SLVSB69C June 2012 – September 2021 TPS54719
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation And Output Current
- 7.3.3 Bootstrap Voltage (Boot) And Low Dropout Operation
- 7.3.4 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.5 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.6 Adjusting The Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.8 Slow Start/Tracking Pin
- 7.3.9 Sequencing
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 Constant Switching Frequency And Timing Resistor (RT Pin)
- 7.4.2 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.4.3 Frequency Shift
- 7.4.4 Reverse Overcurrent Protection
- 7.4.5 Power Good (PWRGD Pin)
- 7.4.6 Overvoltage Transient Protection
- 7.4.7 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4.8 Small Signal Model For Loop Response
- 7.4.9 Simple Small Signal Model For Peak Current Mode Control
- 7.4.10 Small Signal Model For Frequency Compensation
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 High Frequency, 1.8-V Output Power Supply Design With Adjusted UVLO
- 8.2.2 Design Requirements
- 8.2.3
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.3.1 Selecting The Switching Frequency
- 8.2.3.2 Output Inductor Selection
- 8.2.3.3 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.3.4 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.3.5 Slow-Start Capacitor
- 8.2.3.6 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.3.7 Undervoltage Lockout Set Point
- 8.2.3.8 Output Voltage And Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.3.9 Compensation
- 8.2.4 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
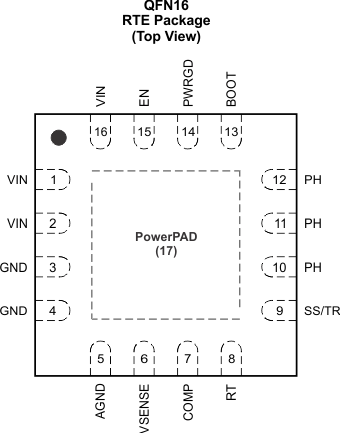 Figure 5-1 16-Pin RTE QFN Package (Top View)
Figure 5-1 16-Pin RTE QFN Package (Top View)Table 5-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| AGND | 5 | Analog Ground should be electrically connected to GND close to the device. | |
| BOOT | 13 | I | A bootstrap capacitor is required between BOOT and PH. If the voltage on this capacitor is below the minimum required by the BOOT UVLO, the output is forced to switch off until the capacitor is refreshed. |
| COMP | 7 | O | Error amplifier output and input to the output switch current comparator. Connect frequency compensation components to this pin. |
| EN | 15 | I | Enable pin, internal pullup current source. Pull below 1.18 V to disable. Float to enable. Can be used to set the on/off threshold (adjust UVLO) with two additional resistors. |
| GND | 3, 4 | Power Ground. This pin should be electrically connected directly to the power pad under the IC. | |
| PH | 10, 11, 12 | O | The source of the internal high-side power MOSFET and drain of the internal low-side (synchronous) rectifier MOSFET. |
| PWRGD | 14 | O | An open-drain output. Asserts low if output voltage is low due to thermal shutdown, overcurrent, overvoltage/undervoltage, or EN shut down. |
| RT | 8 | I | Resistor timing |
| SS/TR | 9 | I/O | Slow start. An external capacitor connected to this pin sets the output voltage rise time. This pin can also be used for tracking. |
| Thermal Pad | 17 | GND pin should be connected to the exposed power pad for proper operation. This thermal pad should be connected to any internal PCB ground plane using multiple vias for good thermal performance. | |
| VIN | 1, 2, 16 | I | Input supply voltage: 2.95 V to 6 V |
| VSENSE | 6 | I | Inverting node of the transconductance (gm) error amplifier |