SLVUBE3B May 2018 – June 2021 TPS56637
3.1 Output Voltage Setpoint
To change the output voltage of the EVMs, it is necessary to change the value of resistor R6. Changing the value of R6 can change the output voltage above 0.6 V. The value of R6 for a specific output voltage can be calculated using Equation 1.
Equation 1. 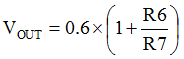
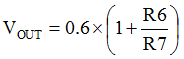
Table 3-1 lists the R6 values for some common output voltages.
Table 3-1 Recommended Component Values
| OUTPUT VOLTAGE(1) (V) | R6(2) (kΩ) | R7 (kΩ) | L1 (µH) | COUT(3) (µF) | C9 (pF)(4) | R8 (kΩ)(4) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | TYP | MAX | ||||||
| 1.05 | 7.5 | 10.0 | 1 | 30 | 35 | 100 | ||
| 1.2 | 10 | 10.0 | 1 | 30 | 35 | 100 | ||
| 1.8 | 20 | 10.0 | 1.2 | 30 | 35 | 100 | ||
| 3.3 | 45.3 | 10.0 | 2.2 | 20 | 35 | 100 | 100 to 220 | 20 |
| 5 | 73.2 | 10.0 | 3.3 | 20 | 30 | 100 | 100 to 220 | 20 |
| 12 | 191 | 10.0 | 5.6 | 25 | 30 | 100 | 100 to 220 | 20 |
(1) Please use the recommended L1 and COUT combination of the higher and closest output rail for unlisted output rails.
(2) R6=0Ω for VOUT=0.6V
(3) COUT is the sum of effective output capacitance. In this datasheet the effective capacitance is defined as the actual capacitance under DC bias and temperature, not the rated or nameplate values. All high value ceramic capacitors have a large voltage coefficient in addition to normal tolerances and temperature effects. A careful study of bias and temperature variation of any capacitor bank should be made in order to ensure that the minimum value of effective capacitance is provided. Refer to the information of DC bias and temperature characteristics from manufacturers of ceramic capacitors.
(4) R8 and C9 can be used to improve the load transient response or improve the loop-phase margin. The application report Optimizing Transient Response of Internally Compensated DCDC Converters with Feed-forward Capacitor is helpful when experimenting with a feed-forward capacitor.