SPRUJ17H March 2022 – October 2024 AM2631 , AM2631-Q1 , AM2632 , AM2632-Q1 , AM2634 , AM2634-Q1
- 1
- Read This First
-
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Overview
- 1.2 Device Block Diagram
- 1.3 Module Allocation and Instances
- 1.4
Device Modules
- Arm Cortex-R5F Processor (R5FSS)
- 1.4.1 Programmable Real-Time Unit and Industrial Communication Subsystem (PRU-ICSS)
- 1.4.2 Hardware Security Module (HSM)
- 1.4.3 Real-time Control Subsystem (CONTROLSS)
- 1.4.4 Spinlock (SPINLOCK)
- 1.4.5 Enhanced Data Movement Architecture (EDMA)
- 1.4.6 General Purpose Input/Output Interface (GPIO)
- 1.4.7 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface (I2C)
- 1.4.8 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 1.4.9 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 1.4.10 3-port Gigabit Ethernet Switch (CPSW)
- 1.4.11 Quad Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI)
- 1.4.12 General Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 1.4.13 Error Location Module (ELM)
- 1.4.14 Multi-Media Card/Secure Digital Interface (MMCSD)
- 1.4.15 Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 1.4.16 Local Interconnect Network (LIN)
- 1.4.17 Timers
- 1.4.18 Internal Diagnostics Modules
- 1.5 Device Identification
- 2 Memory Map
-
3 System Interconnect
- 3.1 System Interconnect Overview
- 3.2 CORE VBUSM Interconnect
- 3.3 CORE VBUSP Interconnect
- 3.4 PERI VBUSP Interconnect
- 3.5 INFRA0 VBUSP Interconnect
- 3.6 INFRA1 VBUSP Interconnect
- 3.7 CONTROLSS Interconnect
- 3.8 Interconnect Safety
- 3.9 Bus Safety Errors
- 3.10 System Memory Protection Unit (MPU)/Firewalls
-
4 Module Integration
- 4.1 ADC Integration
- 4.2 DAC Integration
- 4.3 eCAP Integration
- 4.4 EPWM Integration
- 4.5 EQEP Integration
- 4.6 FSI Integration
- 4.7 SDFM Integration
- 4.8 SOC_TIMESYNC_XBAR0 Integration
- 4.9 SOC_TIMESYNC_XBAR1 Integration
- 4.10 GPIO Integration
- 4.11 I2C Integration
- 4.12 SPI Integration
- 4.13 UART Integration
- 4.14 CPSW Integration
- 4.15 GPMC Integration
- 4.16 ELM Integration
- 4.17 MMCSD Integration
- 4.18 QSPI Integration
- 4.19 MCAN Integration
- 4.20 LIN Integration
- 4.21 RTI Integration
- 4.22 WWDT Integration
- 4.23 DCC Integration
- 4.24 ESM Integration
- 4.25 ECC Aggregator Integration
- 4.26 MCRC Integration
- 4.27 ICSSM_XBAR_INTROUTER Integration
- 4.28 GPIO_XBAR Integration
-
5 Initialization
- 5.1 Initialization Overview
- 5.2 Boot Process
- 5.3 Boot Mode Pins
- 5.4 Boot Modes
- 5.5 Redundant boot support
- 5.6 PLL Configuration
- 5.7 Secure Boot Flow
- 5.8 Boot Image Format
- 5.9 Boot Memory Maps
-
6 Device Configuration
- 6.1
Control Module
- 6.1.1 Control Overview
- 6.1.2 TOP_CTRL
- 6.1.3
MSS_CTRL
- 6.1.3.1 MSS_CTRL Integration
- 6.1.3.2
MSS_CTRL Functional Description
- 6.1.3.2.1 R5FSS CPU Global Configuration and Control
- 6.1.3.2.2 Memory Initialization
- 6.1.3.2.3 EDMA Configuration
- 6.1.3.2.4 CPSW Global Configuration
- 6.1.3.2.5 ICSSM Global Configuration
- 6.1.3.2.6 GPMC Global Configuration
