SLOS545D November 2008 – December 2014 TLV320AIC3107
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Simplified Block Diagram
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Description (Continued)
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
-
10Detailed Description
- 10.1 Overview
- 10.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 10.3
Feature Description
- 10.3.1 Hardware Reset
- 10.3.2 Digital Audio Data Serial Interface
- 10.3.3 Audio Data Converters
- 10.3.4 Audio Analog Inputs
- 10.3.5 Analog Line Output Drivers
- 10.3.6 Analog High Power Output Drivers
- 10.3.7 Input Impedance and VCM Control
- 10.3.8 General Purpose I/O
- 10.3.9 MICBIAS Generation
- 10.3.10 Class-D Speaker Driver
- 10.3.11 Short Circuit Output Protection
- 10.3.12 Jack and Headset Detection
- 10.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10.5 Programming
- 10.6 Register Maps
- 11Application and Implementation
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14Device and Documentation Support
- 15Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
13 Layout
13.1 Layout Guidelines
PCB design is made considering the application, and the review is specific for each system requirements. However, general considerations can optimize the system performance.
- The TLV320AIC3107IRSB thermal pad should be connected to analog output driver ground using multiple VIAS to minimize impedance between the device and ground.
- SPVSS balls of TLV320AIC3107IYZF are recommended to be soldered directly to Class-D ground.
- SPVSS balls of TLV320AIC3107IYZF are recommended to be soldered directly to Class-D ground.
- The TLV320AIC3107 requires the decoupling capacitors to be placed as close as possible to the device power supply terminals.
- If possible, route the differential audio signals differentially on the PCB. This is recommended to get better noise immunity.
13.2 Layout Example
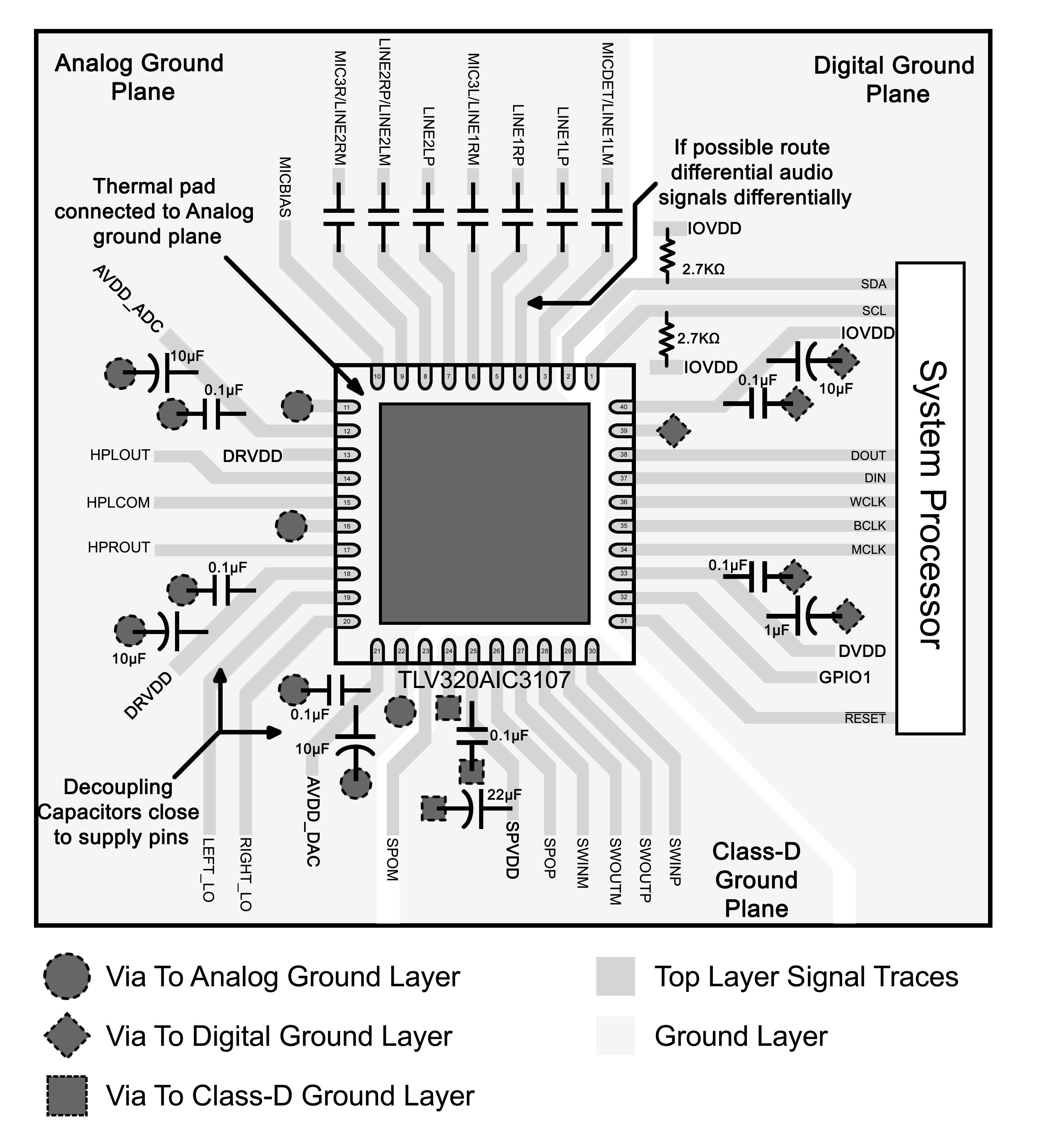 Figure 41. AIC3107 WQFN Layout Example
Figure 41. AIC3107 WQFN Layout Example
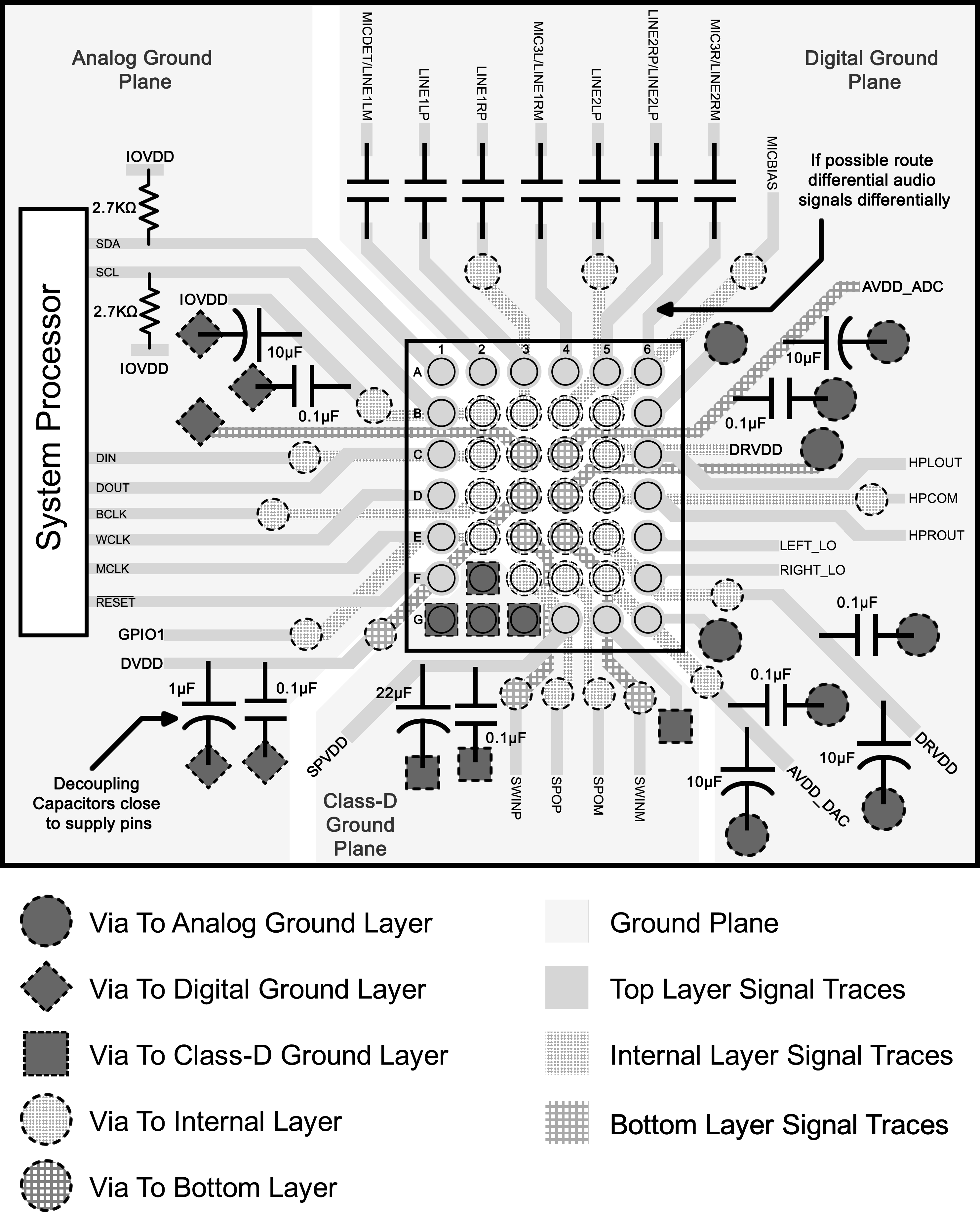 Figure 42. AIC3107 DSBGA Layout Example
Figure 42. AIC3107 DSBGA Layout Example