SLUSES3B October 2023 – July 2024 UCC25660
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Protections
- 7.5 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 LLC Power Stage Requirements
- 8.2.2.2 LLC Gain Range
- 8.2.2.3 Select Ln and Qe
- 8.2.2.4 Determine Equivalent Load Resistance
- 8.2.2.5 Determine Component Parameters for LLC Resonant Circuit
- 8.2.2.6 LLC Primary-Side Currents
- 8.2.2.7 LLC Secondary-Side Currents
- 8.2.2.8 LLC Transformer
- 8.2.2.9 LLC Resonant Inductor
- 8.2.2.10 LLC Resonant Capacitor
- 8.2.2.11 LLC Primary-Side MOSFETs
- 8.2.2.12 Design Considerations for Adaptive Dead-Time
- 8.2.2.13 LLC Rectifier Diodes
- 8.2.2.14 LLC Output Capacitors
- 8.2.2.15 HV Pin Series Resistors
- 8.2.2.16 BLK Pin Voltage Divider
- 8.2.2.17 ISNS Pin Differentiator
- 8.2.2.18 TSET Pin
- 8.2.2.19 OVP/OTP Pin
- 8.2.2.20 Burst Mode Programming
- 8.2.2.21 Application Curves
- 8.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.4 Layout
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