- 6.1.3.2.7 MPU Interrupt Aggregator
- 6.1.3.2.8 MMR Access Error Interrupt Aggregator
- 6.1.3.2.9 Safety Registers
- 6.1.3.2.10 MSS_CTRL MMR Kick Protection Registers
- 6.1.3.2.11 MSS_CTRL MMR Access Error Registers
- 6.1.4 CONTROLSS_CTRL (CTRLMMR2)
- 6.1.5 IOMUX (PADCFG_CTRLMMR0)
- 6.1.6 TOPRCM (RCM_CTRLMMR0): SoC-level Clock and Reset control registers
- 6.1.7 MSS_RCM (RCM_CTRLMMR1): SoC and Peripheral-level Clock and Reset control registers
- 6.2 Power
- 6.3 Reset
- 6.4
Clocking
- 6.4.1 Overview
- 6.4.2 Clock IO
- 6.4.3 IP Clocking
- 6.4.4 Clock Gating
- 6.4.5 Limp Mode
- 6.4.6 Clocking Registers
- 6.4.7
Programming Guide
- 6.4.7.1 PLL and Root Clocks Programming Guide
- 6.4.7.2
IP Clock Configurations
- 6.4.7.2.1 RTI CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.2 WDT CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.3 QSPI CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.4 MCSPI CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.5 I2C CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.6 LIN_UART CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.7 ICSSM UART CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.8 MCAN CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.9 MMCx CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.10 CPTS CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.11 HSM RTI CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.12 HSM WDT CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.13 HSM RTC CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.14 HSM DMTA CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.15 HSM DMTB CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.16 GPMC CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.17 CONTROLSS PLL CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.18 RGMII5 CLK
- 6.4.7.2.19 RGMII50 CLK
- 6.4.7.2.20 RGMII250 CLK
- 6.4.7.2.21 XTAL MMC 32K CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.22 XTAL TEMPSENSE 32K CLOCK
- 6.4.7.2.23 MSS_ELM CLOCK
- 6.1
Control Module
-
7 Processors and
Accelerators
- 7.1
Arm Cortex R5F Subsystem (R5FSS)
- 7.1.1 R5FSS Overview
- 7.1.2 R5FSS Integration
- 7.1.3
R5FSS Functional Description
- 7.1.3.1 R5FSS Block Diagram
- 7.1.3.2 R5FSS Cortex-R5F Core
- 7.1.3.3 R5FSS Interfaces
- 7.1.3.4 R5FSS Power, Clocking and Reset
- 7.1.3.5 R5FSS Vectored Interrupt Manager (VIM)
- 7.1.3.6 R5FSS ECC Support
- 7.1.3.7 R5FSS Memory View
- 7.1.3.8 R5FSS Interrupts
- 7.1.3.9 R5FSS Debug and Trace
- 7.1.3.10 R5FSS Boot Options
- 7.1.3.11 R5FSS Events
- 7.1.3.12 R5FSS TCM Address Parity Error
- 7.1.3.13
R5FSS Lockstep
Compare
- 7.1.3.13.1 Overview
- 7.1.3.13.2 Module Operation
- 7.1.3.13.3
Control Registers
- 7.1.3.13.3.1 CCM-R5F Status Register 1 (CCMSR1)
- 7.1.3.13.3.2 CCM-R5F Key Register 1 (CCMKEYR1)
- 7.1.3.13.3.3 CCM-R5F Status Register 2 (CCMSR2)
- 7.1.3.13.3.4 CCM-R5F Key Register 2 (CCMKEYR2)
- 7.1.3.13.3.5 CCM-R5F Status Register 3 (CCMSR3)
- 7.1.3.13.3.6 CCM-R5F Key Register 3 (CCMKEYR3)
