SLVS503F November 2003 – February 2020 TPS2490 , TPS2491
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
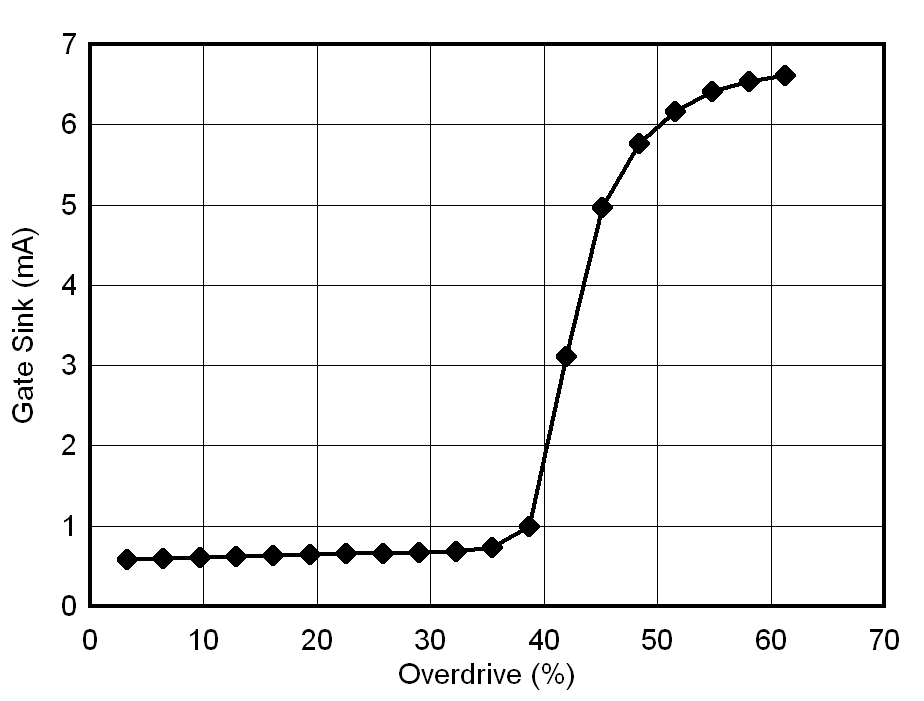
6.7 Typical Characteristics
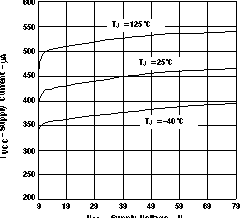 Figure 1. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 1. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage 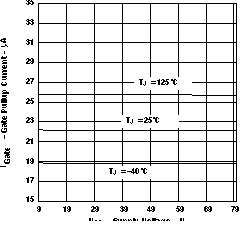 Figure 3. Gate Pullup Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 3. Gate Pullup Current vs Supply Voltage 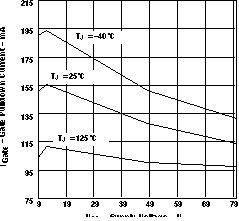 Figure 5. Gate Pulldown Current vs Supply Voltage (EN = 4 V, V(VCC – Sense) = 200 mV)
Figure 5. Gate Pulldown Current vs Supply Voltage (EN = 4 V, V(VCC – Sense) = 200 mV) 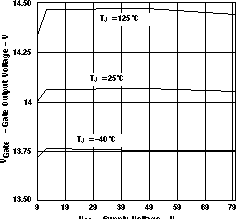 Figure 7. Gate Output Voltage vs Supply Voltage
Figure 7. Gate Output Voltage vs Supply Voltage 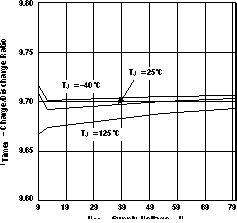 Figure 9. Timer Charge/Discharge Ratio vs Supply Voltage and Temperature
Figure 9. Timer Charge/Discharge Ratio vs Supply Voltage and Temperature 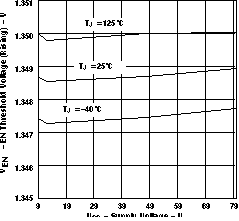 Figure 11. EN Threshold Voltage (Rising) vs Supply Voltage
Figure 11. EN Threshold Voltage (Rising) vs Supply Voltage 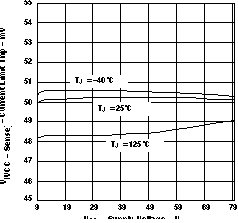 Figure 2. Current Limit Trip vs Supply Voltage
Figure 2. Current Limit Trip vs Supply Voltage 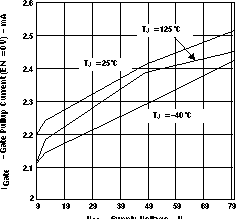 Figure 4. Gate Pulldown Current (EN = 0 V) vs Supply Voltage
Figure 4. Gate Pulldown Current (EN = 0 V) vs Supply Voltage 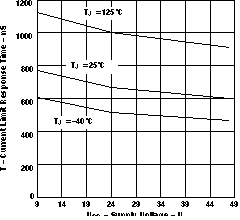 Figure 6. Current Limit Response Time vs Supply Voltage (EN = 4 V, V(VCC – Sense) = 200 mV)
Figure 6. Current Limit Response Time vs Supply Voltage (EN = 4 V, V(VCC – Sense) = 200 mV) 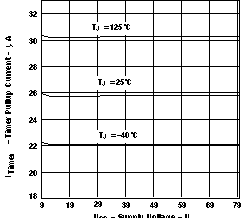 Figure 8. Timer Pullup Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 8. Timer Pullup Current vs Supply Voltage 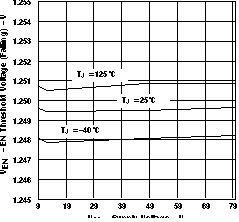 Figure 10. EN Threshold Voltage (Falling) vs Supply Voltage
Figure 10. EN Threshold Voltage (Falling) vs Supply Voltage