SNOSD91B March 2019 – February 2020 LMG3410R150 , LMG3411R150
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Safe Operation Area (SOA)
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
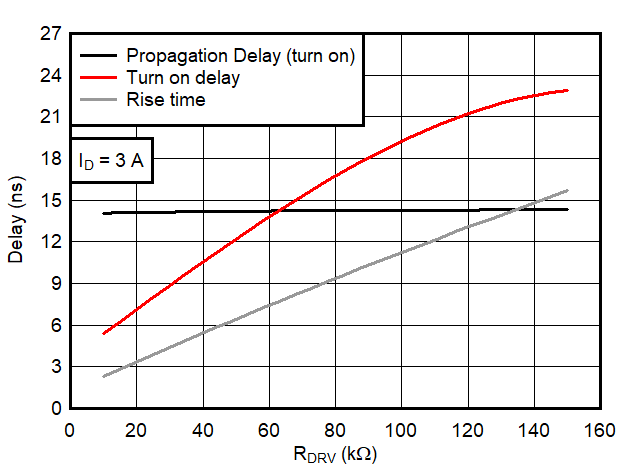
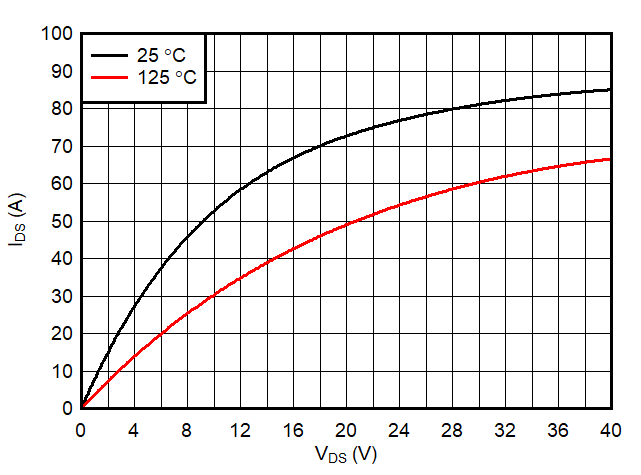
