure 3-1 Efficiency Curve of SEPIC HV Power Supply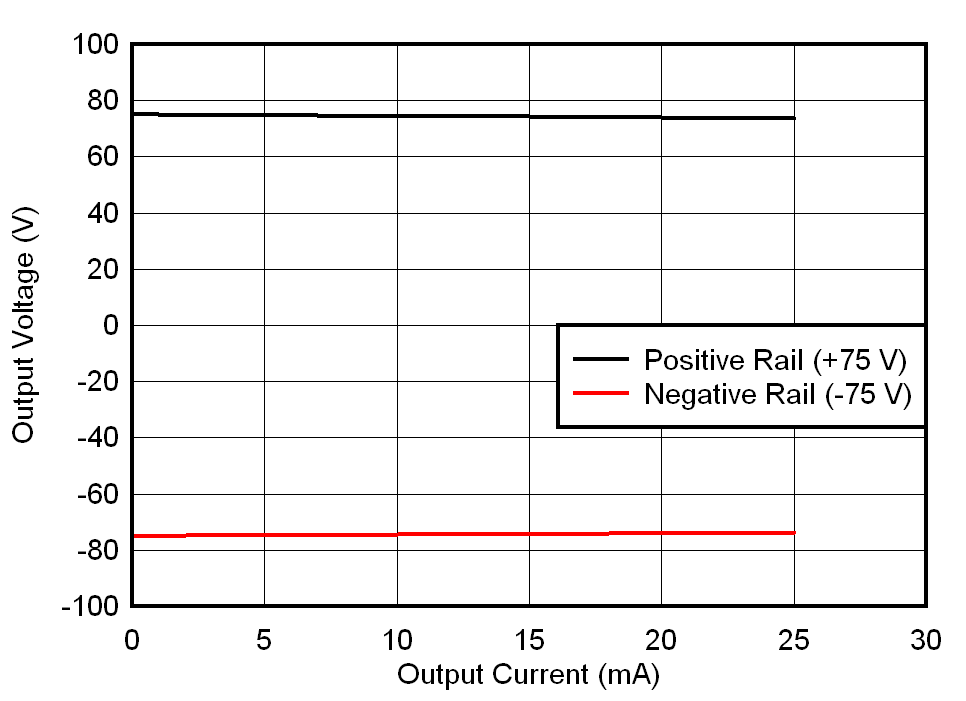 Figure 3-2 Load Symmetry of SEPIC Showing Accuracy of Less Than 1% and Load Regulation Less Than 2%
Figure 3-2 Load Symmetry of SEPIC Showing Accuracy of Less Than 1% and Load Regulation Less Than 2%