SPNU118Z September 1995 – March 2023 66AK2E05 , 66AK2H06 , 66AK2H12 , 66AK2H14 , AM1705 , AM1707 , AM1802 , AM1806 , AM1808 , AM1810 , AM5K2E04 , OMAP-L132 , OMAP-L137 , OMAP-L138 , SM470R1B1M-HT , TMS470R1A288 , TMS470R1A384 , TMS470R1A64 , TMS470R1B1M , TMS470R1B512 , TMS470R1B768
- Read This First
- 1 Introduction to the Software Development Tools
- 2 Introduction to Object Modules
- 3 Program Loading and Running
-
4 Assembler Description
- 4.1 Assembler Overview
- 4.2 The Assembler's Role in the Software Development Flow
- 4.3 Invoking the Assembler
- 4.4 Controlling Application Binary Interface
- 4.5 Naming Alternate Directories for Assembler Input
- 4.6 Source Statement Format
- 4.7 Literal Constants
- 4.8 Assembler Symbols
- 4.9 Expressions
- 4.10 Built-in Functions and Operators
- 4.11 Unified Assembly Language Syntax Support
- 4.12 Source Listings
- 4.13 Debugging Assembly Source
- 4.14 Cross-Reference Listings
-
5 Assembler Directives
- 5.1 Directives Summary
- 5.2 Directives that Define Sections
- 5.3 Directives that Change the Instruction Type
- 5.4 Directives that Initialize Values
- 5.5 Directives that Perform Alignment and Reserve Space
- 5.6 Directives that Format the Output Listings
- 5.7 Directives that Reference Other Files
- 5.8 Directives that Enable Conditional Assembly
- 5.9 Directives that Define Union or Structure Types
- 5.10 Directives that Define Enumerated Types
- 5.11 Directives that Define Symbols at Assembly Time
- 5.12 Miscellaneous Directives
- 5.13
Directives Reference
- .align
- .asg/.define/.eval
- .asmfunc/.endasmfunc
- .bits
- .bss
- .byte/.ubyte/.char/.uchar
- .cdecls
- .common
- .copy/.include
- .cstruct/.cunion/.endstruct/.endunion/.tag
- .data
- .double
- .drlist/.drnolist
- .elfsym
- .emsg/.mmsg/.wmsg
- .end
- .fclist/.fcnolist
- .field
- .float
- .global/.def/.ref
- .group/.gmember/.endgroup
- .half/.short/.uhalf/.ushort
- .if/.elseif/.else/.endif
- .int/.unint/.long/.ulong/.word/.uword
- .label
- .length/.width
- .list/.nolist
- .loop/.endloop/.break
- .macro/.endm
- .mlib
- .mlist/.mnolist
- .newblock
- .option
- .page
- .retain / .retainrefs
- .sect
- .set/.equ
- .space/.bes
- .sslist/.ssnolist
- .state16
- .state32/.arm
- .string/.cstring
- .struct/.endstruct/.tag
- .symdepend
- .tab
- .text
- .thumb
- .title
- .unasg/.undefine
- .union/.endunion/.tag
- .usect
- .var
- .weak
-
6 Macro Language Description
- 6.1 Using Macros
- 6.2 Defining Macros
- 6.3 Macro Parameters/Substitution Symbols
- 6.4 Macro Libraries
- 6.5 Using Conditional Assembly in Macros
- 6.6 Using Labels in Macros
- 6.7 Producing Messages in Macros
- 6.8 Using Directives to Format the Output Listing
- 6.9 Using Recursive and Nested Macros
- 6.10 Macro Directives Summary
- 7 Archiver Description
-
8 Linker Description
- 8.1 Linker Overview
- 8.2 The Linker's Role in the Software Development Flow
- 8.3 Invoking the Linker
- 8.4
Linker Options
- 8.4.1 Wildcards in File, Section, and Symbol Patterns
- 8.4.2 Specifying C/C++ Symbols with Linker Options
- 8.4.3 Relocation Capabilities (--absolute_exe and --relocatable Options)
- 8.4.4 Allocate Memory for Use by the Loader to Pass Arguments (--arg_size Option)
- 8.4.5 Changing Encoding of Big-Endian Instructions
- 8.4.6 Compression (--cinit_compression and --copy_compression Option)
- 8.4.7 Compress DWARF Information (--compress_dwarf Option)
- 8.4.8 Control Linker Diagnostics
- 8.4.9 Automatic Library Selection (--disable_auto_rts Option)
- 8.4.10 Do Not Remove Unused Sections (--unused_section_elimination Option)
- 8.4.11 Linker Command File Preprocessing (--disable_pp, --define and --undefine Options)
- 8.4.12 Error Correcting Code Testing (--ecc Options)
- 8.4.13 Define an Entry Point (--entry_point Option)
- 8.4.14 Set Default Fill Value (--fill_value Option)
- 8.4.15 Generate List of Dead Functions (--generate_dead_funcs_list Option)
- 8.4.16 Define Heap Size (--heap_size Option)
- 8.4.17 Hiding Symbols
- 8.4.18 Alter the Library Search Algorithm (--library, --search_path, and TI_ARM_C_DIR )
