SLUSE26C June 2021 – January 2022 UCC27614
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Applications and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.8 Typical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, VDD = 12 V, IN+ = 3.3 V, IN- = GND, TJ = 25 °C, No load
 Figure 6-4 Peak
Source Current vs VDD
Figure 6-4 Peak
Source Current vs VDD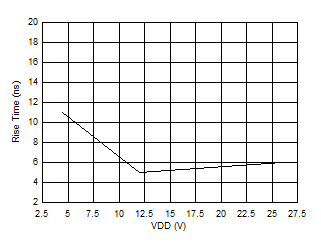
| CLOAD = 1.8 nF |

| CLOAD = 1.8 nF |

| CLOAD = 1.8 nF |
 Figure 6-12 Operating Supply Current vs VDD
Figure 6-12 Operating Supply Current vs VDD Figure 6-14 Input
Threshold vs VDD
Figure 6-14 Input
Threshold vs VDD Figure 6-16 Input
Threshold
Hysteresis vs Temperature
Figure 6-16 Input
Threshold
Hysteresis vs Temperature  Figure 6-18 Output Pullup Resistance vs
Temperature
Figure 6-18 Output Pullup Resistance vs
Temperature Figure 6-20 Output Pulldown Resistance vs
Temperature
Figure 6-20 Output Pulldown Resistance vs
Temperature Figure 6-22 UVLO Hysteresis vs Temperature
Figure 6-22 UVLO Hysteresis vs Temperature  Figure 6-5 Peak
Sink Current vs VDD
Figure 6-5 Peak
Sink Current vs VDD
| CLOAD = 1.8 nF |

| CLOAD = 1.8 nF |

| CLOAD = 1.8 nF |
 Figure 6-13 Operating Static Supply Current vs Temperature
Figure 6-13 Operating Static Supply Current vs Temperature Figure 6-15 Input Threshold vs Temperature
Figure 6-15 Input Threshold vs Temperature  Figure 6-17 Output Pullup Resistance vs VDD
Figure 6-17 Output Pullup Resistance vs VDD Figure 6-19 Output Pulldown Resistance vs VDD
Figure 6-19 Output Pulldown Resistance vs VDD Figure 6-21 UVLO Threshold vs Temperature
Figure 6-21 UVLO Threshold vs Temperature