SLVS514P April 2004 – August 2024 TPS2041B , TPS2042B , TPS2043B , TPS2044B , TPS2051B , TPS2052B , TPS2053B , TPS2054B
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 General Switch Catalog
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Revision History
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.2.2.1 Low-Power Bus-Powered and High-Power Bus-Powered Functions
Both low-power and high-power bus-powered functions obtain all power from upstream ports; low-power functions always draw less than 100 mA; high-power functions must draw less than 100 mA at power up and can draw up to 500 mA after enumeration. If the load of the function is more than the parallel combination of 44 Ω and 10 μF at power up, the device must implement inrush current limiting (see Figure 9-17).
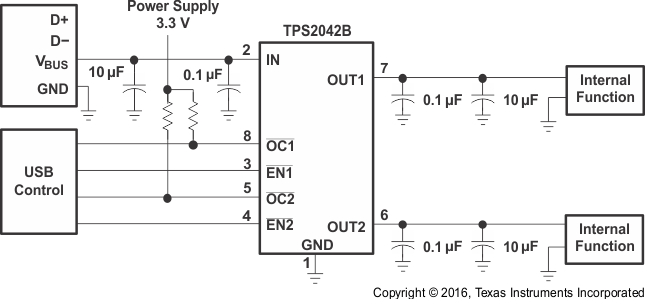 Figure 9-17 High-Power Bus-Powered Function (Example, TPS2042B)
Figure 9-17 High-Power Bus-Powered Function (Example, TPS2042B)