-
Real-Time Control Reference Guide SLYY211 October 2021 TMS320F2800132 , TMS320F2800133 , TMS320F2800135 , TMS320F2800137 , TMS320F2800152-Q1 , TMS320F2800153-Q1 , TMS320F2800154-Q1 , TMS320F2800155 , TMS320F2800155-Q1 , TMS320F2800156-Q1 , TMS320F2800157 , TMS320F2800157-Q1 , TMS320F280021 , TMS320F280021-Q1 , TMS320F280023 , TMS320F280023-Q1 , TMS320F280023C , TMS320F280025 , TMS320F280025-Q1 , TMS320F280025C , TMS320F280025C-Q1 , TMS320F280033 , TMS320F280034 , TMS320F280034-Q1 , TMS320F280036-Q1 , TMS320F280036C-Q1 , TMS320F280037 , TMS320F280037-Q1 , TMS320F280037C , TMS320F280037C-Q1 , TMS320F280038-Q1 , TMS320F280038C-Q1 , TMS320F280039 , TMS320F280039-Q1 , TMS320F280039C , TMS320F280039C-Q1 , TMS320F280040-Q1 , TMS320F280040C-Q1 , TMS320F280041 , TMS320F280041-Q1 , TMS320F280041C , TMS320F280041C-Q1 , TMS320F280045 , TMS320F280048-Q1 , TMS320F280048C-Q1 , TMS320F280049 , TMS320F280049-Q1 , TMS320F280049C , TMS320F280049C-Q1 , TMS320F28075 , TMS320F28075-Q1 , TMS320F28076 , TMS320F28374D , TMS320F28374S , TMS320F28375D , TMS320F28375S , TMS320F28375S-Q1 , TMS320F28376D , TMS320F28376S , TMS320F28377D , TMS320F28377D-EP , TMS320F28377D-Q1 , TMS320F28377S , TMS320F28377S-Q1 , TMS320F28378D , TMS320F28378S , TMS320F28379D , TMS320F28379D-Q1 , TMS320F28379S
-
Real-Time Control Reference Guide
- 1 Message from the editors
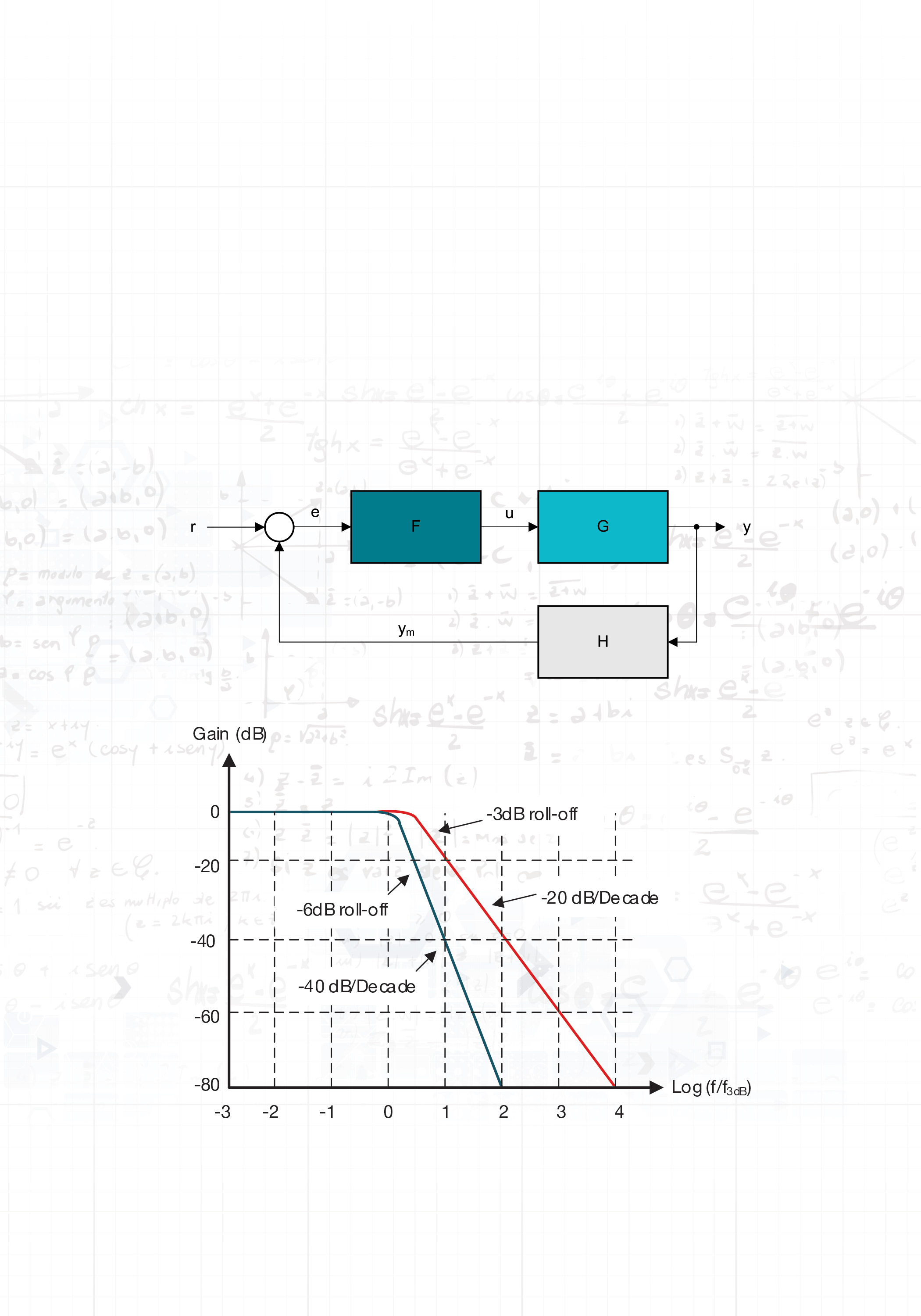
- 2 System Design
- 3 Controllers
- 4 ADC
- 5 Comparator
- 6 Processing
- 7 Encoders
- 8 Pulse width modulation (PWM)
- 9 DAC
- 10Mathematical models
- 11Important Notice
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Real-Time Control Reference Guide
1 Message from the editors
This document is intended as a valuable quick guide for often used system-level design formulae and real-time control concepts in order to help facilitate real-time control application design. We hope you find this collection of material useful.
Here is a brief overview of the key areas included:
- Mathematical Models
- First and Second Order Systems
- Filters
- Controller Types
- A/D Conversions
- Comparator Basics
- Characteristics of a Real-Time Processor
- Encoder Basics
- Pulse Width Modulation Basics
- D/A Conversions
Additional resources to explore:
- A four-part technical seminar that offers an introduction to control theory covering fundamental concepts, feedback systems, transient response, and discrete-time systems.
- A four-part course in control theory based on the state space modeling paradigm covering state space models, properties of linear systems, state feedback control, and linear state estimators