- 7.1.3.13.3.7 CCM-R5F Polarity Control Register (CCMPOLCNTRL)
- 7.1.3.14 R5FSS Selftest Logic
- 7.2
Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRU-ICSS)
- 7.2.1 PRU-ICSS Overview
- 7.2.2 PRU-ICSS Environment
- 7.2.3 PRU-ICSS Integration
- 7.2.4 PRU-ICSS Top Level Resources Functional Description
- 7.2.5
PRU-ICSS PRU Cores
- 7.2.5.1 PRU Cores Overview
- 7.2.5.2
PRU Cores Functional Description
- 7.2.5.2.1 PRU Constant Table
- 7.2.5.2.2
PRU Module Interface
- 7.2.5.2.2.1 Real-Time Status Interface Mapping (R31): Interrupt Events Input
- 7.2.5.2.2.2 Event Interface Mapping (R31): PRU System Events
- 7.2.5.2.2.3
General-Purpose Inputs (R31): Enhanced PRU GP Module
- 7.2.5.2.2.3.1 PRU EGPIs Direct Input
- 7.2.5.2.2.3.2 PRU EGPIs 16-Bit Parallel Capture
- 7.2.5.2.2.3.3 PRU EGPIs 28-Bit Shift In
- 7.2.5.2.2.3.4 General-Purpose Outputs (R30): Enhanced PRU GP Module
- 7.2.5.2.2.3.5 Sigma Delta (SD) Decimation Filtering
- 7.2.5.2.2.3.6 Three Channel Peripheral Interface
- 7.2.5.3 PRU-ICSS RAM Index Allocation
- 408
- 7.2.6
PRU-ICSS Broadside Accelerators
- 7.2.6.1 PRU-ICSS Broadside Accelerators Overview
- 7.2.6.2 PRU-ICSS Data Processing Accelerators Functional
- 7.2.6.3 PRU-ICSS Data Movement Accelerators Functional
- 435
- 7.2.7
PRU-ICSS Local INTC
- 7.2.7.1
PRU-ICSS Interrupt Controller Functional Description
- 7.2.7.1.1 PRU-ICSS Interrupt Controller System Events Flow
- 7.2.7.1.2 PRU-ICSS Interrupt Disabling
- 7.2.7.2 PRU-ICSS Interrupt Controller Basic Programming Model
- 7.2.7.3 PRU-ICSS Interrupt Requests Mapping
- 450
- 7.2.7.1
PRU-ICSS Interrupt Controller Functional Description
- 7.2.8
PRU-ICSS
UART Module
- 7.2.8.1 PRU-ICSS UART Overview
- 7.2.8.2 PRU-ICSS UART Environment
- 7.2.8.3
PRU-ICSS UART Functional Description
- 7.2.8.3.1 PRU-ICSS UART Functional Block Diagram
- 7.2.8.3.2 PRU-ICSS UART Reset Considerations
- 7.2.8.3.3 PRU-ICSS UART Power Management
- 7.2.8.3.4 PRU-ICSS UART Interrupt Support
- 7.2.8.3.5 PRU-ICSS UART DMA Event Support
- 7.2.8.3.6 PRU-ICSS UART Operations
- 7.2.8.3.7 PRU-ICSS UART Emulation Considerations
- 7.2.8.3.8 PRU-ICSS UART Exception Processing
- 484
- 7.2.9
PRU-ICSS ECAP Module
- 7.2.9.1 PRU-ICSS eCAP Overview
- 7.2.9.2
PRU-ICSS ECAP Functional Description
- 7.2.9.2.1 PRU-ICSS Capture and APWM Operating Mode
- 7.2.9.2.2
PRU-ICSS eCAP Capture Mode Description
- 7.2.9.2.2.1 PRU-ICSS eCAP Event Prescaler
- 7.2.9.2.2.2 PRU-ICSS eCAP Edge Polarity Select and Qualifier
- 7.2.9.2.2.3 eCAP Continuous/One-Shot Control
- 7.2.9.2.2.4 PRU-ICSS eCAP 32-bit Counter and Phase Control
- 7.2.9.2.2.5 PRU-ICSS Enhanced Capture CAP1-CAP4 Registers
- 7.2.9.2.2.6 PRU-ICSS eCAP Interrupt Control
- 7.2.9.2.2.7 PRU-ICSS eCAP Shadow Load and Lockout Control
- 7.2.9.2.2.8 CEVT Flag Registers
- 7.2.9.2.3 PRU-ICSS eCAP Module APWM Mode Operation
- 501
- 7.2.10
PRU-ICSS MII_RT
Module
- 7.2.10.1 PRU-ICSS MII_RT Introduction
- 7.2.10.2
MII_RT Functional Description
- 7.2.10.2.1 MII_RT Data Path Configuration
- 7.2.10.2.2 MII_RT Definition and Terms