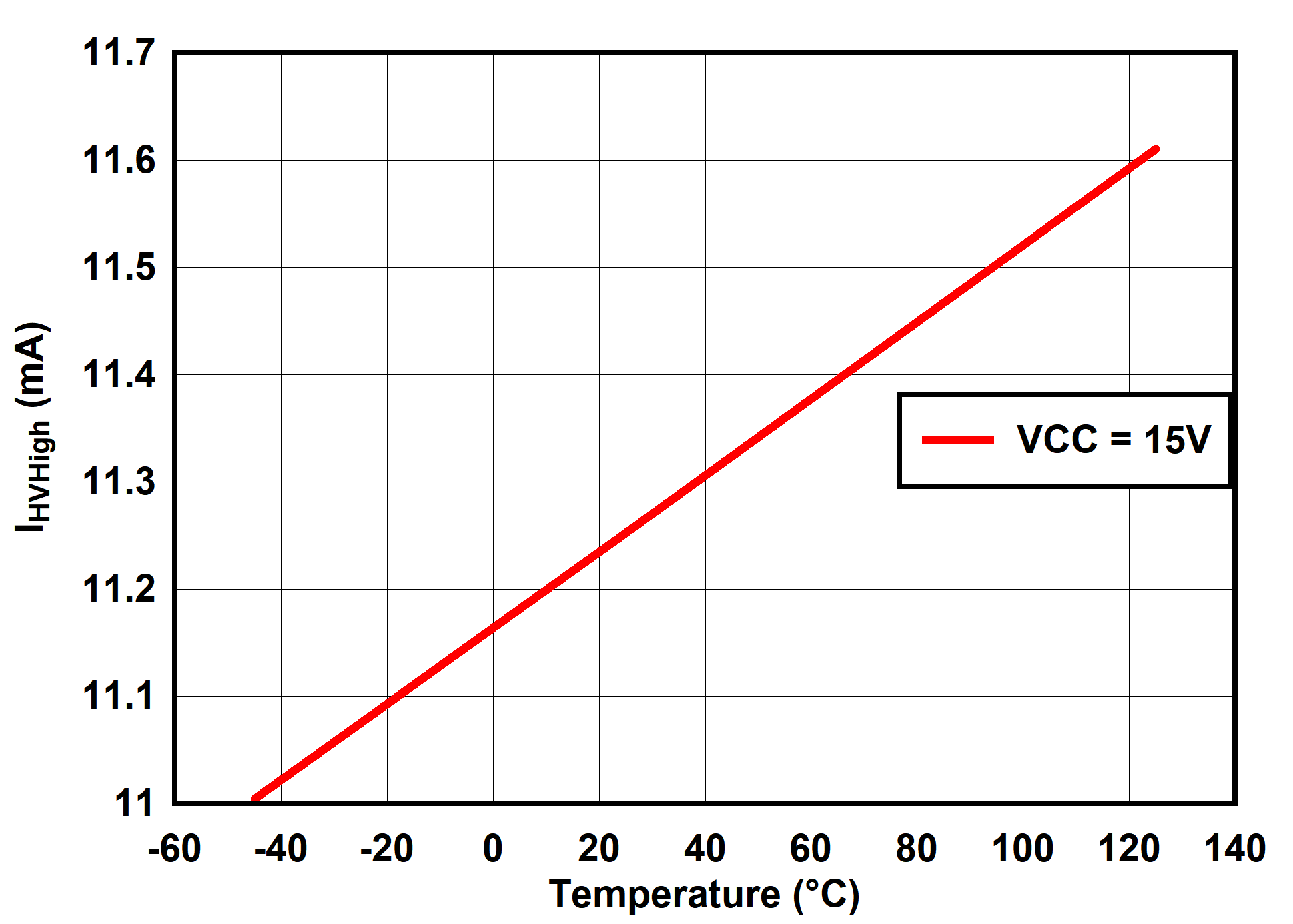
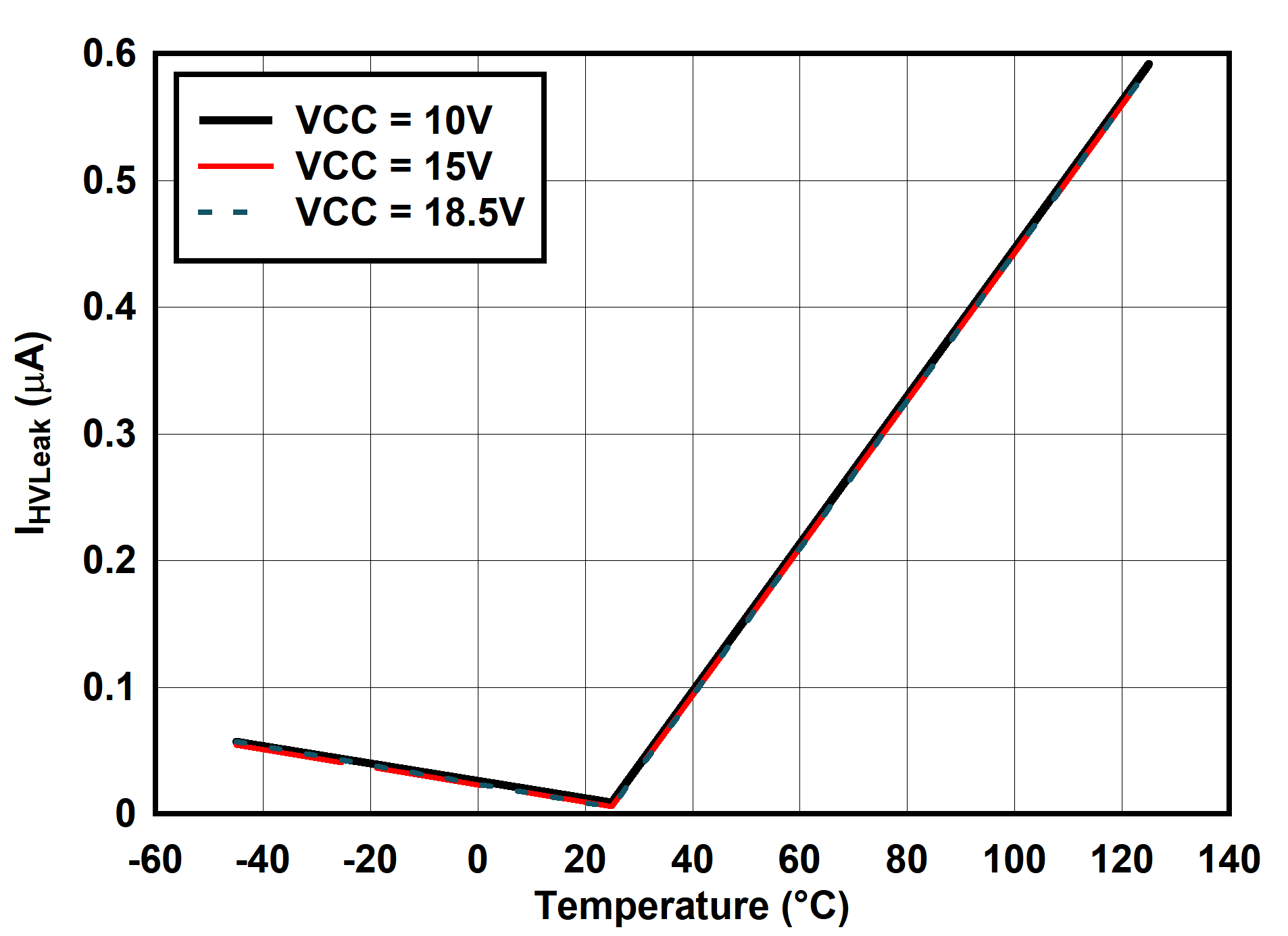
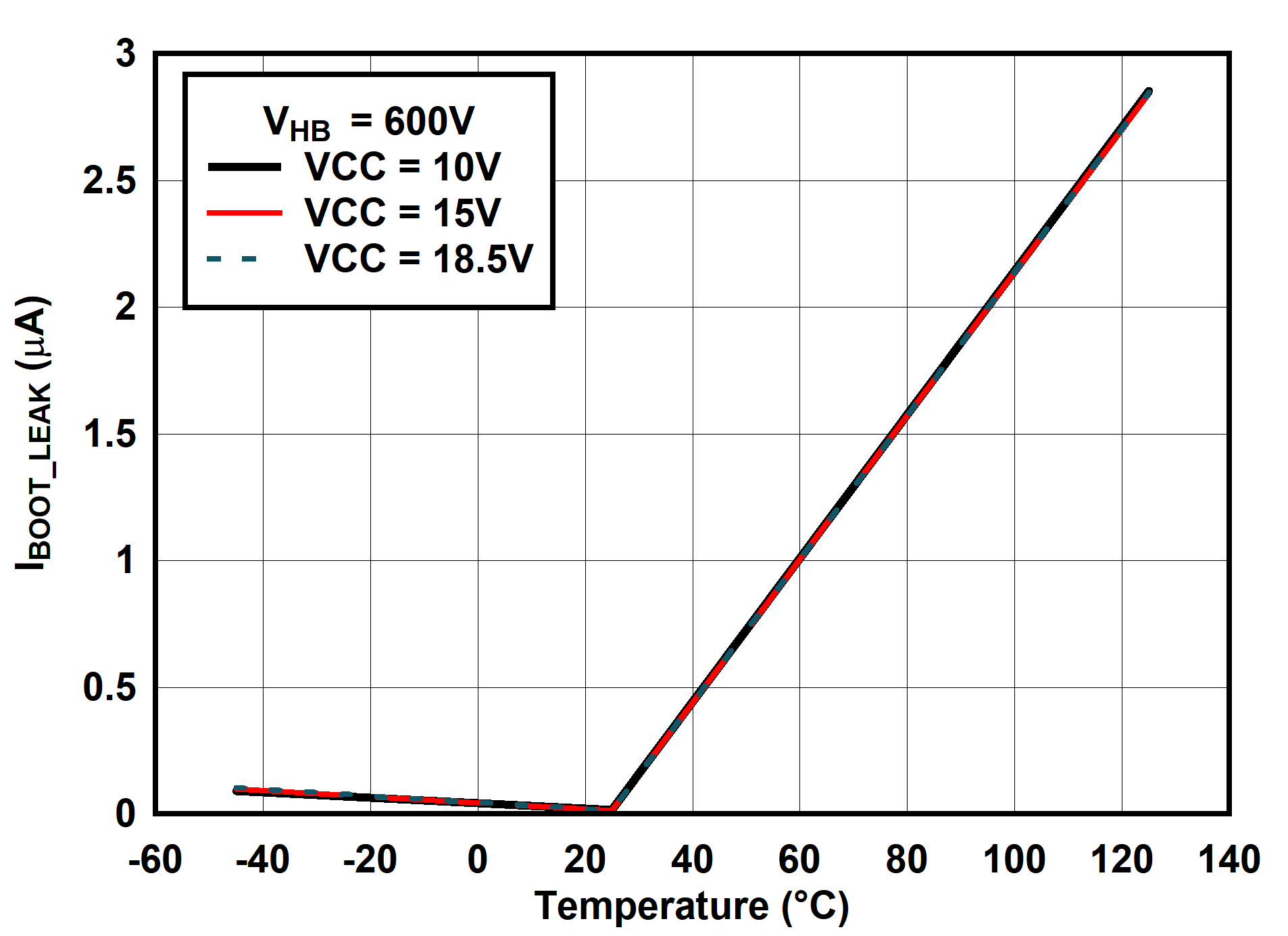
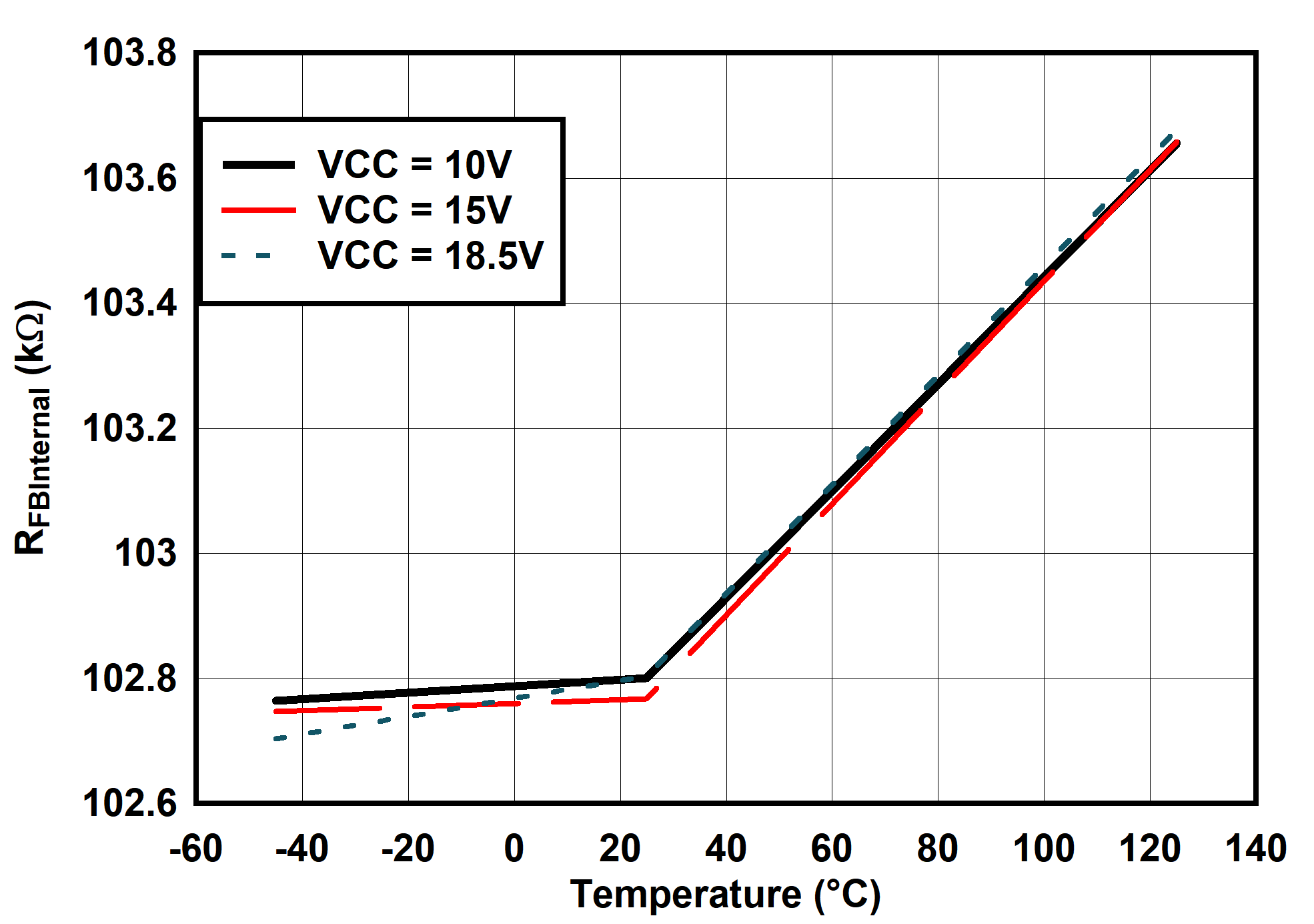
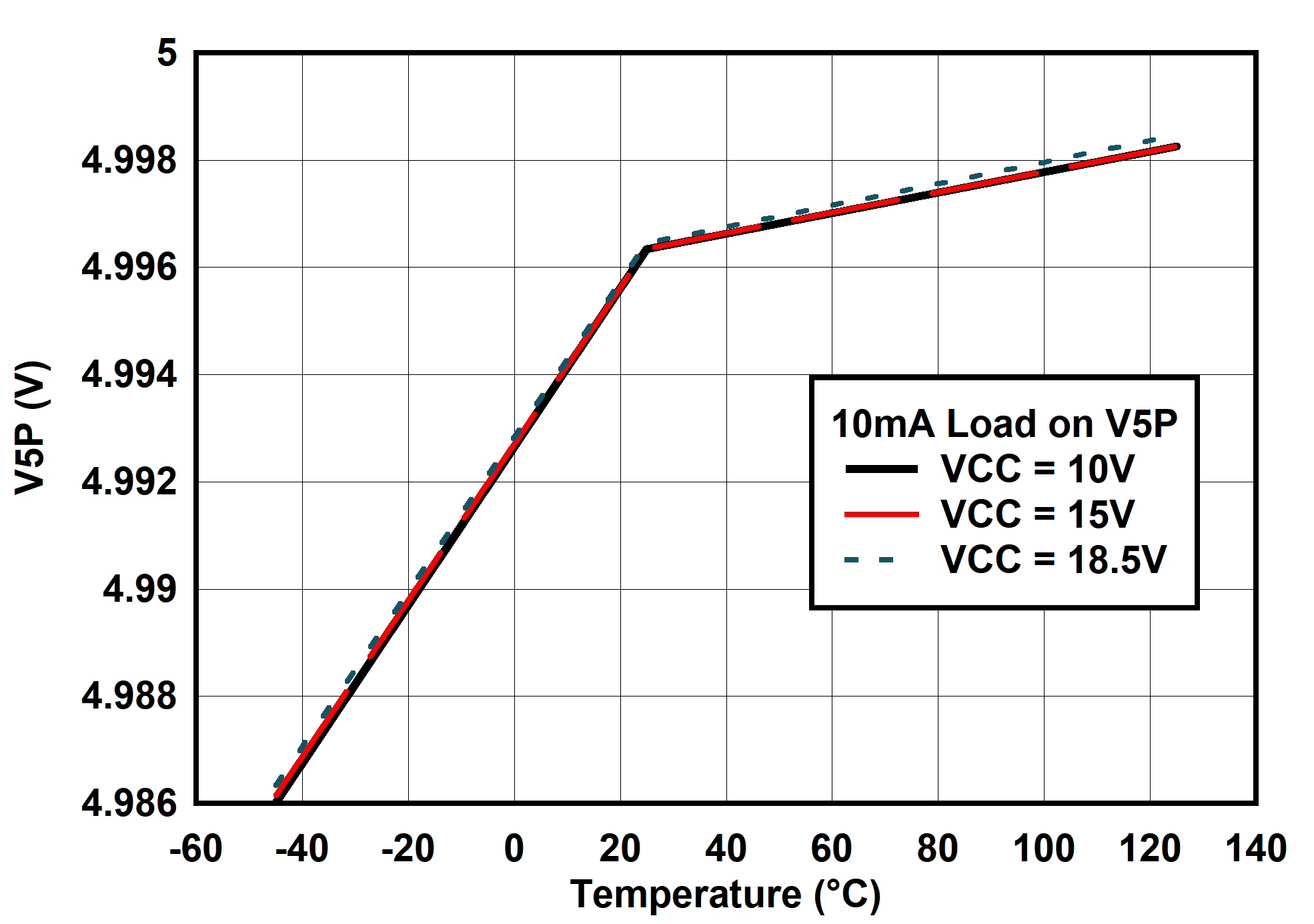
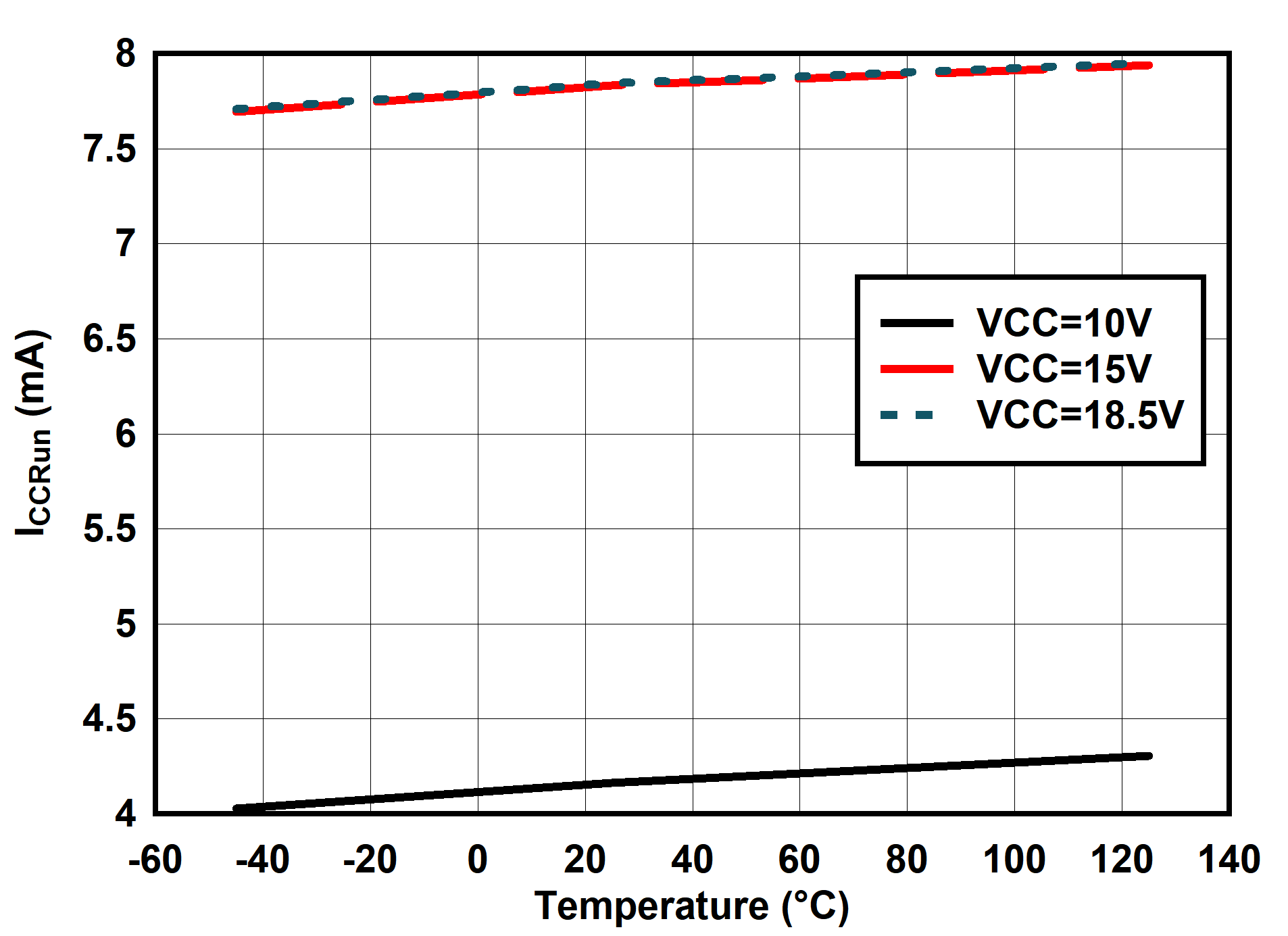