Introduction to Microcontroller Programming for Power Electronics Control Applications
- This book contains the fundamental subjects of the interdisciplinary field of power electronic based systems, which draws knowledge from circuit and control theory, (digital) signal processing for embedded implementation electrical machines/drives and power semiconductor devices. This book also presents state-of-the-art techniques to implement modulation schemes and control algorithms in a commercial microcontroller (MCU) suitable for rapid prototyping approach, and hint for designing analog circuits, such as low voltage converter, output filters/load.
- This book provides a readable introduction to control of both continuous time and discrete time systems. The first four chapters of the book cover classical methods using transfer functions. The remaining chapters cover analysis and design using state space methods. Worked examples are included to illustrate key topics in each section. The book contains five appendices; a review of matrix algebra, reference tables of Laplace and z transforms, supporting Matlab scripts, and a case study in controller design using state space methods.
Digital Control of Dynamic Systems
- This book's emphasis is on designing digital controls to achieve good dynamic response and small errors while using signals that are sampled in time and quantized in amplitude. Both transform (classical control) and state-space (modern control) methods are described and applied to illustrative examples.
Digitally Controlled High Efficiency and High Power Density PFC Cicuits - 3 Part Series
- These series of presentations introduce two bridgeless PFC designs using C2000™ MCU. TI high voltage GaN is used to implement a 3.3kW interleaved CCM totem-pole PFC and a 1.6kW interleaved TRM totem-pole PFC designs. Detailed design considerations are provided to minimize switching loss, current crossover distortion, input current THD and improve efficiency and PF.
- C2000's Digital Power SDK is a cohesive set of software infrastructure, tools, and documentation designed to minimize C2000™ MCU-based digital power system development time targeted for various AC-DC, DC-DC and DC-AC power supply applications
- The BOOSTXL-BUCKCONV reference design provides a quick and easy way to learn about digital power supply control and design using C2000 devices.
- Ready-to-use reference designs with theory, calculations, simulations, schematics, PCB files and bench test results.
- On-demand courses and tutorials ranging from introductory to advanced concepts that focus on application-specific problem solving
- Support forums for all TI products
2 System Design