SPRADI9 June 2024 AM623 , AM625
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Design-Based Approach
- 3Background
- 4Comparison of Design-Based Approach vs. HTOL Approach
- 5AM625/623 Lifetime Reliability Analysis Results
- 6Conclusion
- 7Revision History
- A Appendix – The HTOL-Based Approach
- B Appendix – The Mathematic Basis for EM Reliability Estimates
3.2 SPICE Models for Circuit Behavior
The next step is generation of SPICE Model libraries integrating the underlying component reliability models (and, critically, aging effects). The output of these electrical models at base component characterized across Process, Voltage, and Temperature (commonly known as PVT). Process means the critical parameters of the elemental components, such as transistor Threshold Voltage, drive (ON state) currents, OFF state currents (sub-threshold leakage), or metal sheet resistances. Statistical modeling simulations also include potential localized variances in parameters that can significantly affect final performance, and builds further robustness into the models.
For digital core logic, memories, (digital) IOs and ESD cells, libraries are constructed of re-usable cells, building on the fundamental components and end-of-life (aged) SPICE models. Analog circuits are not directly constructed from re-usable cell components, but have a separate work flow also leveraging aged SPICE models and maintains operation within safe operating limits. Signal integrity and parameters such as gain, noise, offset, and linearity, must maintain functional and parametric performance within published specifications across specified lifetime profile, which is generally published in data manuals for Embedded Processing products. All digital and analog components, including memories, must furthermore be maintained within physical design-rule limits encompassed within the PDK, with those limits inherently comprehending reliability. At the IP and SoC development and integration stage, DRCs are once again applied. Design Rule Checkers (DRCs) rigorously enforce these rules prior to Pattern Generation (PG), with any violations requiring action and disposition before mask generation. Figure 3-2 shows a more detailed view of the PDK scope.
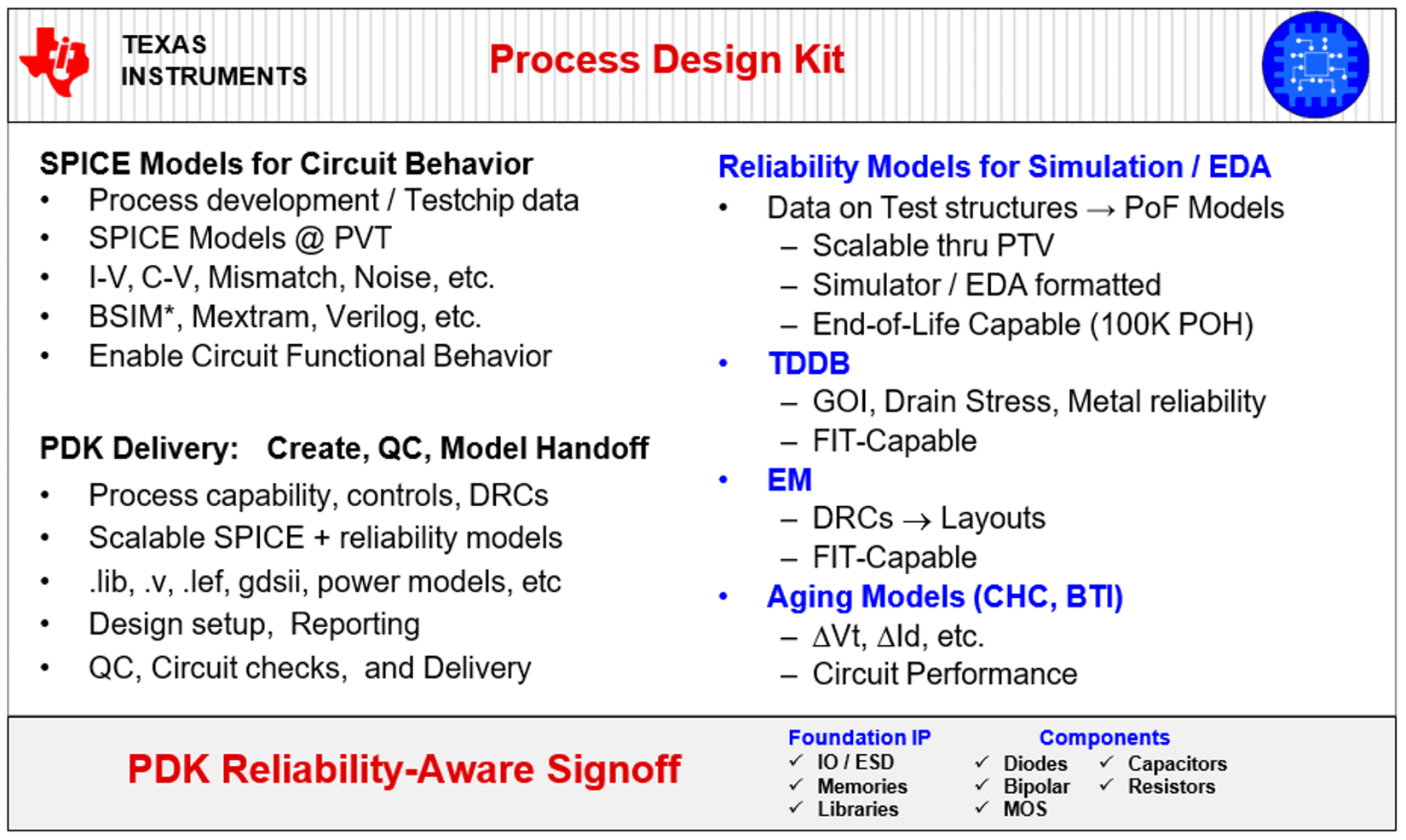
Figure 3-2 Process Design Kit Overview