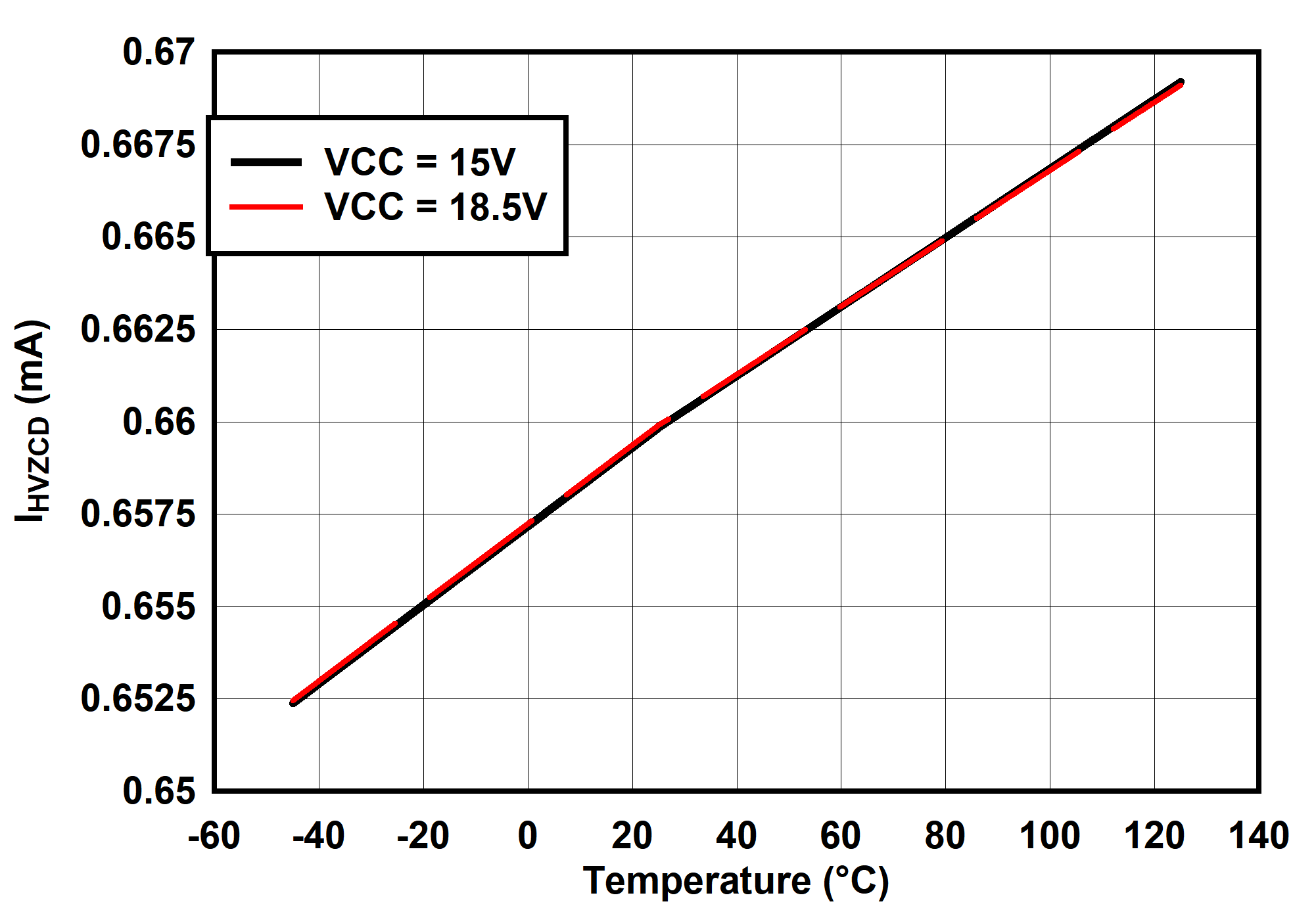
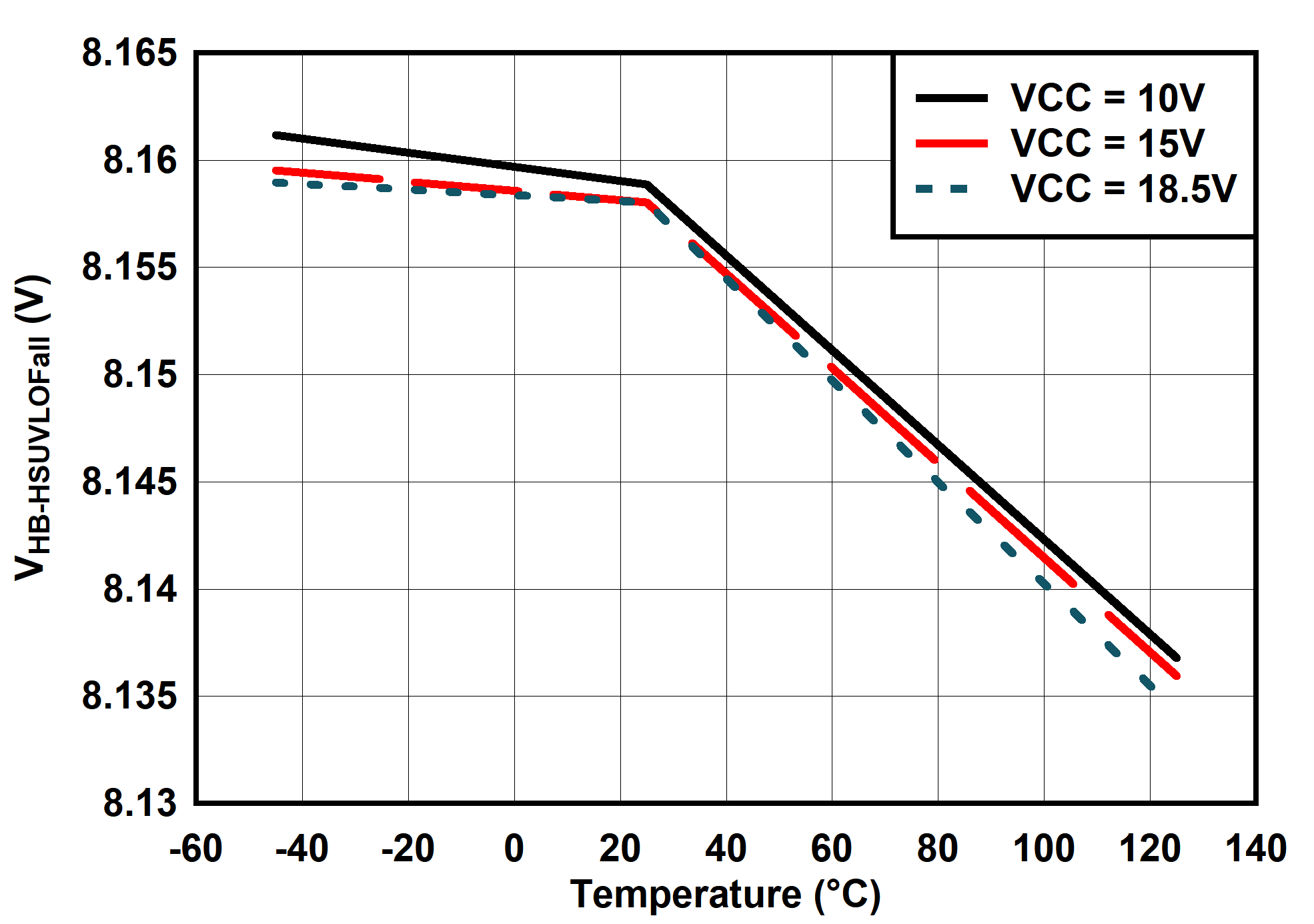
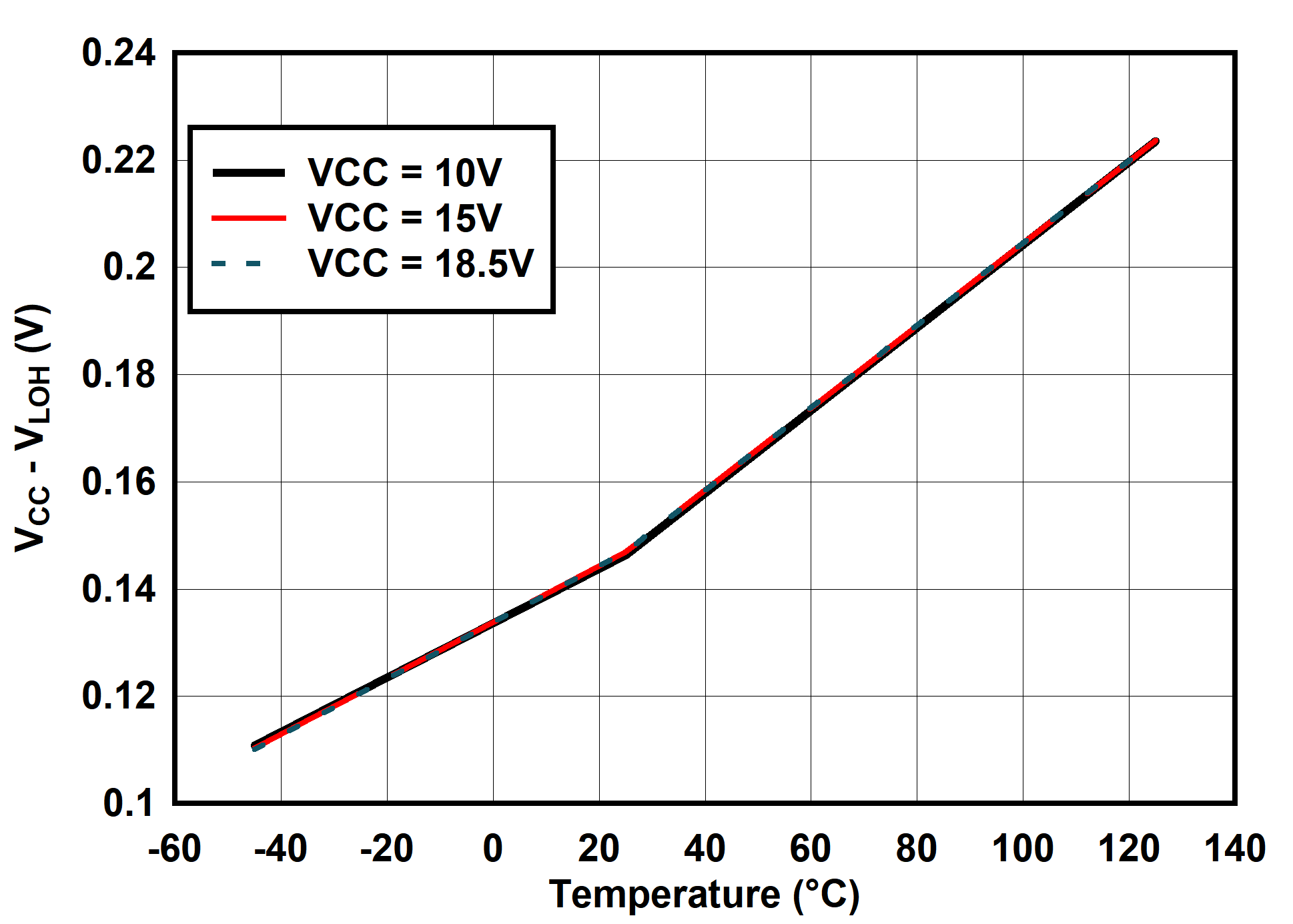
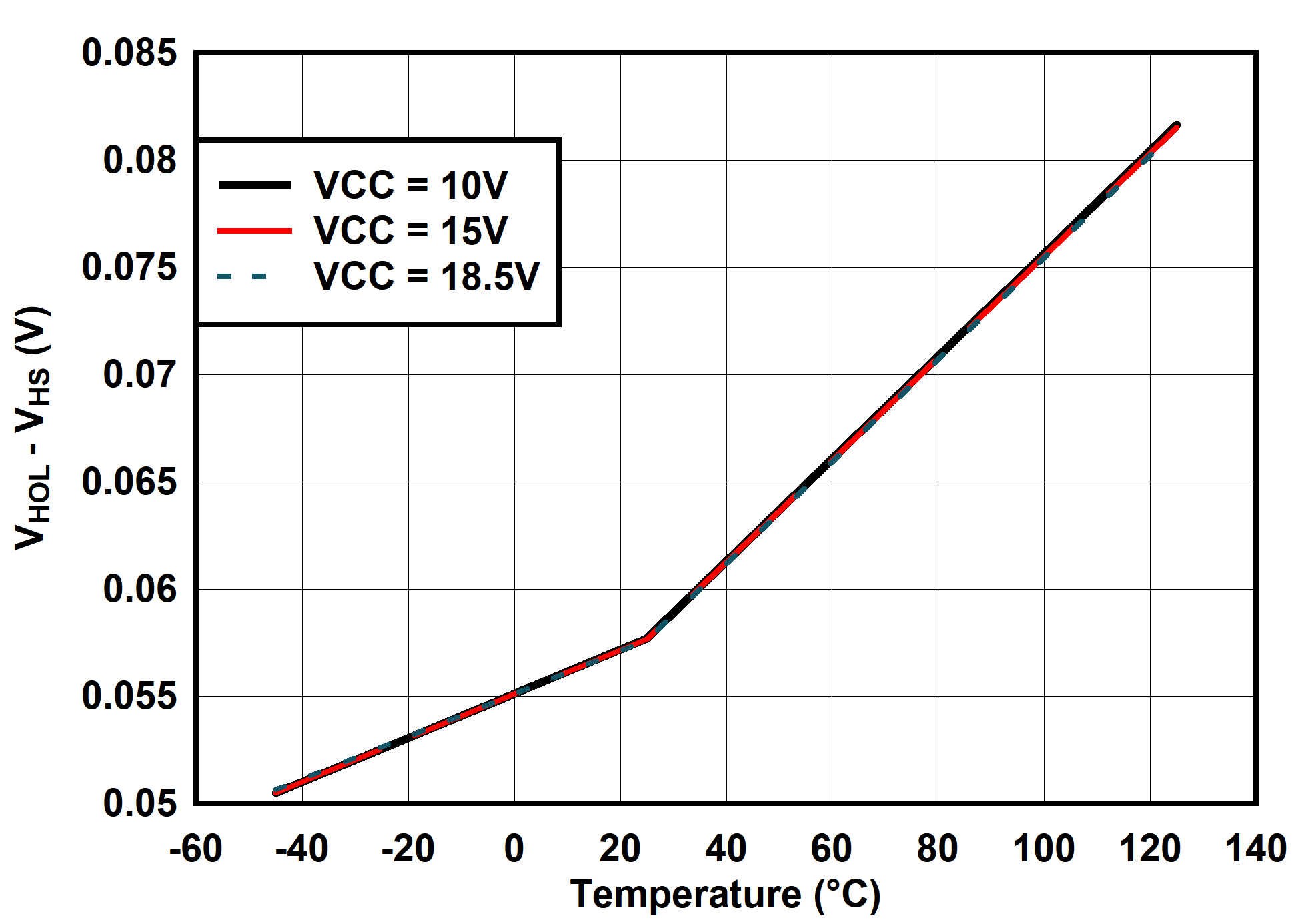
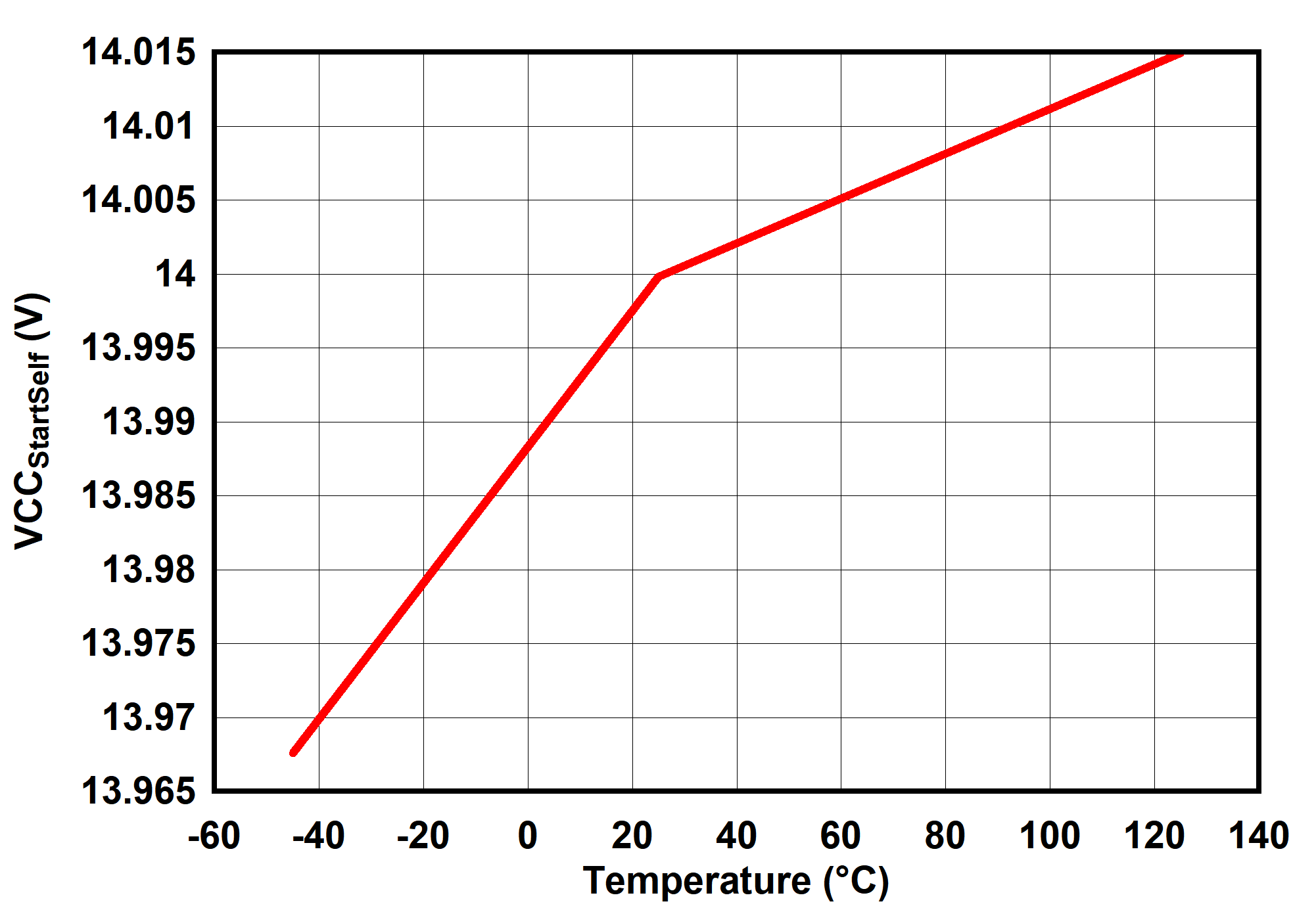
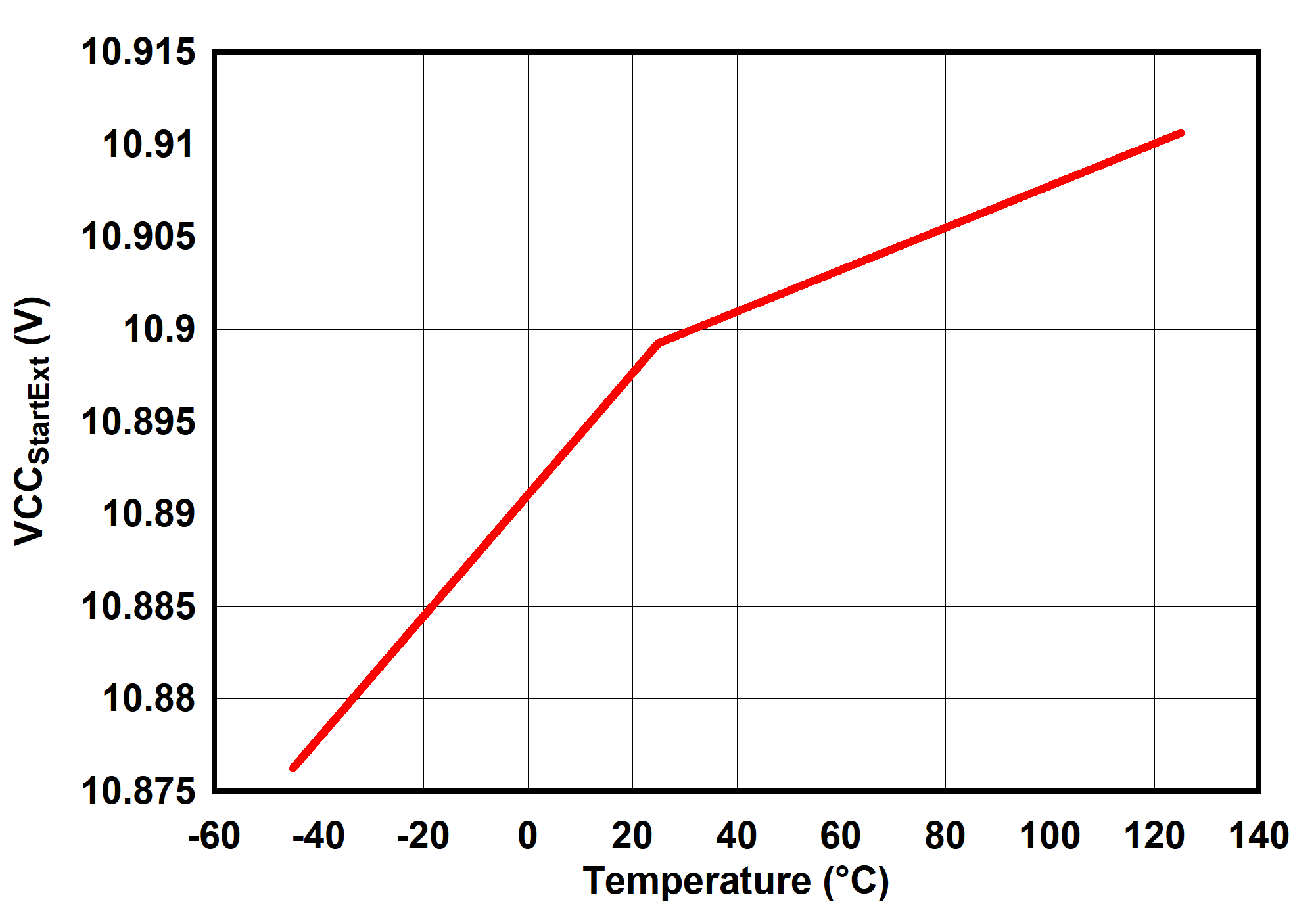