- 7.2.10.2.3
RX MII Interface
- 7.2.10.2.3.1 RX MII Receive Data Latch
- 7.2.10.2.3.2 RX MII Start of Frame Detection
- 7.2.10.2.3.3 CRC Error Detection
- 7.2.10.2.3.4 RX Error Detection and Action
- 7.2.10.2.3.5 RX Data Path Options to PRU
- 7.2.10.2.3.6 RX MII Port → RX L1 FIFO → PRU
- 7.2.10.2.3.7 RX MII Port → RX L1 FIFO → RX L2 Buffer → PRU
- 7.2.10.2.4 PRU-ICSS TX MII Interface
- 7.2.10.2.5 PRU R31 Command Interface
- 7.2.10.2.6 Other Configuration Options
- 547
- 7.2.11
PRU-ICSS MII MDIO Module
- 7.2.11.1 PRU-ICSS MII MDIO Overview
- 7.2.11.2 PRU-ICSS MII MDIO Functional Description
- 7.2.11.3 PRU-ICSS MII MDIO Receive/Transmit Frame Host Software Interface
- 560
- 7.2.12
PRU-ICSS IEP
- 7.2.12.1 PRU-ICSS IEP Overview
- 7.2.12.2
PRU-ICSS IEP Functional Description
- 7.2.12.2.1 PRU-ICSS IEP Clock Generation
- 7.2.12.2.2 PRU-ICSS IEP Timer
- 7.2.12.2.3 32-Bit Shadow Mode
- 7.2.12.2.4 PRU-ICSS IEP Timer Basic Programming Sequence
- 7.2.12.2.5 Industrial Ethernet Mapping
- 7.2.12.2.6 PRU-ICSS IEP Sync0/Sync1 Module
- 7.2.12.2.7 PRU-ICSS IEP WatchDog
- 7.2.12.2.8 PRU-ICSS IEP DIGIO
- 578
- 7.3
Hardware Security Module (HSM)
- 7.3.1 Security Features
- 7.3.2 Security Features not Supported
- 7.3.3 Security Device Types
- 7.3.4
Crypto Hardware Accelerators
- 7.3.4.1 DTHE
- 7.3.4.2 CRC Engine
- 7.3.4.3
AES Engine - Symmetric Encryption and Decryption
- 7.3.4.3.1 Functional Description
- 7.3.4.3.2 Global Control FSM and DMA I/O
- 7.3.4.3.3 Register Interface
- 7.3.4.3.4 AES Wide-bus Engine
- 7.3.4.3.5 AES Algorithm
- 7.3.4.3.6
Supported Modes of Operation
- 7.3.4.3.6.1 ECB Feedback Mode
- 7.3.4.3.6.2 CBC Feedback Mode
- 7.3.4.3.6.3 CTR Feedback Mode
- 7.3.4.3.6.4 CFB128 Feedback Mode
- 7.3.4.3.6.5 f8 Feedback Mode
- 7.3.4.3.6.6 XTS Operation
- 7.3.4.3.6.7 f9 Authentication Mode
- 7.3.4.3.6.8 CBC-MAC Authentication Mode
- 7.3.4.3.6.9 GCM Operation
- 7.3.4.3.6.10 CCM Operation
- 7.3.4.3.7 Extended/Combined Modes of Operations
- 7.3.4.3.8 AES Module Programming Guide
- 7.3.4.3.9 HSM_AES Memory Map
- 7.3.4.4
Asymmetric Cryptography
- 7.3.4.4.1
Public Key Accelerator (PKA)
- 7.3.4.4.1.1 PKA Introduction and Features
- 7.3.4.4.1.2 PKA Embedded Memories
- 7.3.4.4.1.3 PKA Clock Management
- 7.3.4.4.1.4 PKA PKCP Operations
- 7.3.4.4.1.5 PKA LNME Operations
- 7.3.4.4.1.6 PKA GF(2m) Operations
- 7.3.4.4.1.7
PKA Sequencer Controlled Operations
- 7.3.4.4.1.7.1 Sequencer Command Execution
- 7.3.4.4.1.7.2 Sequencer Complex Commands
- 7.3.4.4.1.7.3
Sequencer Command Descriptions
- 7.3.4.4.1.7.3.1 Operations for Modular Exponentiation
- 7.3.4.4.1.7.3.2 Operations for Modular Inversion
- 7.3.4.4.1.7.3.3 Operations for ECC on Curves over Prime Fields
- 7.3.4.4.1.7.3.4 Operations for ECC on Curves over Binary Fields
- 7.3.4.4.1.7.3.5 Single-command ECDSAp Signature Generation and Verification
- 7.3.4.4.1.7.3.6 Basic Operations for Montgomery Curves (Curve25519 and Curve448)
- 7.3.4.4.1.7.4 Sequencer Operation Examples
- 7.3.4.4.1.7.5 Sequencer Firmware Download
