at Vs+ = 5 V,
Vs– = GND, Vocm is open, 50-Ω single-ended input to differential output, gain = 2
V/V, Rload = 500 Ω, and TA ≈ 25°C (unless otherwise noted)
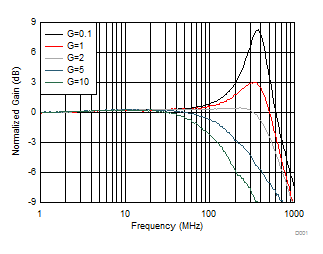 Figure 6-1 Small-Signal Frequency Response vs Gain
Figure 6-1 Small-Signal Frequency Response vs Gain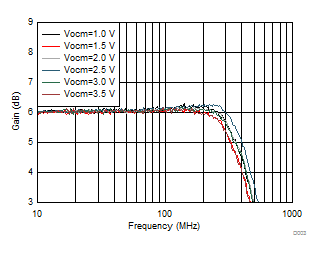
| Vout
= 100 mVPP, see Figure 7-1 with Vocm adjusted |
Figure 6-3 Small-Signal Frequency Response vs Vocm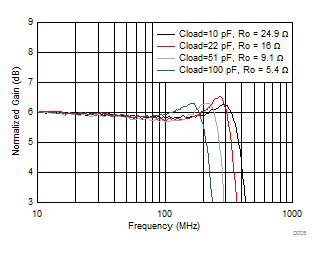
| 100
mVPP at load, Av = 2 (see Figure 7-11), two series Ro added at output before Cload |
Figure 6-5 Small-Signal Frequency Response vs Cload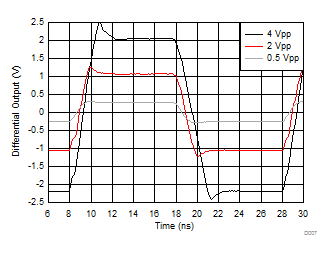
| 50-MHz input, 0.3-ns input edge rate, single-ended to
differential output, DC coupled, see Figure 7-3 |
Figure 6-7 Small- and Large-Signal Step Response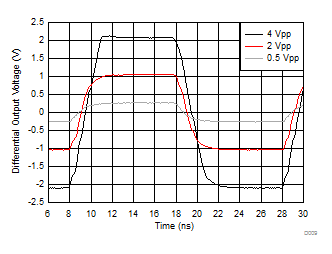
| G =
5 V/V, 50-MHz input, 0.3-ns input edge rate,
single-ended input to differential output, see Figure 7-3 |
Figure 6-9 Small- and Large-Signal Step Response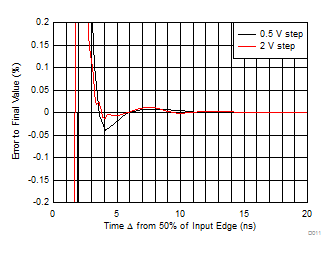
Simulated with 2-ns input transition time,
see Figure 7-3 |
|
Figure 6-11 Small- and Large-Signal Step Settling Time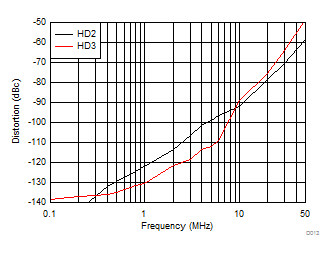 Figure 6-13 Harmonic Distortion Over Frequency
Figure 6-13 Harmonic Distortion Over Frequency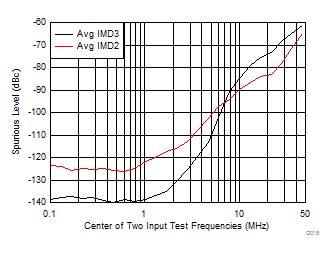 Figure 6-15 IMD2
and IM3 Over Frequency
Figure 6-15 IMD2
