SPRAD86A March 2023 – May 2024 AM62A3 , AM62A3-Q1 , AM62A7 , AM62A7-Q1 , AM67A , AM68A , AM69A
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Tuning Overview
- 3 Hardware Requirement
- 4 Software Requirement
- 5 Sensor Software Integration
- 6 Tuning Procedure
- 7 Perform Basic Tuning
- 8 Perform Fine Tuning
- 9 Live Tuning
- 10Summary
- 11Revision History
7.3 Black Level Subtraction
The Black Level Subtraction (BLC) plug-in tuning is only needed for RGB-only sensors. For RGB-IR sensors, this plug-in needs not to be tuned because of the IR subtraction performed by PCID.
For linear sensors including the IMX219, subtract the black level or pedestal from the raw image pixels before applying any gains (for example, gains for white balance) later in the ISP. Even though the pedestal value is coded in the sensor driver, measure the actual value for each sensor working mode supported by the sensor driver. For example, the IMX219 camera has a measured black level around 63 in 10-bit mode (shown in the figure below) and 16 in 8-bit mode.
Follow these steps to tune Black Level Subtraction for the target sensor:
- Completely cover the camera lens and capture a black RAW image.
- Choose Black Level Subtraction from the Plug-ins drop-down menu.
- Select the RAW image in the Browse window and the image ought to appear black in the Preview window.
- Provide the raw image in the RAW file window and click Process plugin as shown below.
- The measured black level is displayed in the Advanced params tab of the upper right window.
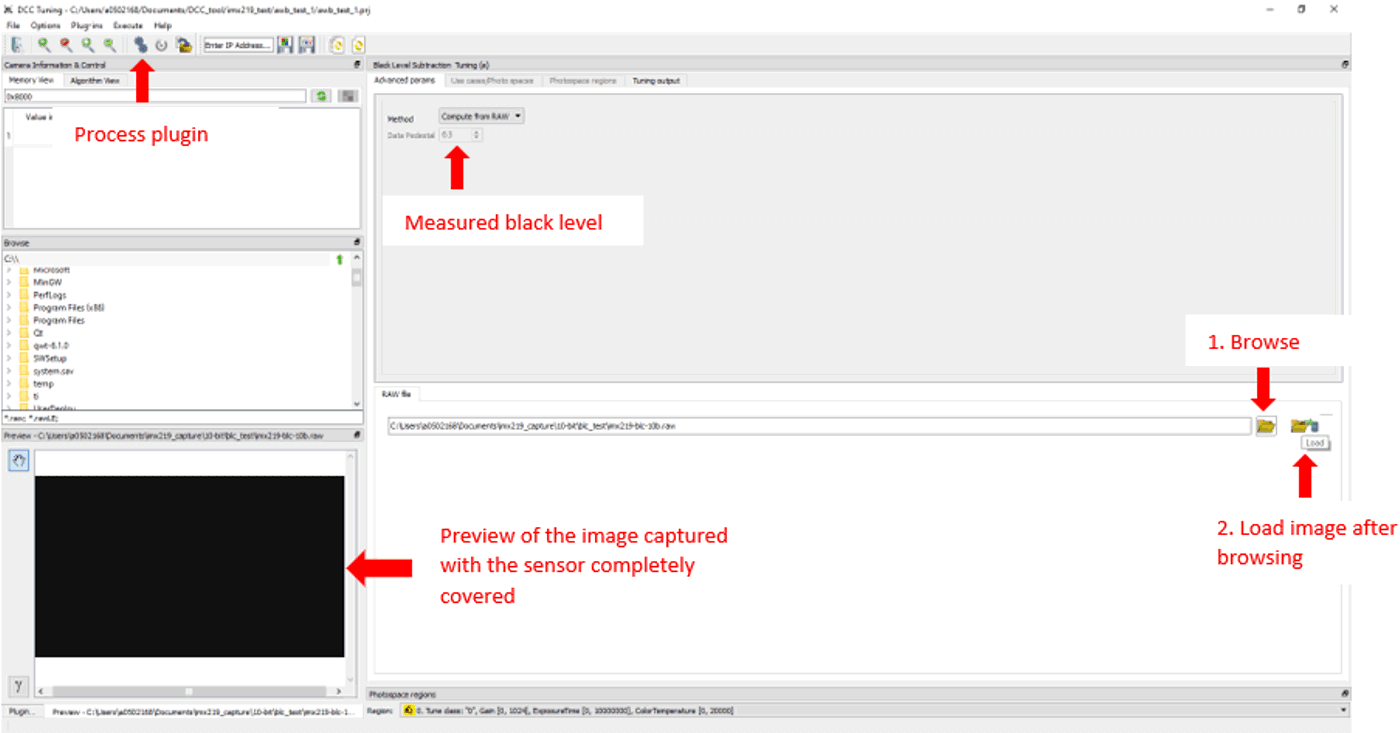 Figure 7-4 Black Level Subtraction
Tuning
Figure 7-4 Black Level Subtraction
TuningFor WDR sensors, the black level subtraction is usually combined with WDR decompanding and re-compression to generate a single lookup table (LUT). This can be achieved by the CFA + WDR plug-in in the tuning tool. See the user guide of the plug-in for more details in case of a WDR sensor.