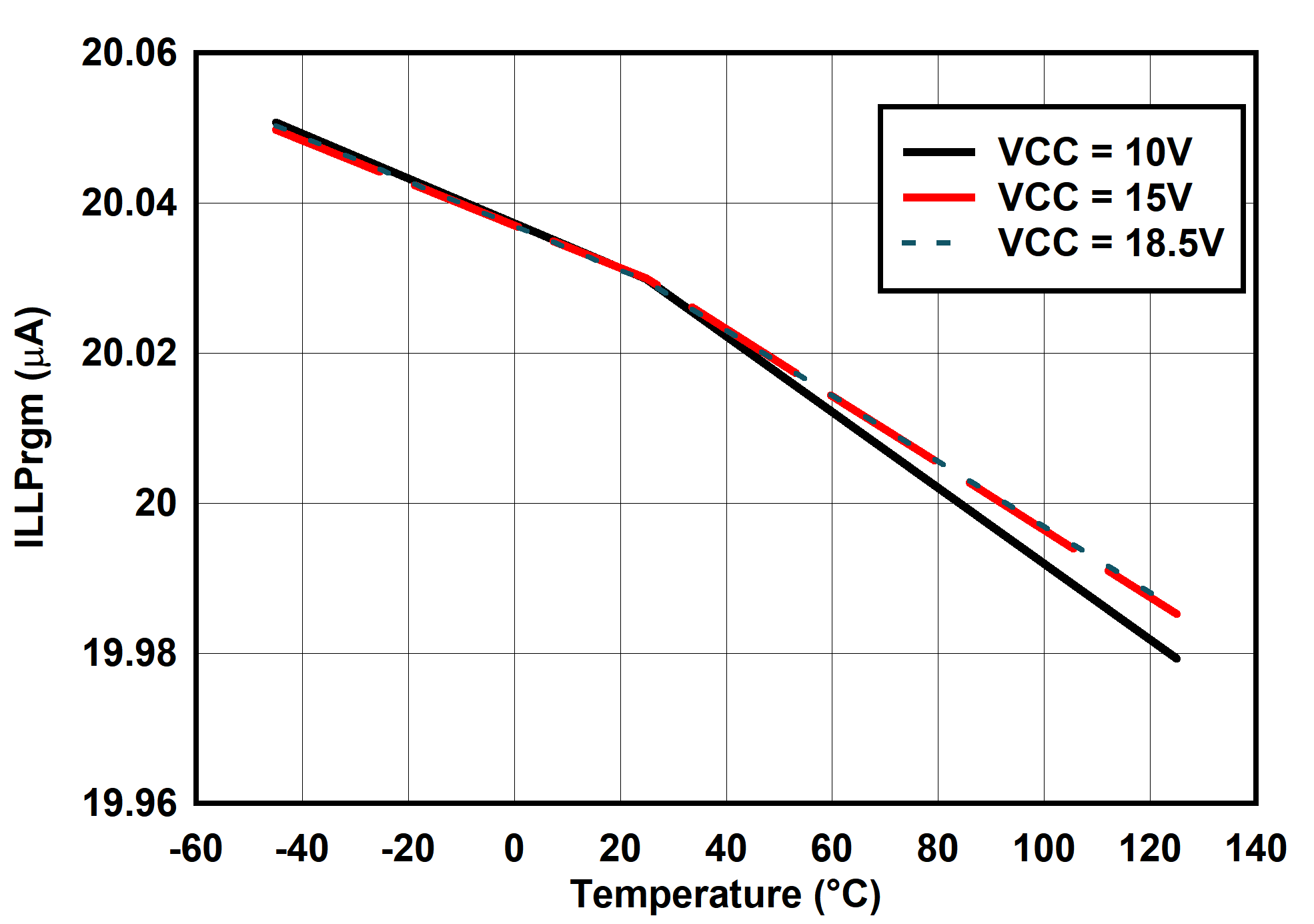
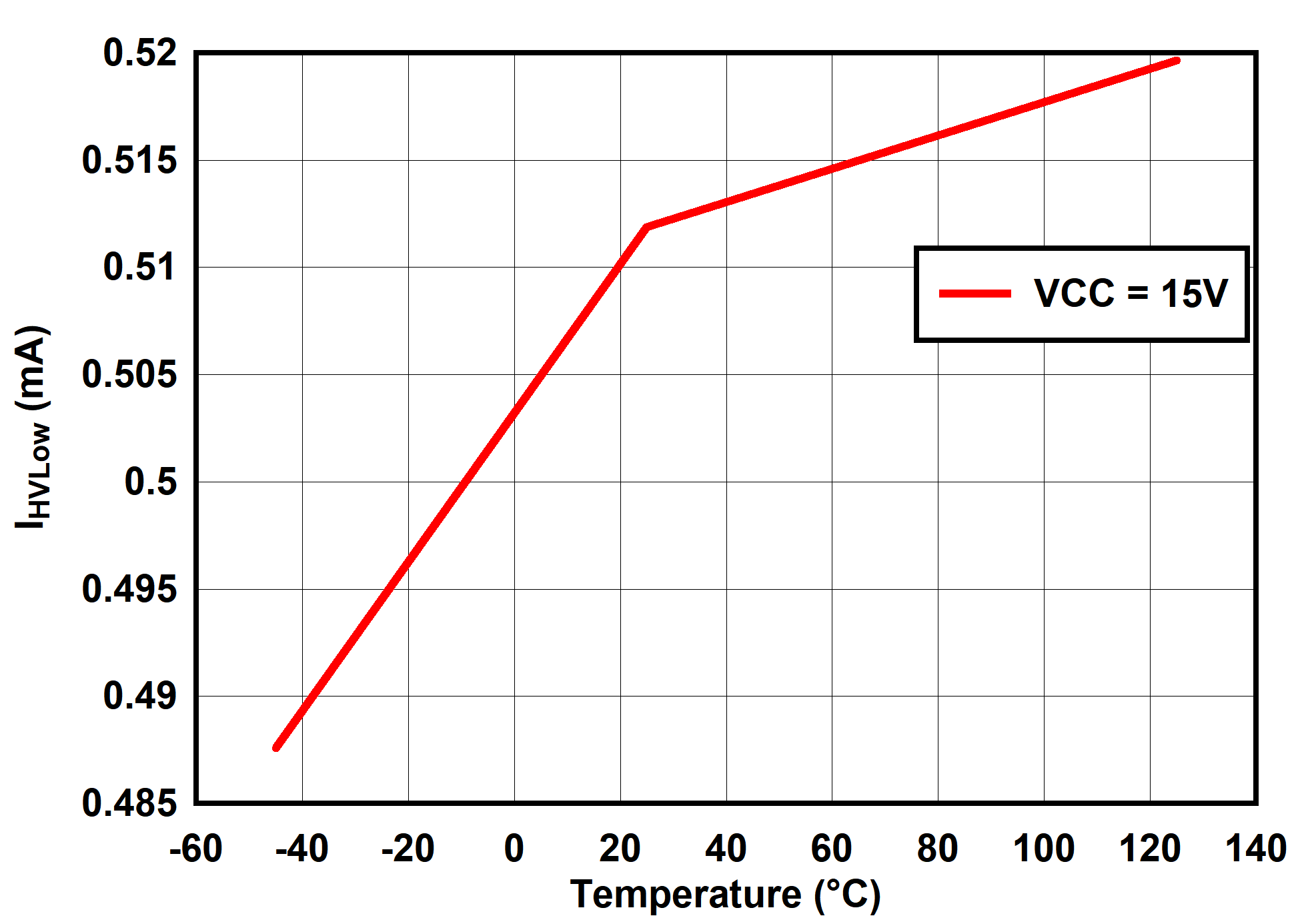
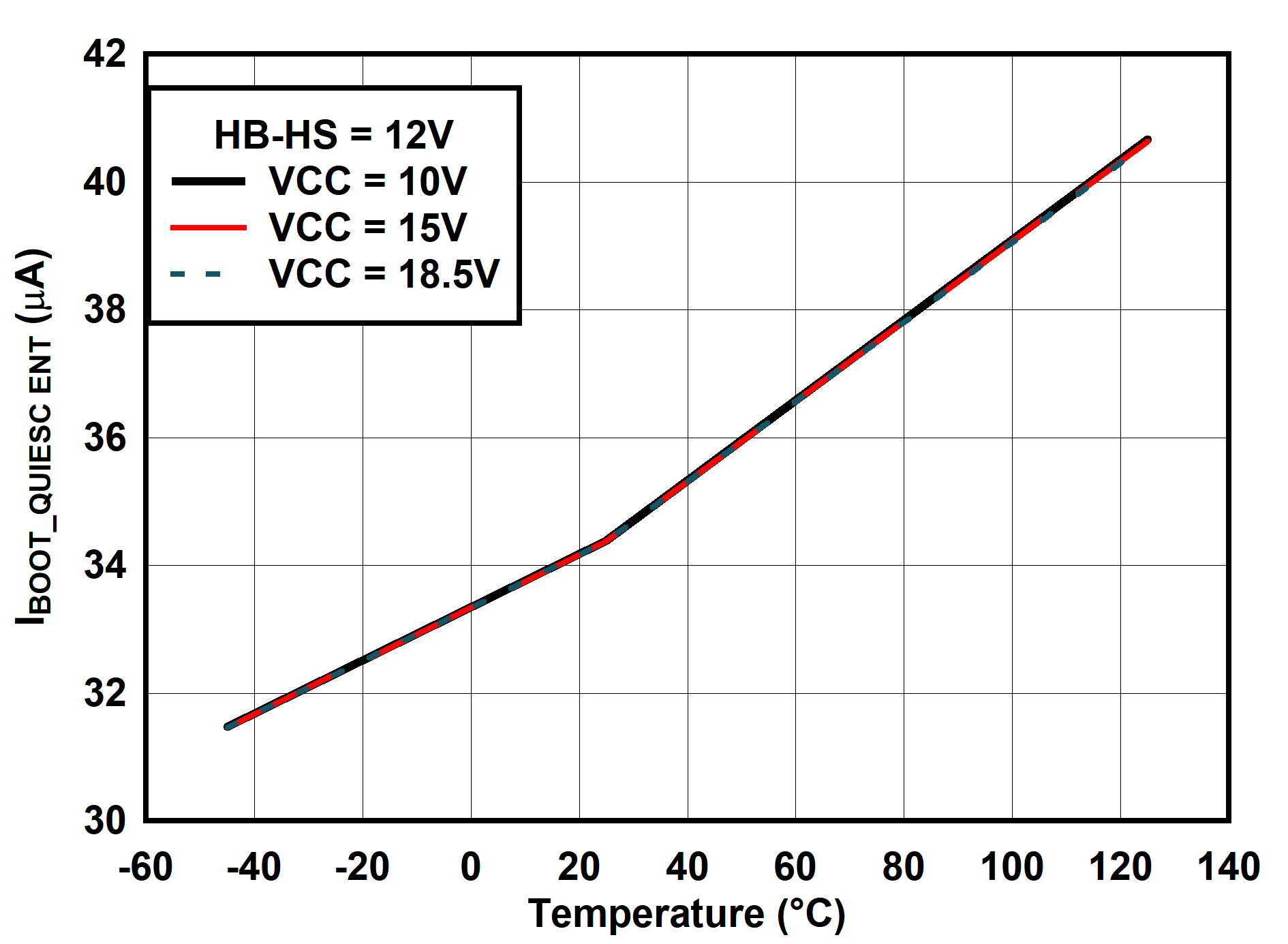
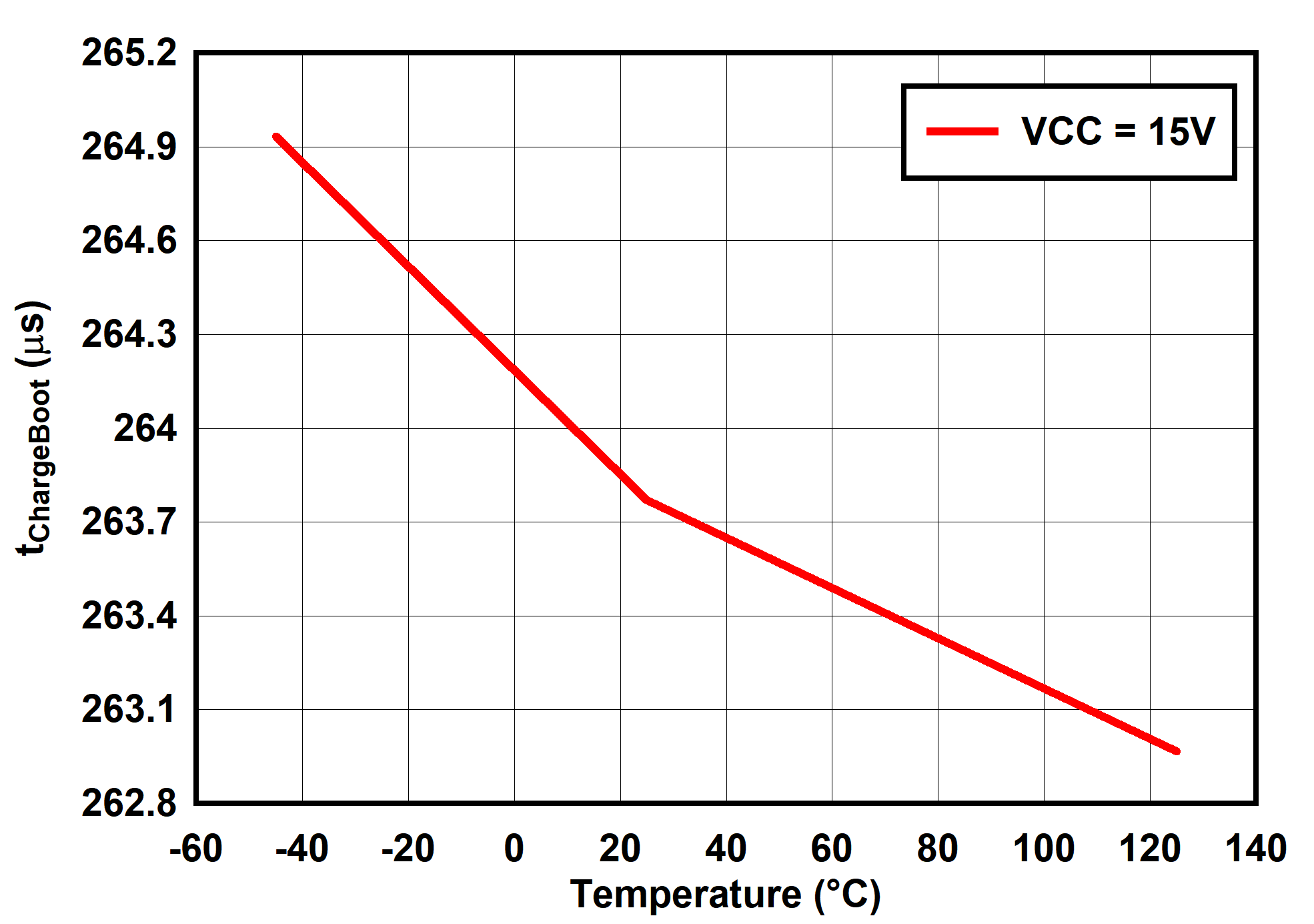
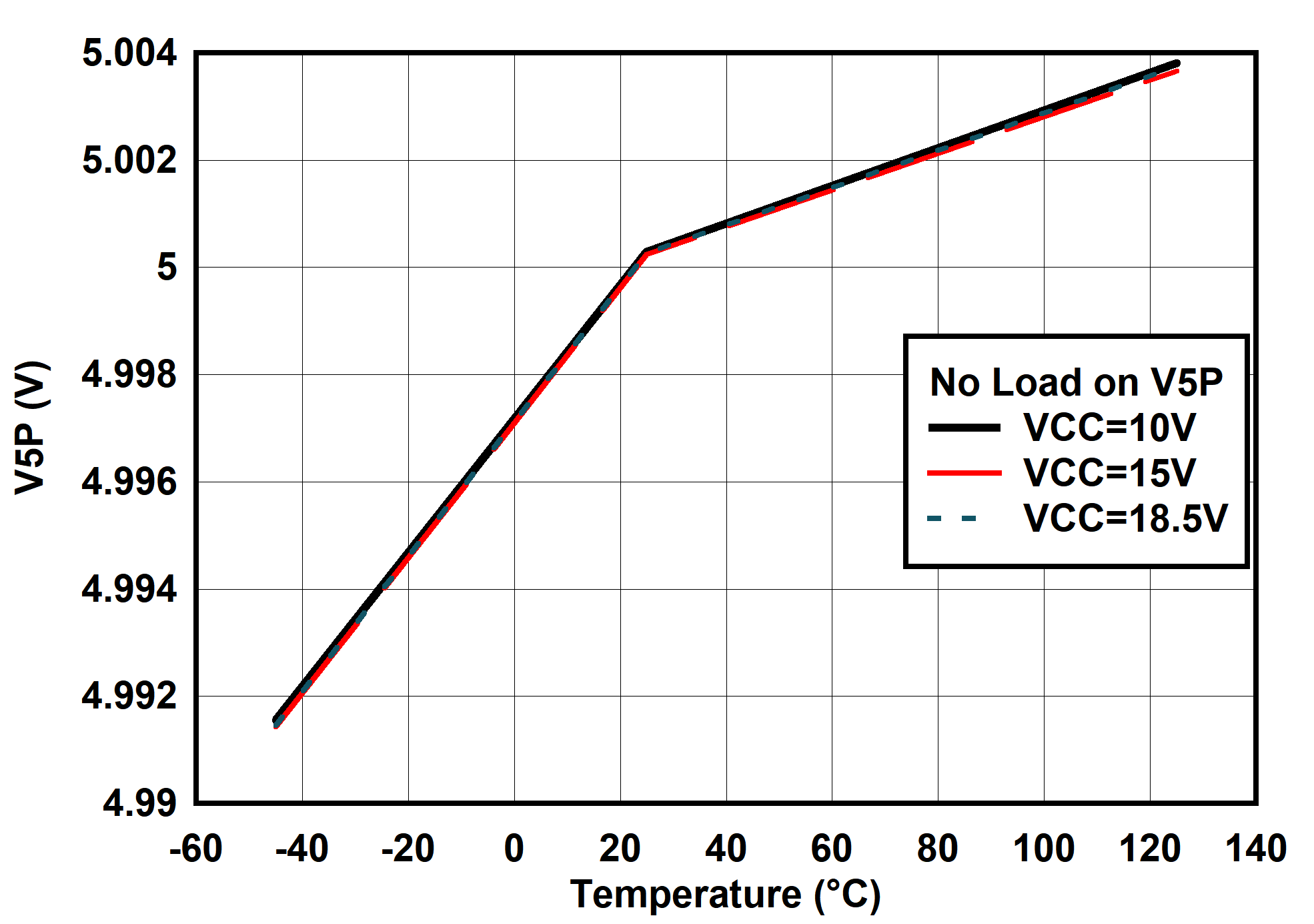
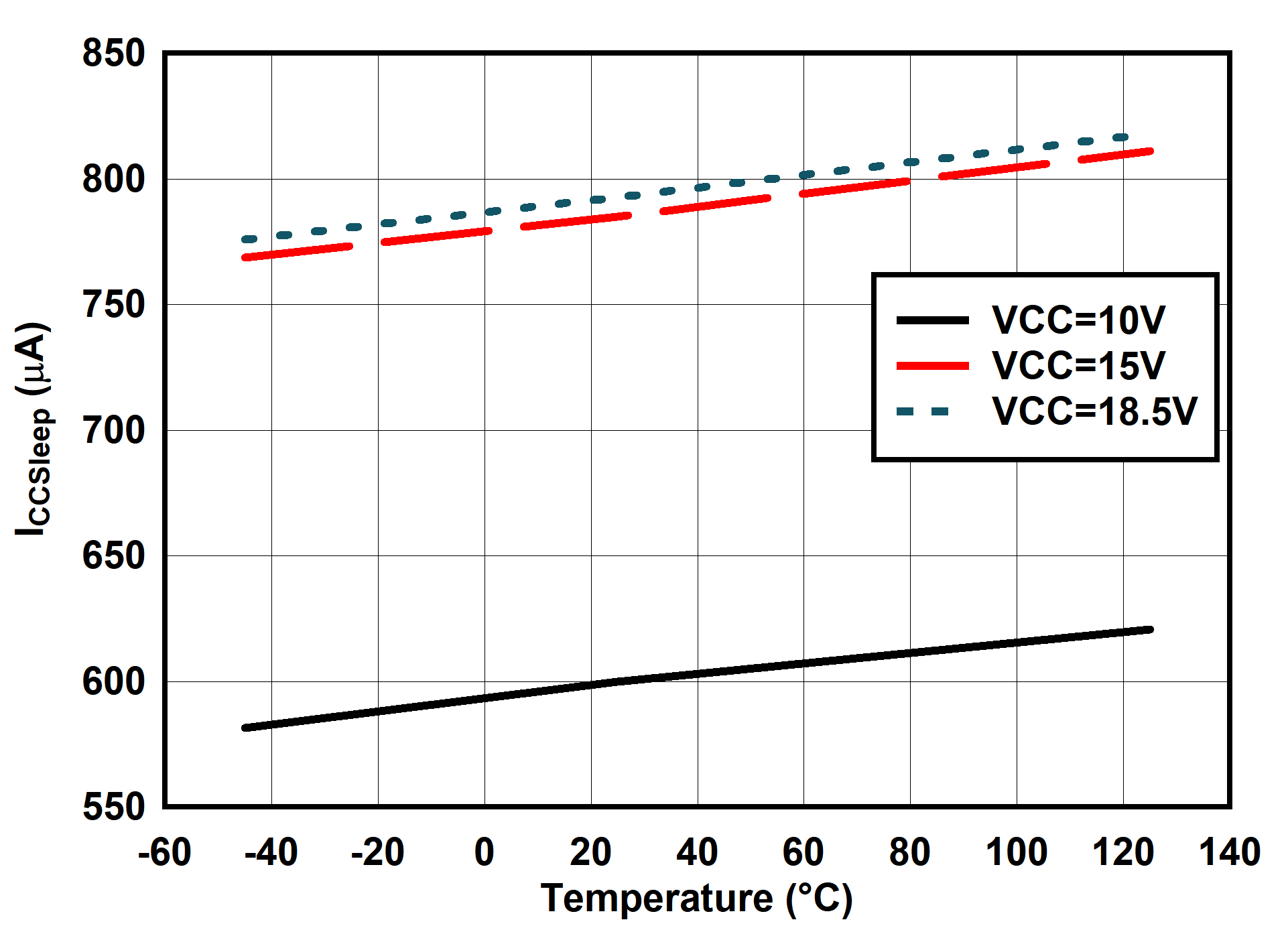
