SPRSP65G April 2021 – May 2024 AM2431 , AM2432 , AM2434
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
-
5 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 5.1 Pin Diagram
- 5.2 Pin Attributes
- 5.3
Signal Descriptions
- 17
- 5.3.1 AM243x_ALX Package - Unsupported Interfaces and Signals
- 5.3.2 ADC
- 5.3.3 CPSW
- 5.3.4 CPTS
- 5.3.5 DDRSS
- 5.3.6 ECAP
- 5.3.7 Emulation and Debug
- 5.3.8 EPWM
- 5.3.9 EQEP
- 5.3.10 FSI
- 5.3.11 GPIO
- 5.3.12 GPMC
- 5.3.13 I2C
- 5.3.14 MCAN
- 5.3.15 SPI (MCSPI)
- 5.3.16 MMC
- 5.3.17 OSPI
- 5.3.18 Power Supply
- 5.3.19 PRU_ICSSG
- 5.3.20 Reserved
- 5.3.21 SERDES
- 5.3.22 System and Miscellaneous
- 5.3.23 TIMER
- 5.3.24 UART
- 5.3.25 USB
- 5.4 Pin Connectivity Requirements
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Operating Performance Points
- 6.6 Power Consumption Summary
- 6.7
Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.1 I2C Open-Drain, and Fail-Safe (I2C OD FS) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.2 Fail-Safe Reset (FS RESET) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.3 High-Frequency Oscillator (HFOSC) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.4 eMMCPHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.5 SDIO Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.6 LVCMOS Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.7 ADC12B Electrical Characteristics (ALV package)
- 6.7.8 ADC10B Electrical Characteristics (ALX package)
- 6.7.9 USB2PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.10 SerDes PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7.11 DDR Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8 VPP Specifications for One-Time Programmable (OTP) eFuses
- 6.9 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 6.10
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 6.10.1 Timing Parameters and Information
- 6.10.2 Power Supply Requirements
- 6.10.3 System Timing
- 6.10.4 Clock Specifications
- 6.10.5
Peripherals
- 6.10.5.1 CPSW3G
- 6.10.5.2 DDRSS
- 6.10.5.3 ECAP
- 6.10.5.4 EPWM
- 6.10.5.5 EQEP
- 6.10.5.6 FSI
- 6.10.5.7 GPIO
- 6.10.5.8 GPMC
- 6.10.5.9 I2C
- 6.10.5.10 MCAN
- 6.10.5.11 MCSPI
- 6.10.5.12 MMCSD
- 6.10.5.13 CPTS
- 6.10.5.14 OSPI
- 6.10.5.15 PCIe
- 6.10.5.16
PRU_ICSSG
- 6.10.5.16.1 PRU_ICSSG Programmable Real-Time Unit (PRU)
- 6.10.5.16.2 PRU_ICSSG Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
- 6.10.5.16.3 PRU_ICSSG Industrial Ethernet Peripheral (IEP)
- 6.10.5.16.4 PRU_ICSSG Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART)
- 6.10.5.16.5 PRU_ICSSG Enhanced Capture Peripheral (ECAP)
- 6.10.5.16.6 PRU_ICSSG RGMII, MII_RT, and Switch
- 6.10.5.17 Timers
- 6.10.5.18 UART
- 6.10.5.19 USB
- 6.10.6 Emulation and Debug
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Processor Subsystems
- 7.3 Accelerators and Coprocessors
- 7.4
Other Subsystems
- 7.4.1 PDMA Controller
- 7.4.2
Peripherals
- 7.4.2.1 ADC
- 7.4.2.2 DCC
- 7.4.2.3 Dual Date Rate (DDR) External Memory Interface (DDRSS)
- 7.4.2.4 ECAP
- 7.4.2.5 EPWM
- 7.4.2.6 ELM
- 7.4.2.7 ESM
- 7.4.2.8 GPIO
- 7.4.2.9 EQEP
- 7.4.2.10 General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 7.4.2.11 I2C
- 7.4.2.12 MCAN
- 7.4.2.13 MCRC Controller
- 7.4.2.14 MCSPI
- 7.4.2.15 MMCSD
- 7.4.2.16 OSPI
- 7.4.2.17 Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe)
- 7.4.2.18 Serializer/Deserializer (SerDes) PHY
- 7.4.2.19 Real Time Interrupt (RTI/WWDT)
- 7.4.2.20 Dual Mode Timer (DMTIMER)
- 7.4.2.21 UART
- 7.4.2.22 Universal Serial Bus Subsystem (USBSS)
-
8 Applications,
Implementation, and Layout
- 8.1 Device Connection and Layout Fundamentals
- 8.2