Once tuning for a plug-in is done, click the Export DCC profile binary button to generate the output XML files for this plug-in. The XML files are located in the .plugoutdir\XML folder under the project folder created in Section 7.1. For Black Level Subtraction, there is only one output XML file: imx219_viss_blc.xml. Replace the same XML file generated from initial configuration. Then rerun the Python script to generate new DCC binary files as described in Generate DCC Binary Files. Use the newly-generated DCC binaries to improve streaming quality in the next step. Complete this action after tuning each plug-in in the following sections.
To see the image quality improvement after tuning each plug-in, capture ISP-processed still images with newly-generated DCC binary files. For example, use the following GStreamer pipeline with new binary files after tuning the Black Level Subtraction plug-in for IMX219:
gst-launch-1.0 -v v4l2src num-buffers=5 device=/dev/video3 io-mode=dmabuf-import ! \
video/x-bayer, width=1920, height=1080, framerate=30/1, format=rggb10 ! \
tiovxisp sink_0::device=/dev/v4l-subdev2 \
sensor-name="SENSOR_SONY_IMX219_RPI" \
dcc-isp-file=/opt/imaging/imx219/dcc_viss_10b.bin \
sink_0::dcc-2a-file=/opt/imaging/imx219/dcc_2a_10b.bin format-msb=9 ! \
video/x-raw, format=NV12, width=1920, height=1080, framerate=30/1 ! \
jpegenc ! multifilesink location="imx219-image-%d.jpg"Figure 7-5 shows an example of the captured images before Black Level Subtraction tuning (using the initial configuration) and Figure 7-6 shows the image after Black Level Subtraction tuning (compare the appearance of black).
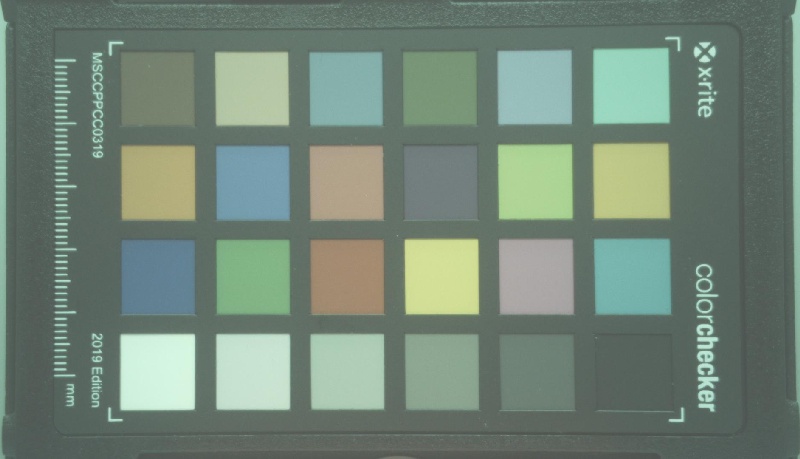 Figure 7-5 Image Before Black Level
Subtraction
Figure 7-5 Image Before Black Level
Subtraction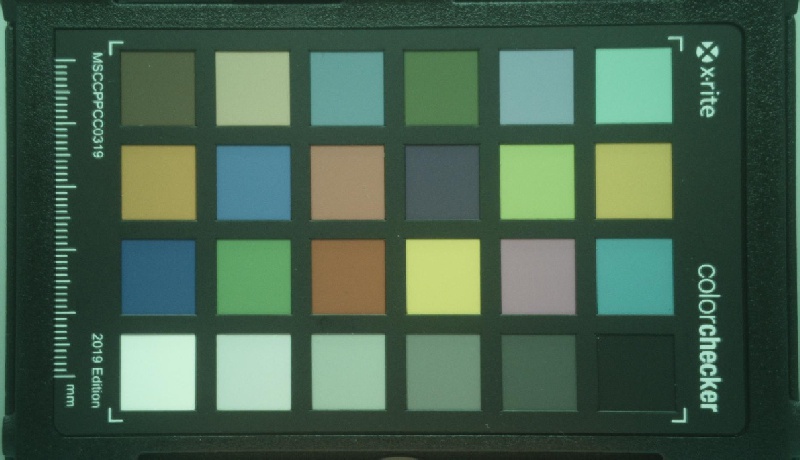 Figure 7-6 Image After Black Level
Subtraction
Figure 7-6 Image After Black Level
Subtraction