SLVAFH1A December 2022 – December 2023 TPS62933 , TPS62933F , TPS62933O , TPS62933P
- 1
- Create an Inverting Power Supply Using a TPS6293x Buck Converter With Internal Compensation
- Trademarks
- 1Configuring the Buck Converter for Inverting Buck-Boost Topology Application
- 2Choosing the Correct Buck Converter for Inverting Power Application
- 3Selecting Applicable External Components for Inverting Power Application
- 4Experimental Results
- 5Summary
- 6References
- 7Revision History
1 Configuring the Buck Converter for Inverting Buck-Boost Topology Application
The inverting buck-boost topology is similar to the buck topology. In the buck configuration, shown in Figure 1-1, the positive connection (VOUT) is connected to the inductor, and the return connection is connected to the integrated circuit (IC) ground (GND). However, in the inverting buck-boost configuration, shown in Figure 1-2, the IC GND is used as the negative output voltage pin. What was the positive output in the buck configuration is used as the GND. This inverting topology allows the output voltage to be inverted and always lower than the GND.
 Figure 1-1 Buck Converter Application
Figure 1-1 Buck Converter Application Figure 1-2 Buck-Boost Converter
Application
Figure 1-2 Buck-Boost Converter
ApplicationThe circuit operation in the inverting buck-boost topology is different from the buck topology. Figure 1-3 (a) shows that the output voltage terminals are reversed, though the components are wired the same as a buck converter. During the on time of the control MOSFET, shown in Figure 1-3 (b), the inductor is charged with current while the output capacitor supplies the load current. The inductor does not provide current to the load during that time. During the off time of the control MOSFET and the on time of the synchronous MOSFET, shown in Figure 1-3 (c), the inductor provides current to the load and the output capacitor. These changes affect many parameters as described in the upcoming sections.
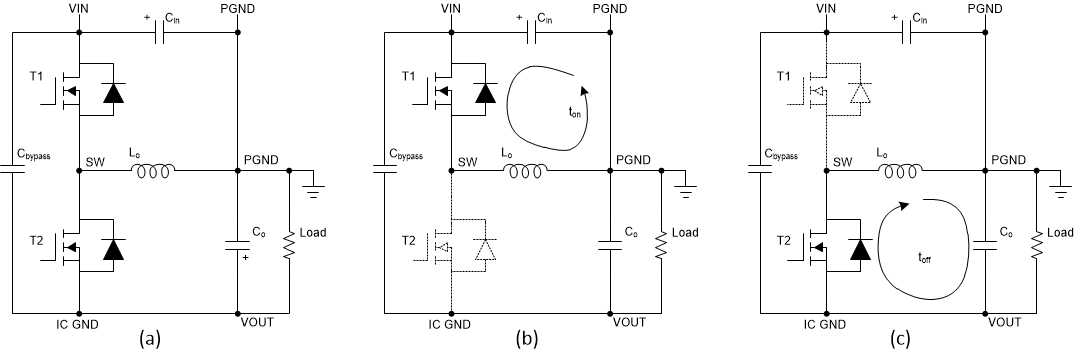 Figure 1-3 Inverting Buck Boost
Configuration
Figure 1-3 Inverting Buck Boost
Configuration