Peripheral- and Interface-Specific Design Information
- 8.2.1 General Routing Guidelines
- 8.2.2 DDR Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.2.3 OSPI/QSPI/SPI Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.2.4 USB VBUS Design Guidelines
- 8.2.5 System Power Supply Monitor Design Guidelines
- 8.2.6 High Speed Differential Signal Routing Guidance
- 8.2.7 Thermal Solution Guidance
- 8.3 Clock Routing Guidelines
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating junction temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)
| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDD_CORE | Core supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V |
| VDDR_CORE | RAM supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V |
| VDD_MMC0 | MMC0 PHY core supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V |
| VDD_DLL_MMC0 | MMC0 PLL analog supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V |
| VDDA_0P85_SERDES0 | SERDES0 0.85V analog supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V |
| VDDA_0P85_SERDES0_C | SERDES0 clock 0.85V analog supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V |
| VDDA_0P85_USB0 | USB0 0.85V analog supply | -0.3 | 1.05 | V |
| VDDS_DDR | DDR PHY IO supply | -0.3 | 1.57 | V |
| VDDS_DDR_C | DDR clock IO supply | -0.3 | 1.57 | V |
| VDDS_MMC0 | MMC0 PHY IO supply | -0.3 | 1.98 | V |
| VDDS_OSC | MCU_OSC0 supply | -0.3 | 1.98 | V |
| VDDA_MCU | POR and MCU PLL analog supply | -0.3 | 1.98 | V |
| VDDA_ADC0 | ADC0 analog supply | -0.3 | 1.98 | V |
| VDDA_PLL0 | Main, PER1, and R5F PLL analog supply | -0.3 | 1.98 | V |
| VDDA_PLL1 | ARM and DDR PLL analog supply | -0.3 | 1.98 | V |
| VDDA_PLL2 | PER0 PLL analog supply | -0.3 | 1.98 | V |
| VDDA_1P8_SERDES0 | SERDES0 1.8V analog supply | -0.3 | 1.98 | V |
| VDDA_1P8_USB0 | USB0 1.8V analog supply | -0.3 | 1.98 | V |
| VDDA_TEMP0 | TEMP0 analog supply | -0.3 | 1.98 | V |
| VDDA_TEMP1 | TEMP1 analog supply | -0.3 | 1.98 | V |
| VPP | eFuse ROM programming supply | -0.3 | 1.98 | V |
| VDDSHV_MCU | IO supply for IO MCU | -0.3 | 3.63 | V |
| VDDSHV0 | IO supply for IO group 0 | -0.3 | 3.63 | V |
| VDDSHV1 | IO supply for IO group 1 | -0.3 | 3.63 | V |
| VDDSHV2 | IO supply for IO group 2 | -0.3 | 3.63 | V |
| VDDSHV3 | IO supply for IO group 3 | -0.3 | 3.63 | V |
| VDDSHV4 | IO supply for IO group 4 | -0.3 | 3.63 | V |
| VDDSHV5 | IO supply for IO group 5 | -0.3 | 3.63 | V |
| VDDA_3P3_USB0 | USB0 3.3V analog supply | -0.3 | 3.63 | V |
| VDDA_3P3_SDIO | SDIO 3.3V analog supply | -0.3 | 3.63 | V |
| Steady-state max voltage at all fail-safe IO pins | MCU_PORz | -0.3 | 3.63 | V |
| MCU_I2C0_SCL, MCU_I2C0_SDA, I2C0_SCL, I2C0_SDA, EXTINTn | -0.3 | 1.98(3) | V | |
| VMON_1P8_MCU, VMON_1P8_SOC | -0.3 | 1.98(3) | V | |
| VMON_3P3_MCU, VMON_3P3_SOC | -0.3 | 3.63 | V | |
| VMON_VSYS(4) | -0.3 | 1.98 | V | |
| Steady-state max voltage at all other IO pins(5) | USB0_VBUS(6) | -0.3 | 3.6 | V |
| USB0_ID(7) | -0.3 | 3.6 | V | |
| All other IO pins | -0.3 | IO Supply Voltage + 0.3 |
V | |
| Transient overshoot and undershoot at IO pin | 20% of IO supply voltage for up to 20% of the signal period (see Figure 6-1, IO Transient Voltage Ranges) | 0.2 × VDD(8) | V | |
| Latch-up performance | I-Test(9) | -100 | +100 | mA |
| Over-Voltage (OV) Test(10) | 1.5 x VDD(8) | V | ||
| TSTG | Storage temperature(11) | -55 | +150 | °C |
(1) Operation outside the Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent
device damage. Absolute Maximum Ratings do not imply functional operation of the device at
these or any other conditions beyond those listed under Recommended Operating Conditions.