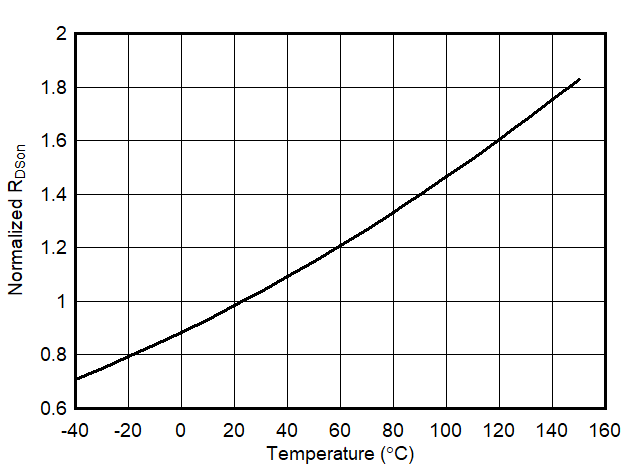
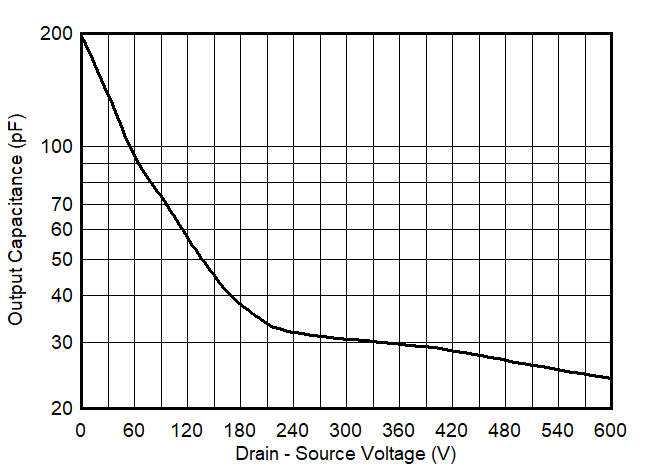
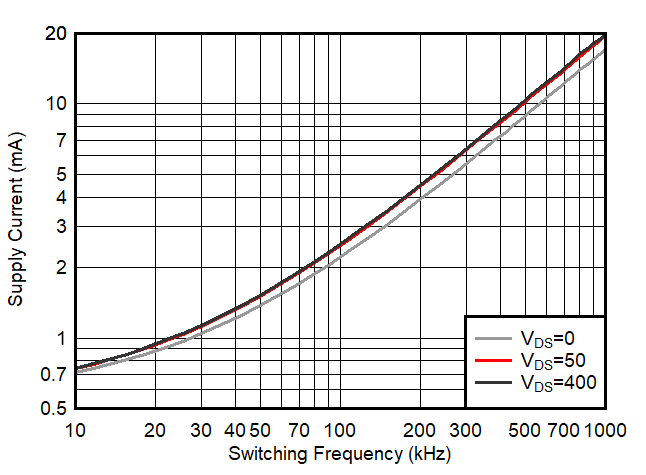
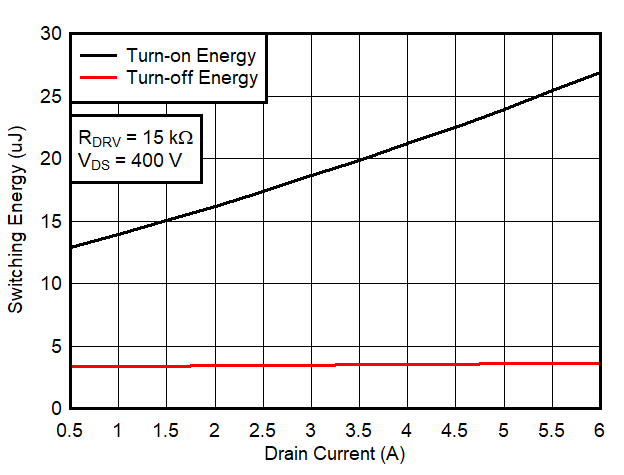
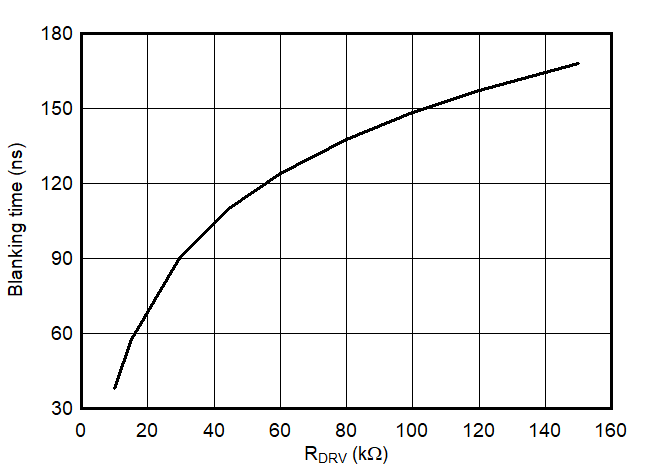
6.7 Typical Characteristics
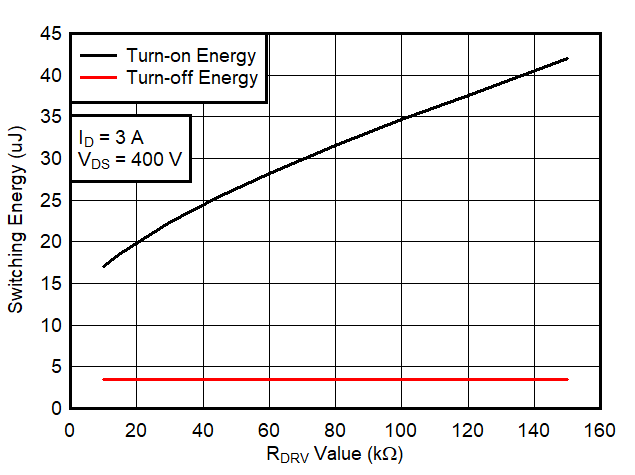
1.
