SPRAD66B February 2023 – December 2024 AM62A3 , AM62A3-Q1 , AM62A7 , AM62A7-Q1 , AM62D-Q1 , AM62P , AM62P-Q1
- 1
- AM62Ax, AM62Px, AM62Dx LPDDR4 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- Trademarks
- 1Overview
-
2LPDDR4 Board Design and Layout Guidance
- 2.1 LPDDR4 Introduction
- 2.2 LPDDR4 Device Implementations Supported
- 2.3 LPDDR4 Interface Schematics
- 2.4 Compatible JEDEC LPDDR4 Devices
- 2.5 Placement
- 2.6 LPDDR4 Keepout Region
- 2.7 Net Classes
- 2.8 LPDDR4 Signal Termination
- 2.9 LPDDR4 VREF Routing
- 2.10 LPDDR4 VTT
- 2.11 CK and ADDR_CTRL Topologies
- 2.12 Data Group Topologies
- 2.13 CK0 and ADDR_CTRL Routing Specification
- 2.14 Data Group Routing Specification
- 2.15 Channel, Byte, and Bit Swapping
- 2.16 Data Bus Inversion
- 3LPDDR4 Board Design Simulations
- 4Additional Information: SOC Package Delays
- 5Summary
- 6References
- 7Revision History
2.11 CK and ADDR_CTRL Topologies
The CK and ADDR_CTRL net classes are routed similarly, and are skew matched from the DDR controller in the processor to the LPDDR4 SDRAM to make sure that the ADDR_CTRL signals are properly sampled at the SDRAM. The CK0 net class requires more care because the net class runs at a higher transition rate and are differential. The CK and ADDR_CTRL topology is balanced T.
Figure 2-6 shows the topology of the CK0 net class. Figure 2-7 and Figure 2-8 shows the topologies for the corresponding ADDR_CTRL_A net class. Note some of the signals within the group are shared between the memory channels, while other signals are dedicated for each channel. Skew matching requirements for the routing segments are detailed in Table 2-6.
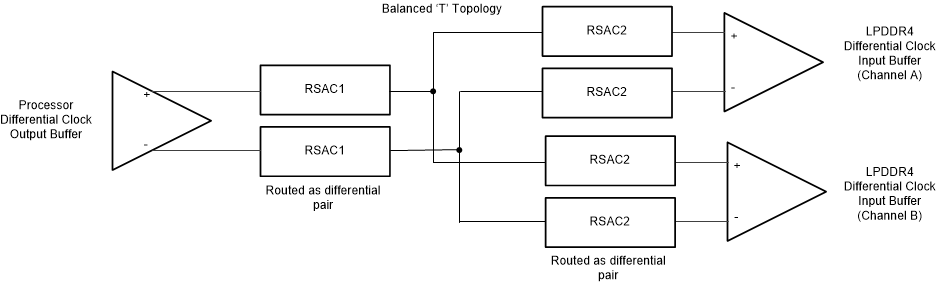 Figure 2-6 LPDDR4 CK
Topology
Figure 2-6 LPDDR4 CK
Topology Figure 2-7 LPDDR4
ADDR_CTRL Topology/Branched Signals
Figure 2-7 LPDDR4
ADDR_CTRL Topology/Branched Signals Figure 2-8 LPDDR4
ADDR_CTRL Topology/Point-to-Point Signals
Figure 2-8 LPDDR4
ADDR_CTRL Topology/Point-to-Point SignalsTI recommends to minimize layer transitions during routing. If a layer transition is necessary, then this is preferable to transition to a layer using the same reference plane. If this cannot be accommodated, then make sure there are nearby stitching vias to allow the return currents to transition between reference planes. The goal is to minimize the size of the return current path thus minimizing the inductance in this path. Lack of these stitching vias results in impedance discontinuities in the signal path that increase crosstalk and signal distortion.
There are no stubs or termination allowed on the nets of the CK and ADDR_CTRL group topologies. All test and probe access points must be in line without any branches or stubs.