and IM3 Over Frequency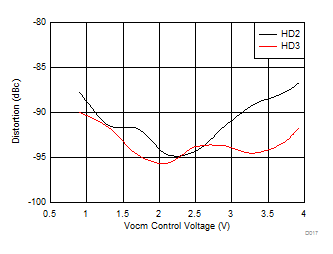
f =
10 MHz, 2-VPP output,
see Figure 7-3 with Vocm adjusted |
|
Figure 6-17 Harmonic Distortion vs Vocm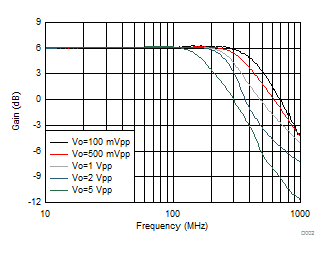 Figure 6-2 Frequency Response vs Vopp
Figure 6-2 Frequency Response vs Vopp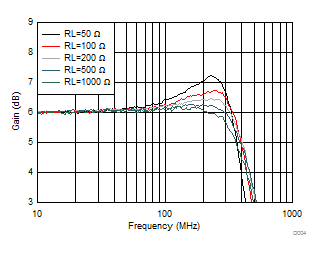 Figure 6-4 Small-Signal Frequency Response vs Rload (RL)
Figure 6-4 Small-Signal Frequency Response vs Rload (RL)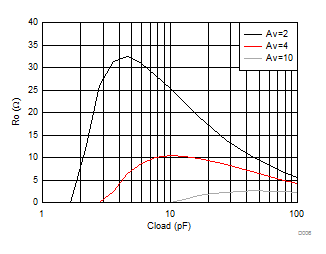
| Ro
is two series output resistors to a differential Cload
in parallel with 500 Ω, see Figure 7-11 and Table 8-1 |
Figure 6-6 Recommended Ro vs Cload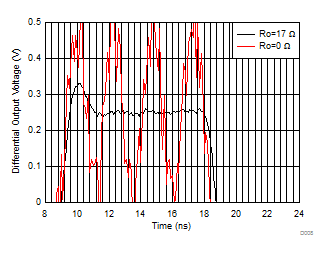
Av =
2, 500-mVPP output into 22-pF Cload,
see Figure 7-11 |
|
|
|
Figure 6-8 Step
Response into Capacitive Load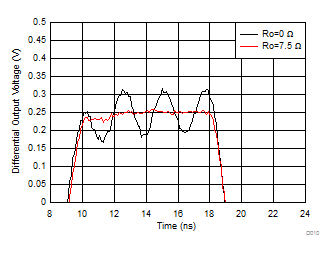 Figure 6-10 Step
Response into Capacitive Load
Figure 6-10 Step
Response into Capacitive Load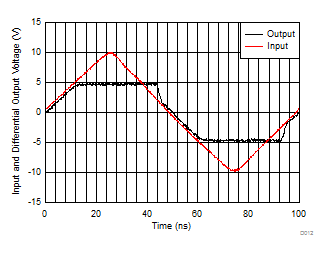
Single-ended to differential gain of 2 (see Figure 7-3),
2 × input
overdrive |
Figure 6-12 Overdrive Recovery Performance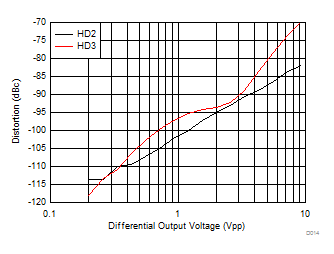 Figure 6-14 Harmonic Distortion vs Output Swing
Figure 6-14 Harmonic Distortion vs Output Swing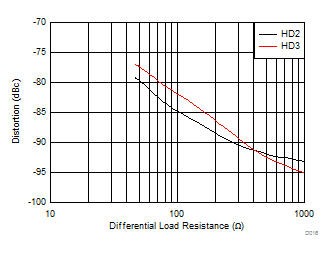 Figure 6-16 Harmonic Distortion vs Rload
Figure 6-16 Harmonic Distortion vs Rload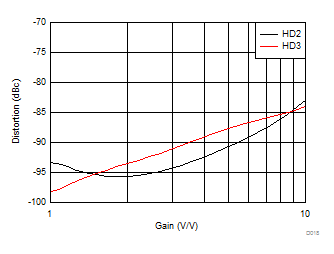 Figure 6-18 Harmonic Distortion vs Gain
Figure 6-18 Harmonic Distortion vs Gain

