- 8.4.19 Change Symbol Localization
- 8.4.20 Create a Map File (--map_file Option)
- 8.4.21 Managing Map File Contents (--mapfile_contents Option)
- 8.4.22 Disable Name Demangling (--no_demangle)
- 8.4.23 Disable Merging of Symbolic Debugging Information (--no_sym_merge Option)
- 8.4.24 Strip Symbolic Information (--no_symtable Option)
- 8.4.25 Name an Output Module (--output_file Option)
- 8.4.26 Prioritizing Function Placement (--preferred_order Option)
- 8.4.27 C Language Options (--ram_model and --rom_model Options)
- 8.4.28 Retain Discarded Sections (--retain Option)
- 8.4.29 Create an Absolute Listing File (--run_abs Option)
- 8.4.30 Scan All Libraries for Duplicate Symbol Definitions (--scan_libraries)
- 8.4.31 Define Stack Size (--stack_size Option)
- 8.4.32 Mapping of Symbols (--symbol_map Option)
- 8.4.33 Generate Far Call Trampolines (--trampolines Option)
- 8.4.34 Introduce an Unresolved Symbol (--undef_sym Option)
- 8.4.35 Display a Message When an Undefined Output Section Is Created (--warn_sections)
- 8.4.36 Generate XML Link Information File (--xml_link_info Option)
- 8.4.37 Zero Initialization (--zero_init Option)
- 8.5
Linker Command Files
- 8.5.1 Reserved Names in Linker Command Files
- 8.5.2 Constants in Linker Command Files
- 8.5.3 Accessing Files and Libraries from a Linker Command File
- 8.5.4 The MEMORY Directive
- 8.5.5
The SECTIONS Directive
- 8.5.5.1 SECTIONS Directive Syntax
- 8.5.5.2 Section Allocation and Placement
- 8.5.5.3 Specifying Input Sections
- 8.5.5.4 Using Multi-Level Subsections
- 8.5.5.5 Specifying Library or Archive Members as Input to Output Sections
- 8.5.5.6 Allocation Using Multiple Memory Ranges
- 8.5.5.7 Automatic Splitting of Output Sections Among Non-Contiguous Memory Ranges
- 8.5.6 Placing a Section at Different Load and Run Addresses
- 8.5.7 Using GROUP and UNION Statements
- 8.5.8 Special Section Types (DSECT, COPY, NOLOAD, and NOINIT)
- 8.5.9 Configuring Error Correcting Code (ECC) with the Linker
- 8.5.10
Assigning Symbols at Link Time
- 8.5.10.1 Syntax of Assignment Statements
- 8.5.10.2 Assigning the SPC to a Symbol
- 8.5.10.3 Assignment Expressions
- 8.5.10.4 Symbols Automatically Defined by the Linker
- 8.5.10.5 Assigning Exact Start, End, and Size Values of a Section to a Symbol
- 8.5.10.6 Why the Dot Operator Does Not Always Work
- 8.5.10.7 Address and Dimension Operators
- 8.5.10.8 LAST Operator
- 8.5.11 Creating and Filling Holes
- 8.6 Linker Symbols
- 8.7 Default Placement Algorithm
- 8.8 Using Linker-Generated Copy Tables
- 8.9 Linker-Generated CRC Tables
- 8.10 Partial (Incremental) Linking
- 8.11 Linking C/C++ Code
- 8.12 Linker Example
- 9 Absolute Lister Description
- 10Cross-Reference Lister Description
- 11Object File Utilities
-
12Hex Conversion Utility Description
- 12.1 The Hex Conversion Utility's Role in the Software Development Flow
- 12.2 Invoking the Hex Conversion Utility
- 12.3 Understanding Memory Widths
- 12.4 The ROMS Directive
- 12.5 The SECTIONS Directive
- 12.6 The Load Image Format (--load_image Option)
- 12.7 Excluding a Specified Section
- 12.8 Assigning Output Filenames
- 12.9 Image Mode and the --fill Option
- 12.10 Array Output Format
- 12.11 Building a Table for an On-Chip Boot Loader
- 12.12 Using Secure Flash Boot on TMS320F2838x Devices
- 12.13 Controlling the ROM Device Address
- 12.14 Control Hex Conversion Utility Diagnostics
- 12.15
Description of the Object Formats
- 12.15.1 ASCII-Hex Object Format (--ascii Option)
- 12.15.2 Intel MCS-86 Object Format (--intel Option)
- 12.15.3 Motorola Exorciser Object Format (--motorola Option)
- 12.15.4 Extended Tektronix Object Format (--tektronix Option)
- 12.15.5 Texas Instruments SDSMAC (TI-Tagged) Object Format (--ti_tagged Option)
- 12.15.6 TI-TXT Hex Format (--ti_txt Option)
-
13Sharing C/C++ Header Files With Assembly Source
- 13.1 Overview of the .cdecls Directive
- 13.2
Notes on C/C++ Conversions
- 13.2.1 Comments
- 13.2.2 Conditional Compilation (#if/#else/#ifdef/etc.)