- 7.3.4.4.1.8 PKA Operation Sequences Basics
- 7.3.4.4.1.9 PKA Memory Address Space Assignment
- 7.3.4.4.2 HSM_PKA_RAM Memory Map
- 7.3.4.4.1
Public Key Accelerator (PKA)
- 7.3.4.5
Hashing Function
- 7.3.4.5.1
SHA/MD5 Functional Description
- 7.3.4.5.1.1 SHA/MD5 Block Diagram
- 7.3.4.5.1.2 DMA and Interrupt Requests
- 7.3.4.5.1.3 Operation Description
- 7.3.4.5.1.4
SHA/MD5 Programming Guide
- 7.3.4.5.1.4.1
Global Initialization
- 7.3.4.5.1.4.1.1 Surrounding Modules Global Initialization
- 7.3.4.5.1.4.1.2 Starting a New HMAC using the SHA-1 Hash Function and HMAC Key Processing
- 7.3.4.5.1.4.1.3 Subsequence - Hashing a Key Bigger than 512 Bits with the SHA-1 Hash Function
- 7.3.4.5.1.4.1.4 Operational Modes Configuration
- 7.3.4.5.1.4.1.5 SHA/MD5 Event Servicing
- 7.3.4.5.1.4.1
Global Initialization
- 7.3.4.5.2 HSM_SHA Memory Map
- 7.3.4.5.1
SHA/MD5 Functional Description
- 7.3.4.6
Random Number Generator
- 7.3.4.6.1 True Random Number Generator (TRNG) with DRBG
- 7.3.4.6.2 HSM_TRNG Memory Map
- 7.3.5 How to Request Access for HSM Addendum
- 7.4
Real-time Control Subsystem (CONTROLSS)
- 7.4.1 Real-time Control Subsystem (CONTROLSS) Overview
- 7.4.2
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 7.4.2.1 Introduction
- 7.4.2.2 ADC Integration
- 7.4.2.3 ADC Configurability
- 7.4.2.4 SOC Principle of Operation
- 7.4.2.5 ADC Conversion Priority
- 7.4.2.6 Burst Mode
- 7.4.2.7 EOC and Interrupt Operation
- 7.4.2.8 Post-Processing Blocks
- 7.4.2.9 Power-Up Sequence
- 7.4.2.10 ADC Timings
- 7.4.2.11 ADC Programming Guide
- 7.4.2.12 Additional Information
- 7.4.3 Comparator Subsystem (CMPSS)
- 7.4.4 Buffered Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
- 7.4.5
Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (ePWM)
- 7.4.5.1 Introduction
- 7.4.5.2 EPWM Integration
- 7.4.5.3 ePWM Modules Overview
- 7.4.5.4
Time-Base (TB) Submodule
- 7.4.5.4.1 Purpose of the Time-Base Submodule
- 7.4.5.4.2 Controlling and Monitoring the Time-Base Submodule
- 7.4.5.4.3 Calculating PWM Period and Frequency
- 7.4.5.4.4 Phase Locking the Time-Base Clocks of Multiple ePWM Modules
- 7.4.5.4.5 Simultaneous Writes to TBPRD and CMPx Registers Between ePWM Modules
- 7.4.5.4.6 Time-Base Counter Modes and Timing Waveforms
- 7.4.5.4.7 Edge Detection Within a Programmable TBCTR Range
- 7.4.5.4.8 Global Load
- 7.4.5.5 Counter-Compare (CC) Submodule
- 7.4.5.6 Action-Qualifier (AQ) Submodule
- 7.4.5.7 Dead-Band Generator (DB) Submodule
- 7.4.5.8 Minimum Dead-Band (MINDB) + Illegal Combination Logic (ICL) Submodules
- 7.4.5.9 PWM Chopper (PC) Submodule
- 7.4.5.10 Trip-Zone (TZ) Submodule
- 7.4.5.11 Diode Emulation (DE) Submodule
- 7.4.5.12 Event-Trigger (ET) Submodule
- 7.4.5.13 Digital Compare (DC) Submodule
- 7.4.5.14 XCMP Submodule
- 7.4.5.15
High-Resolution Pulse Width Modulator (HRPWM)
- 7.4.5.15.1
Operational Description of HRPWM
- 7.4.5.15.1.1 Controlling the HRPWM Capabilities
- 7.4.5.15.1.2 HRPWM Source Clock
- 7.4.5.15.1.3 Configuring the HRPWM
- 7.4.5.15.1.4 Configuring High-Resolution in Deadband Rising-Edge and Falling-Edge Delay
