SLOSEC9 September 2024 TSD5402-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.3.2 Pulse-Width Modulator (PWM)
The PWM converts the analog signal from the preamplifier into a switched signal of varying duty cycle. This is the critical stage that defines the class-D architecture. In the TSD5402-Q1, the modulator is an advanced design with high bandwidth, low noise, low distortion, and excellent stability.
The pulse-width modulation scheme allows increased efficiency at low power. Each output is switching from 0 V to PVDD. The OUTP and OUTN pins are in phase with each other with no input so that there is little or no current in the load. The duty cycle of OUTP is greater than 50% and the duty cycle OUTN is less than 50% for positive output voltages. The duty cycle of OUTN is greater than 50% and the duty cycle of OUTP is less than 50% for negative output voltages. The voltage across the load is at 0 V through most of the switching period, reducing power loss.
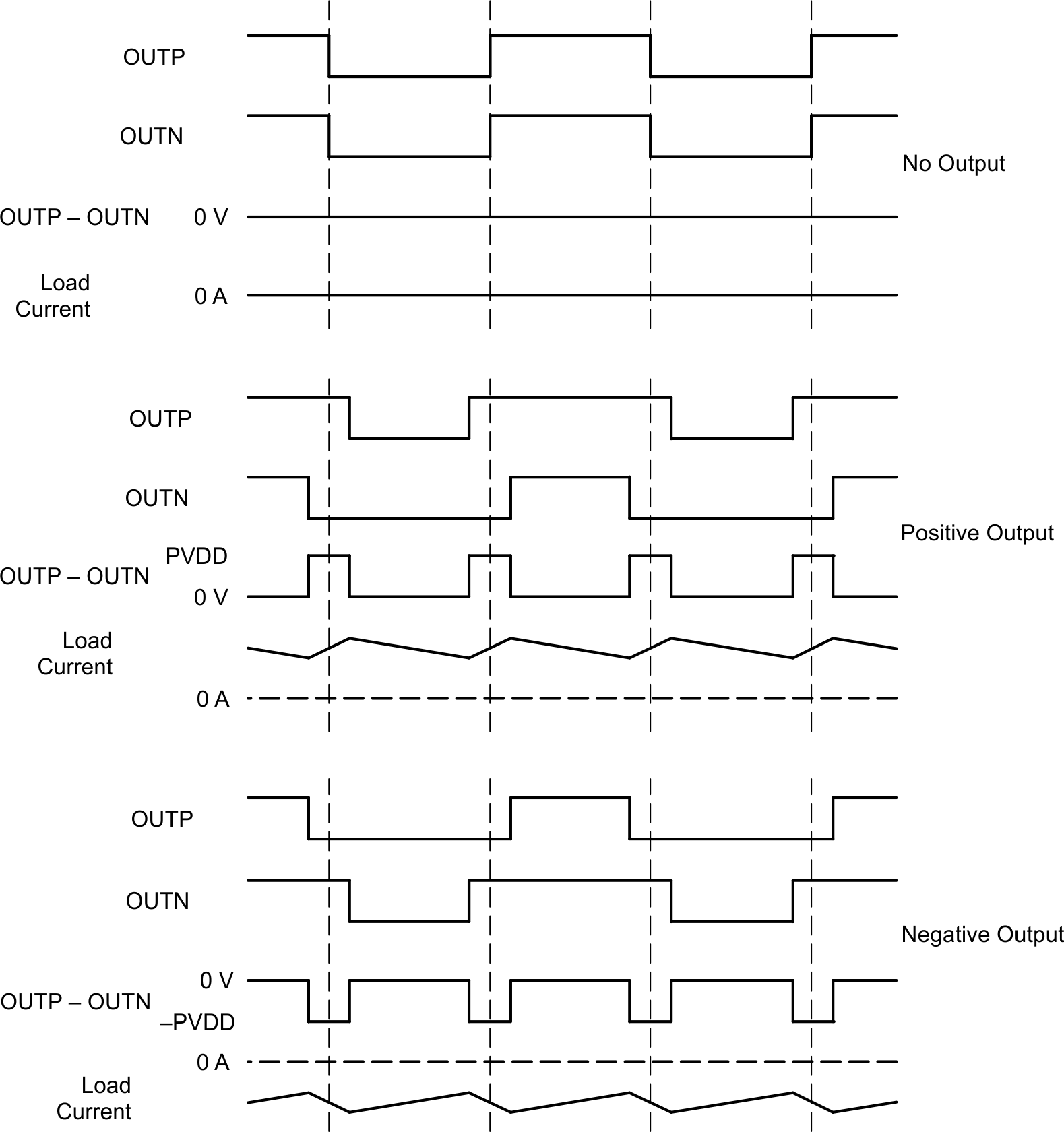 Figure 6-1 BD Mode Modulation
Figure 6-1 BD Mode Modulation