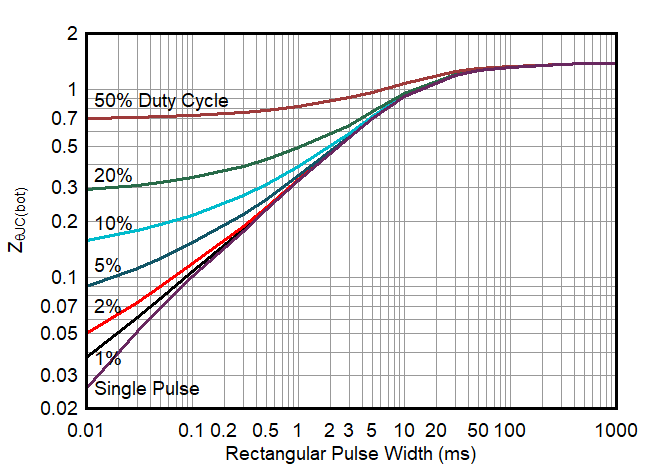
Figure 11. Transient Thermal Impedance 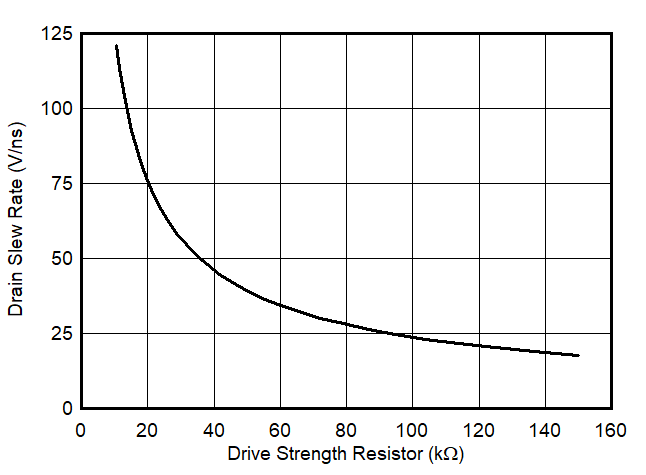
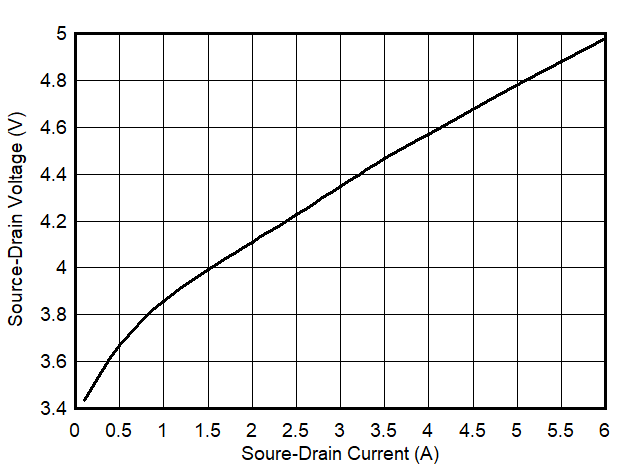
1.
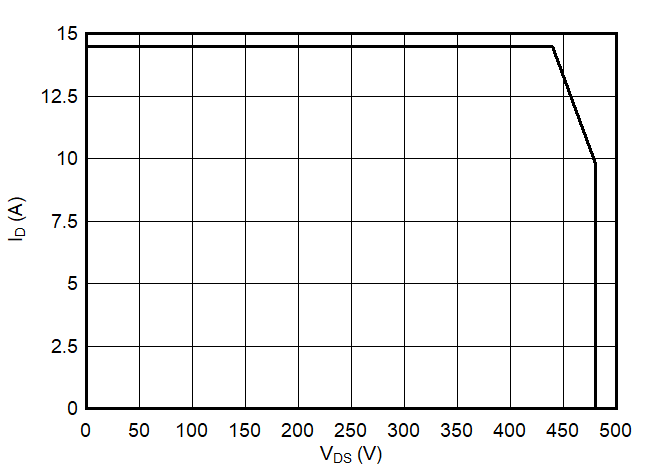
Figure 12. Repetitive Safe Operation Area at Tj ≤ 125 °C