- 13.2.3 Pragmas
- 13.2.4 The #error and #warning Directives
- 13.2.5 Predefined symbol __ASM_HEADER__
- 13.2.6 Usage Within C/C++ asm( ) Statements
- 13.2.7 The #include Directive
- 13.2.8 Conversion of #define Macros
- 13.2.9 The #undef Directive
- 13.2.10 Enumerations
- 13.2.11 C Strings
- 13.2.12 C/C++ Built-In Functions
- 13.2.13 Structures and Unions
- 13.2.14 Function/Variable Prototypes
- 13.2.15 C Constant Suffixes
- 13.2.16 Basic C/C++ Types
- 13.3 Notes on C++ Specific Conversions
- 13.4 Special Assembler Support
- A Symbolic Debugging Directives
- B XML Link Information File Description
- C Hex Conversion Utility Examples
- D Glossary
- E Revision History
- E Earlier Revisions
12.3.2 Specifying the Memory Width
Memory width is the physical width (in bits) of the memory system. Usually, the memory system is physically the same width as the target processor width: a 16-bit processor has a 32-bit memory architecture. However, some applications require target words to be broken into multiple, consecutive, and narrower memory words.
By default, the hex conversion utility sets memory width to the target width (in this case, 32 bits).
You can change the memory width (except for TI-TXT, binary, and TI-Tagged formats) by:
- Using the --memwidth option. This changes the memory width value for the entire file.
- Setting the memwidth parameter of the ROMS directive. This changes the memory width value for the address range specified in the ROMS directive and overrides the --memwidth option for that range. See Section 12.4.
For both methods, use a value that is a power of 2 greater than or equal to 8.
You should change the memory width default value of 16 only when you need to break single target words into consecutive, narrower memory words.
Figure 12-3 demonstrates how the memory width is related to object file data.
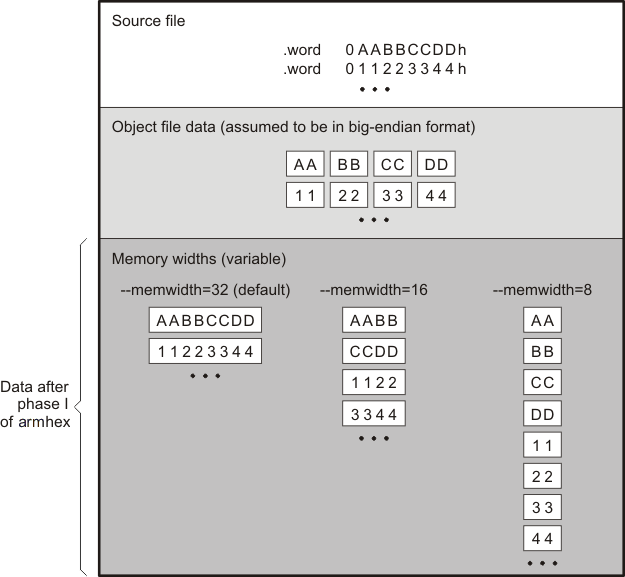 Figure 12-3 Object File Data and Memory Widths
Figure 12-3 Object File Data and Memory Widths