SNVSAI4B November 2017 – November 2020 LM5145
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Input Range (VIN)
- 8.3.2 Output Voltage Setpoint and Accuracy (FB)
- 8.3.3 High-Voltage Bias Supply Regulator (VCC)
- 8.3.4 Precision Enable (EN/UVLO)
- 8.3.5 Power Good Monitor (PGOOD)
- 8.3.6 Switching Frequency (RT, SYNCIN)
- 8.3.7 Configurable Soft Start (SS/TRK)
- 8.3.8 Voltage-Mode Control (COMP)
- 8.3.9 Gate Drivers (LO, HO)
- 8.3.10 Current Sensing and Overcurrent Protection (ILIM)
- 8.3.11 OCP Duty Cycle Limiter
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1 Design 1 – 20-A High-Efficiency Synchronous Buck Regulator for Telecom Power Applications
- 9.2.2 Design 2 – High Density, 12-V, 10-A Rail With LDO Low-Noise Auxiliary Output for RF Power Applications
- 9.2.3 Design 3 – 150-W, Regulated 24-V Rail for Commercial Drone Applications With Output Voltage Tracking Feature
- 9.2.4 Design 4 – Powering a Multicore DSP From a 24-V or 48-V Rail
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.4 Precision Enable (EN/UVLO)
The EN/UVLO input supports adjustable input undervoltage lockout (UVLO) with hysteresis programmed by the resistor values for application specific power-up and power-down requirements. EN/UVLO connects to a comparator-based input referenced to a 1.2-V bandgap voltage. An external logic signal can be used to drive the EN/UVLO input to toggle the output ON and OFF and for system sequencing or protection. The simplest way to enable the operation of the LM5145 is to connect EN/UVLO directly to VIN. This allows self start-up of the LM5145 when VCC is within its valid operating range. However, many applications benefit from using a resistor divider RUV1 and RUV2 as shown in Figure 8-3 to establish a precision UVLO level.
Use Equation 1 and Equation 2 to calculate the UVLO resistors given the required input turnon and turnoff voltages.
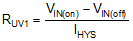
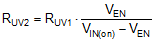
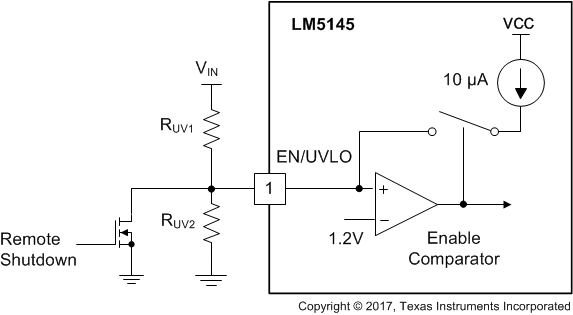 Figure 8-3 Programmable Input Voltage UVLO Turnon and Turnoff
Figure 8-3 Programmable Input Voltage UVLO Turnon and TurnoffThe LM5145 enters a low IQ shutdown mode when EN/UVLO is pulled below approximately 0.4 V. The internal LDO regulator powers off and the internal bias supply rail collapses, shutting down the bias currents of the LM5145. The LM5145 operates in standby mode when the EN/UVLO voltage is between the hard shutdown and precision enable (standby) thresholds.