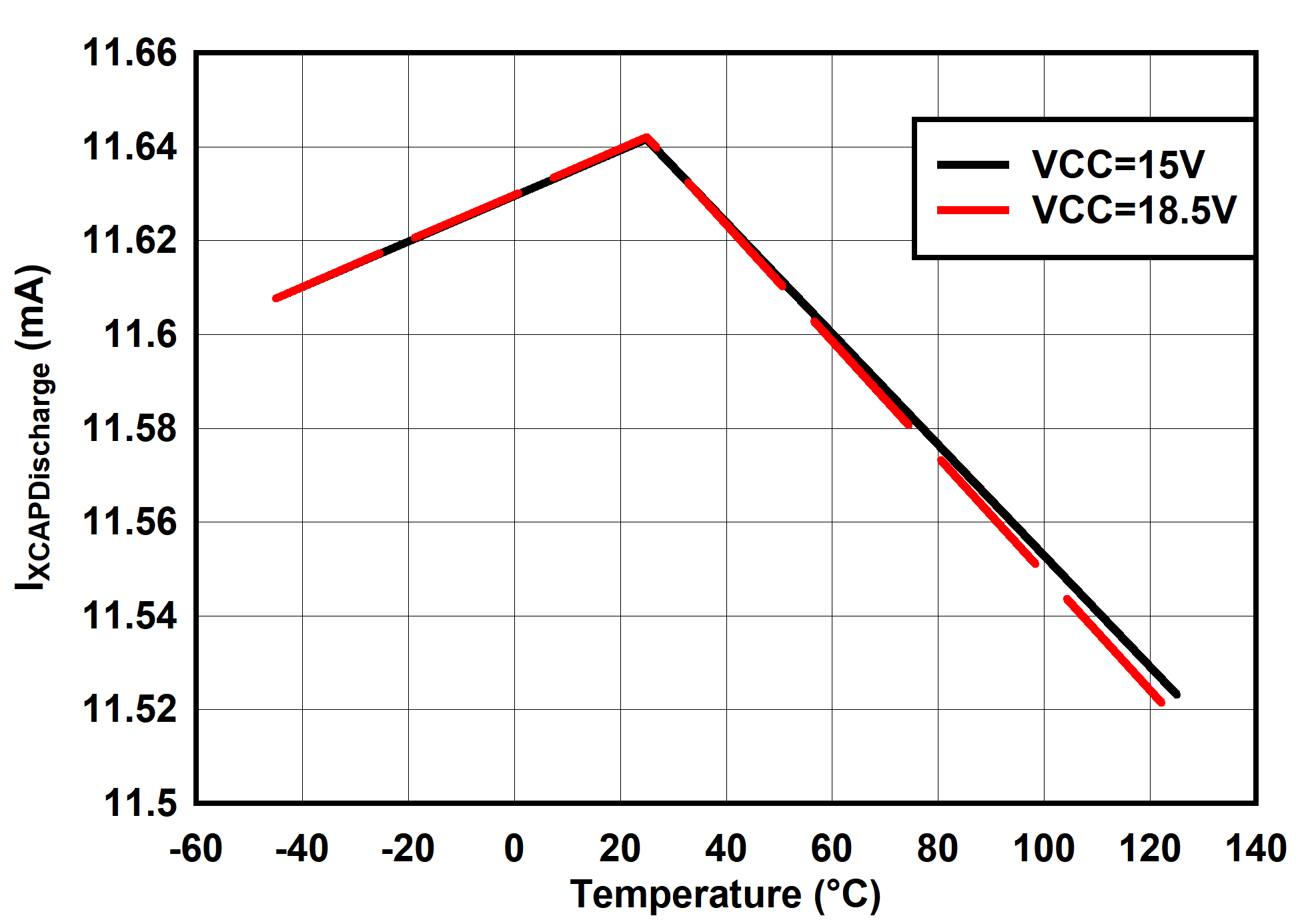
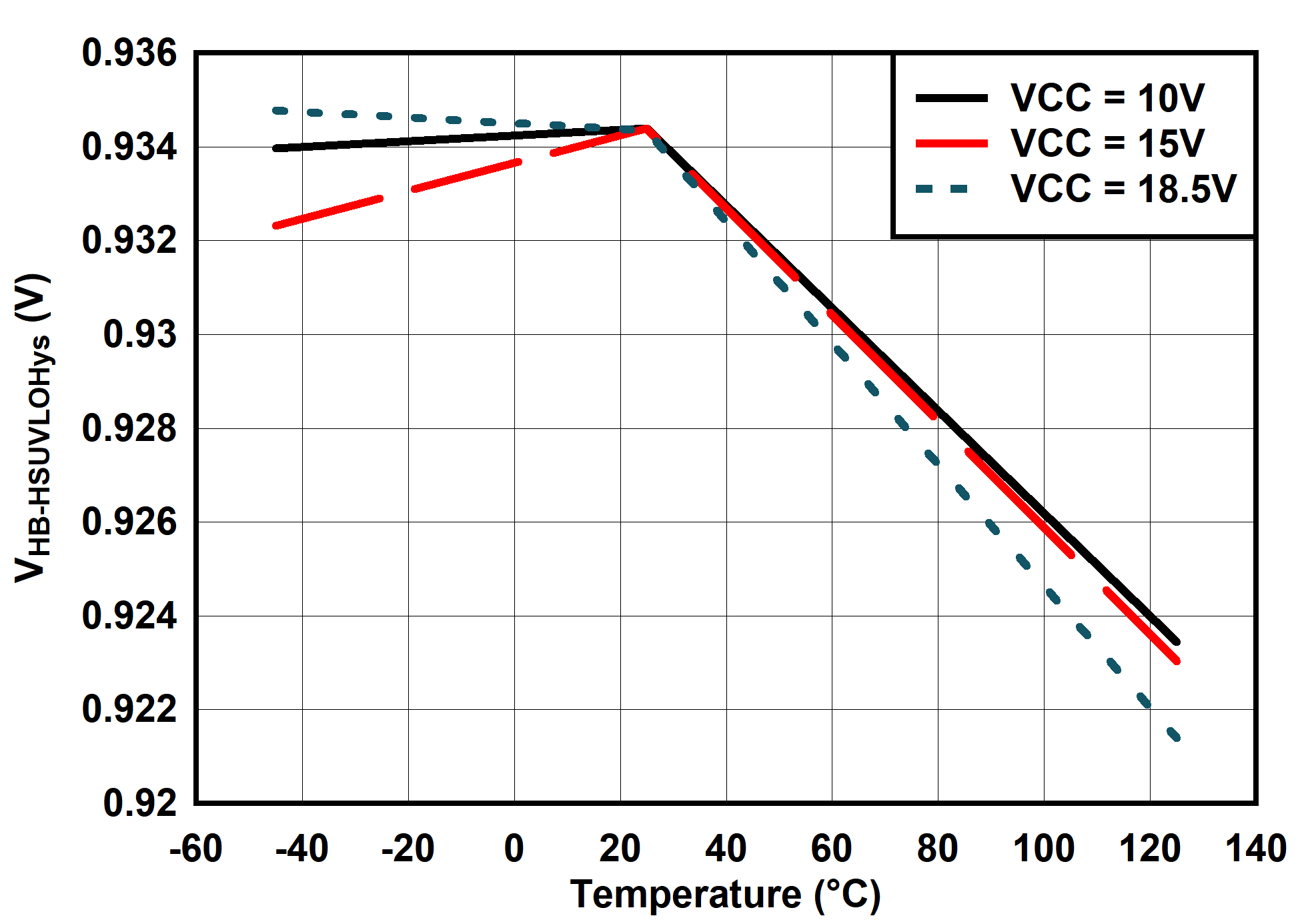
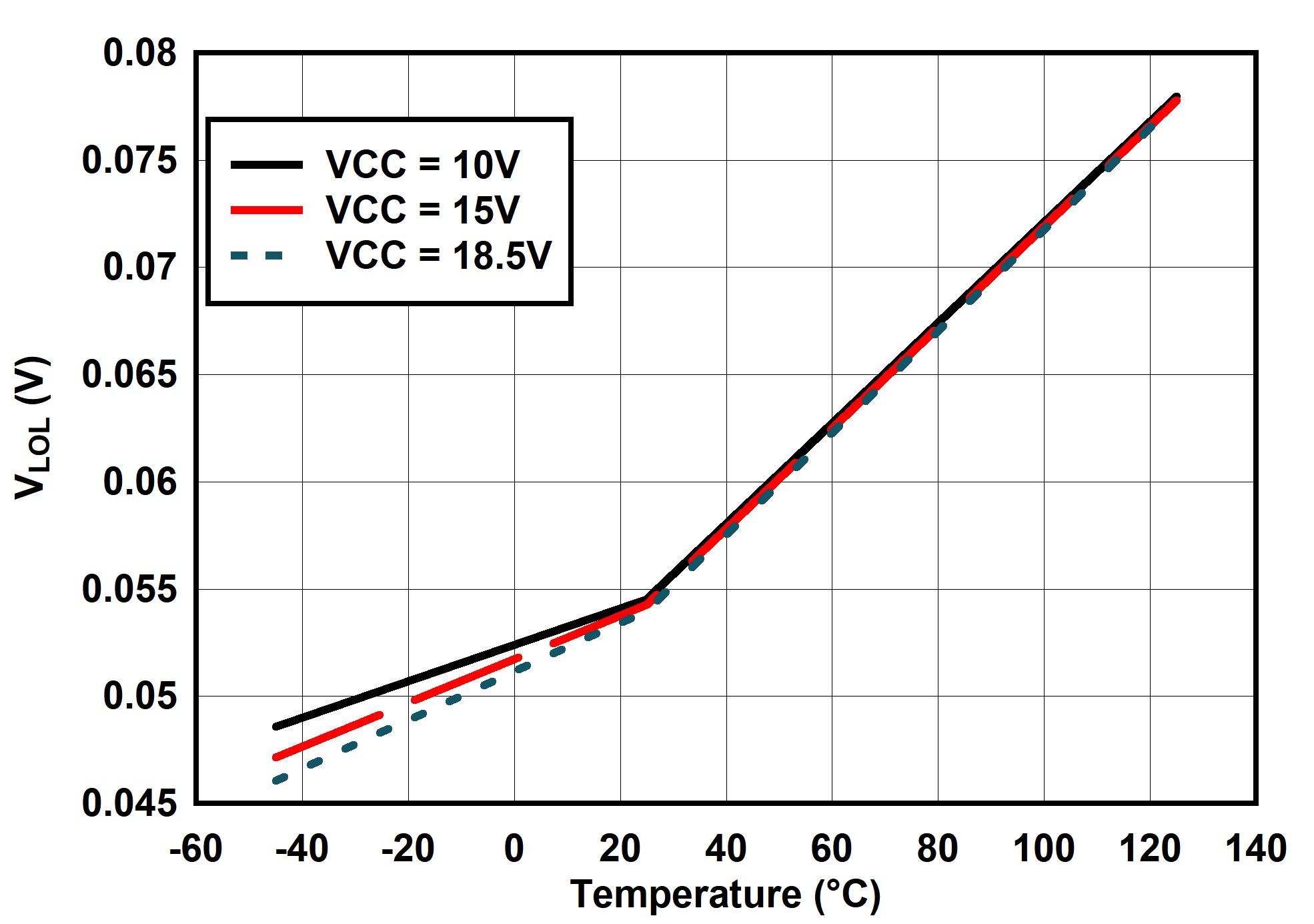
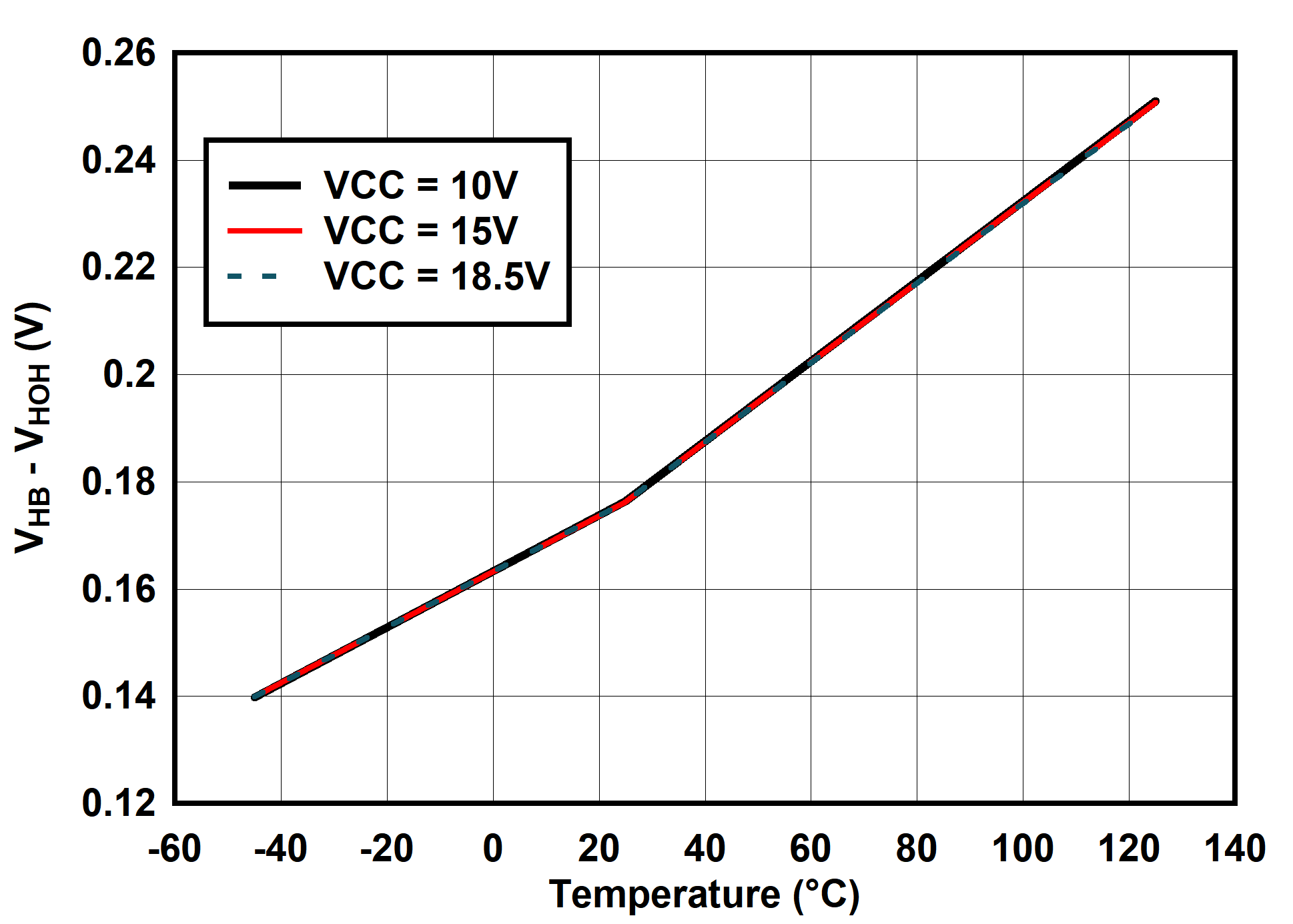
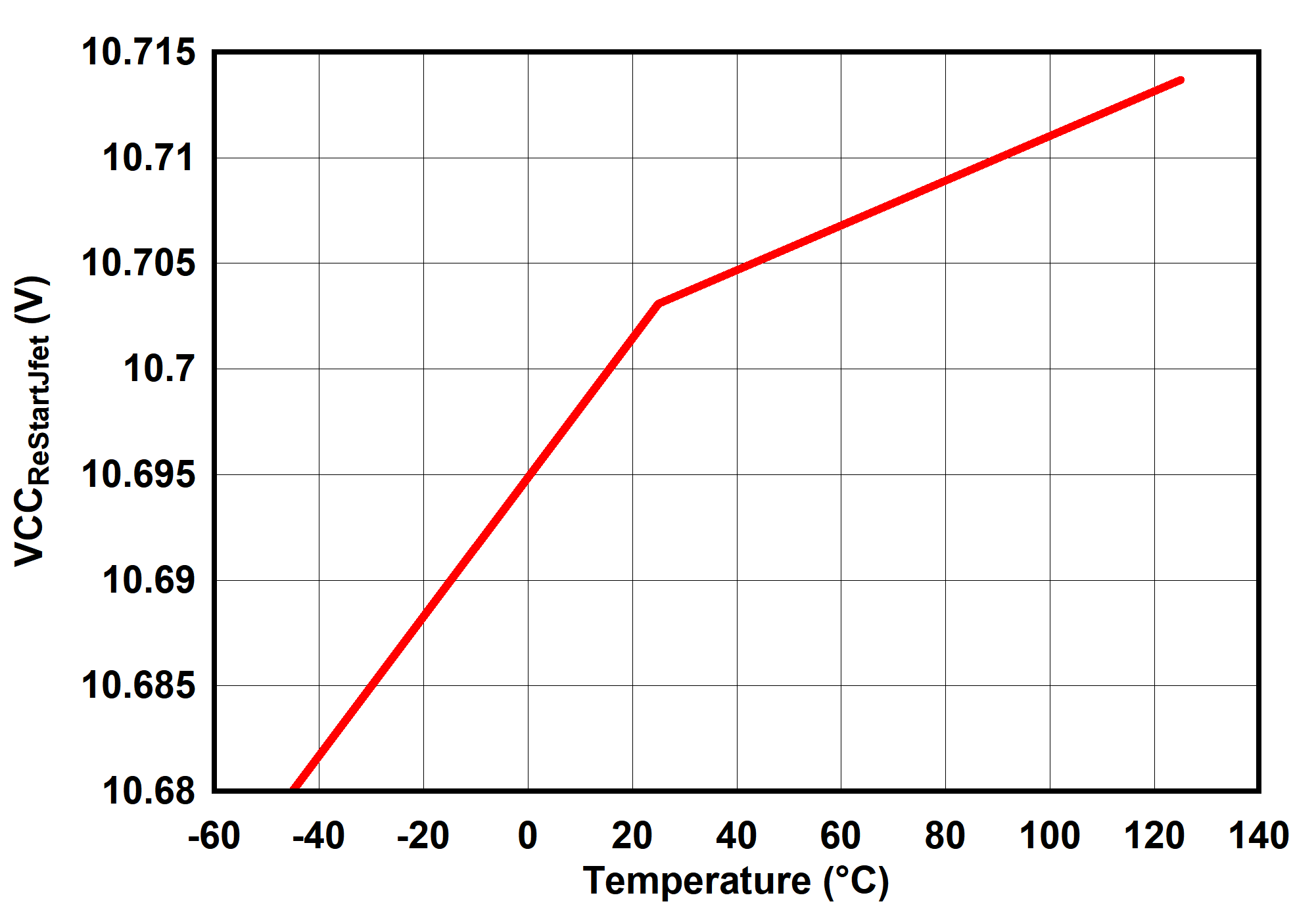
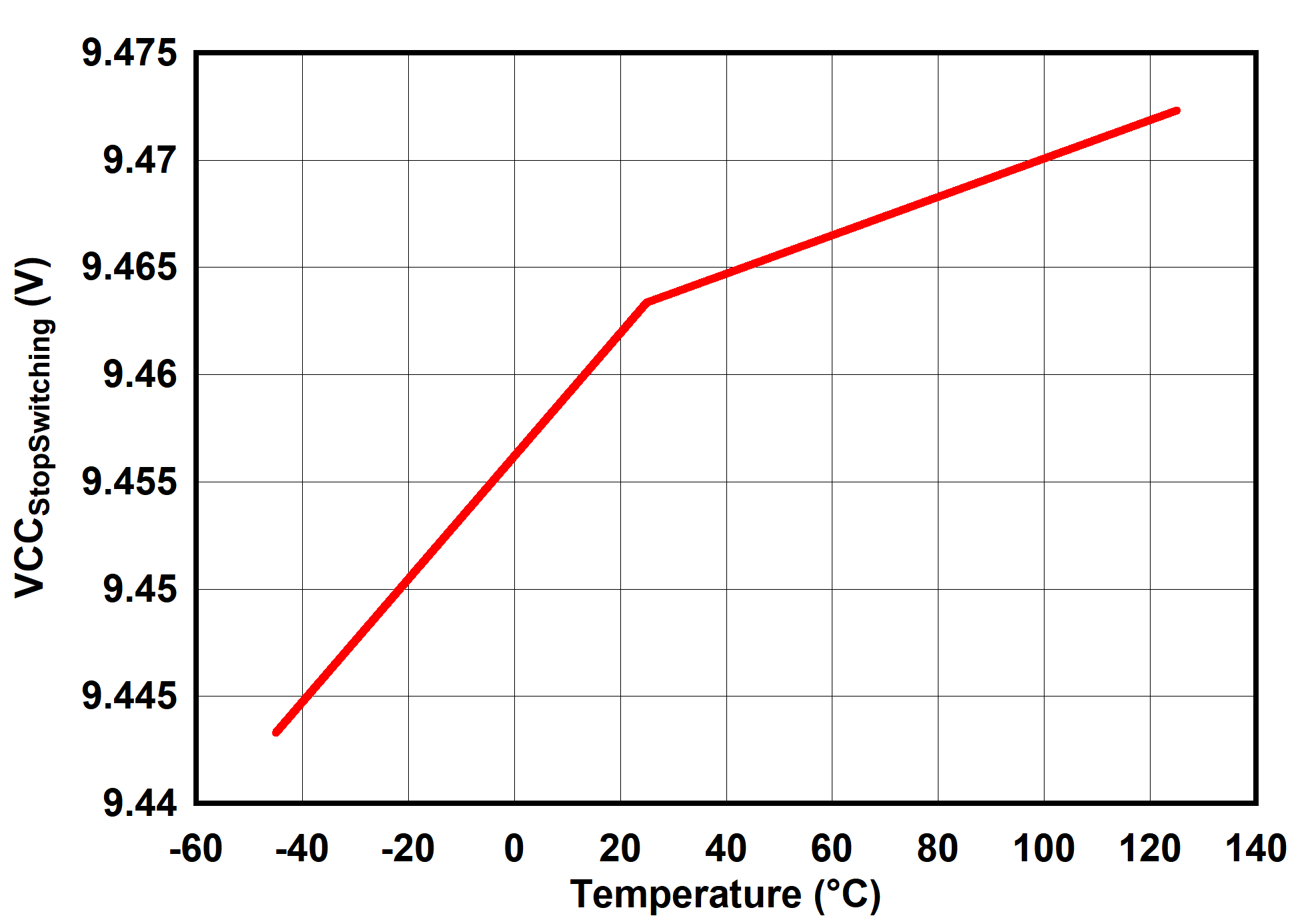
6.7 Typical Characteristics