If used outside the Recommended Operating Conditions, but within the Absolute Maximum Ratings, the
device may not be fully functional, and may affect device reliability, performance,
functionality, and shorten the device lifetime.
(2) All voltage values are with respect to VSS, unless otherwise
noted.
(3) The absolute maximum ratings for these fail-safe pins depends on their
IO supply operating voltage. Therefore, this value is also defined by the maximum
VIH value found in the I2C Open-Drain, and Fail-Safe (I2C OD FS) Electrical Characteristics section,
where the electrical characteristics table has separate parameter values for 1.8-V mode
and 3.3-V mode.
(4) The VMON_VSYS pin provides a way to monitor the system power supply.
For more information, see the System Power Supply Monitor Design Guidelines.
(5) This parameter applies to all IO pins which are not fail-safe and the
requirement applies to all values of IO supply voltage. For example, if the voltage
applied to a specific IO supply is 0 volts the valid input voltage range for any IO
powered by that supply will be –0.3 to +0.3 volts. Special attention should be applied
anytime peripheral devices are not powered from the same power sources used to power the
respective IO supply. It is important the attached peripheral never sources a voltage
outside the valid input voltage range, including power supply ramp-up and ramp-down
sequences.
(6) An external resistor divider is required to limit the voltage
applied to this device pin. For more information, see the USB VBUS Design Guidelines.
(7) The USB0_ID pin is connected to analog circuits in the USB0 PHY. The
analog circuits source a known current while measuring voltage, to determine the
resistance value (RID), if connected to VSS through a resistor. This pin should be
connected to VSS for USB host operation, or left unconnected for USB device operation, and
should never be connected to any external voltage source.
(8) VDD is the voltage on the corresponding power-supply pin(s) for the
IO.
(9) For current pulse injection (I-Test):
- Pins stressed per JEDEC JESD78 (Class II) and passed with specified I/O pin injection current and clamp voltage of 1.5 times maximum recommended I/O voltage and negative 0.5 times maximum recommended I/O voltage.
(10) For over-voltage performance (Over-Voltage (OV) Test):
- Supplies stressed per JEDEC JESD78 (Class II) and passed specified voltage injection.
(11) For tape and reel the storage temperature range is [–10°C; +50°C]
with a maximum relative humidity of 70%. TI recommends returning to ambient room
temperature before usage.
Fail-safe IO terminals are designed without any dependencies on the respective IO power supply voltage. This allows external voltage sources to be connected to these IO terminals when the respective IO power supplies are turned off.
MCU_I2C0_SCL, MCU_I2C0_SDA, I2C0_SCL, I2C0_SDA, EXTINTn, VMON_1P8_MCU, VMON_1P8_SOC, VMON_3P3_MCU, VMON_3P3_SOC, and MCU_PORz are the only fail-safe IO terminals. All other IO terminals are not fail-safe and the voltage applied to them should be limited to the value defined by the Steady state max voltage at all IO pins parameter in Section 6.1.
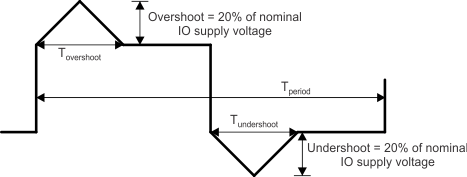
A. Tovershoot + Tundershoot < 20% of Tperiod
Figure 6-1 IO Transient Voltage Range