- 7.4.5.15.1.5 Principle of Operation
- 7.4.5.15.1.6 Deadband High-Resolution Operation
- 7.4.5.15.1.7 Scale Factor Optimizing Software (SFO)
- 7.4.5.15.1
Operational Description of HRPWM
- 7.4.5.16 ePWM Crossbar (XBAR)
- 7.4.5.17 Register Lock Protection
- 7.4.5.18
Applications to Power Topologies
- 7.4.5.18.1 Overview of Multiple Modules
- 7.4.5.18.2 Key Configuration Capabilities
- 7.4.5.18.3 Controlling Multiple Buck Converters With Independent Frequencies
- 7.4.5.18.4 Controlling Multiple Buck Converters With Same Frequencies
- 7.4.5.18.5 Controlling Multiple Half H-Bridge (HHB) Converters
- 7.4.5.18.6 Controlling Dual 3-Phase Inverters for Motors (ACI and PMSM)
- 7.4.5.18.7 Practical Applications Using Phase Control Between PWM Modules
- 7.4.5.18.8 Controlling a 3-Phase Interleaved DC/DC Converter
- 7.4.5.18.9 Controlling Zero Voltage Switched Full Bridge (ZVSFB) Converter
- 7.4.5.18.10 Controlling a Peak Current Mode Controlled Buck Module
- 7.4.5.18.11 Controlling H-Bridge LLC Resonant Converter
- 7.4.5.19 EPWM Programming Guide
- 7.4.6
Enhanced Capture (eCAP)
- 7.4.6.1 Introduction
- 7.4.6.2 eCAP Integration
- 7.4.6.3 Description
- 7.4.6.4 Capture Mode Operation
- 7.4.6.5 APWM Mode Operation
- 7.4.6.6 eCAP Synchronization and Events
- 7.4.6.7 Signal Monitoring Unit
- 7.4.6.8
Application of the eCAP Module
- 7.4.6.8.1 Example 1 - Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising-Edge Trigger
- 7.4.6.8.2 Example 2 - Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising- and Falling-Edge Trigger
- 7.4.6.8.3 Example 3 - Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising-Edge Trigger
- 7.4.6.8.4 Example 4 - Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising- and Falling-Edge Trigger
- 7.4.6.9 Application of the APWM Mode
- 7.4.6.10 eCAP Programming Guide
- 7.4.7
Enhanced Quadrature
Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 7.4.7.1 Introduction
- 7.4.7.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 7.4.7.3 EQEP Integration
- 7.4.7.4 Description
- 7.4.7.5 Quadrature Decoder Unit (QDU)
- 7.4.7.6
Position Counter and Control Unit (PCCU)
- 7.4.7.6.1
Position Counter Operating Modes
- 7.4.7.6.1.1 Position Counter Reset on Index Event (QEPCTL[PCRM] = 00)
- 7.4.7.6.1.2 Position Counter Reset on Maximum Position (QEPCTL[PCRM] = 01)
- 7.4.7.6.1.3 Position Counter Reset on the First Index Event (QEPCTL[PCRM] = 10)
- 7.4.7.6.1.4 Position Counter Reset on Unit Time-out Event (QEPCTL[PCRM] = 11)
- 7.4.7.6.2 Position Counter Latch
- 7.4.7.6.3 Position Counter Initialization
- 7.4.7.6.4 eQEP Position-compare Unit
- 7.4.7.6.1
Position Counter Operating Modes
- 7.4.7.7 eQEP Edge Capture Unit
- 7.4.7.8 eQEP Watchdog
- 7.4.7.9 eQEP Unit Timer Base
- 7.4.7.10 eQEP Interrupt Structure
- 7.4.7.11 EQEP Programming Guide
- 7.4.8
Fast Serial Interface (FSI)
- 7.4.8.1 Introduction
- 7.4.8.2 System-level Integration
- 7.4.8.3
FSI Functional Description
- 7.4.8.3.1 FSI Functional Description
- 7.4.8.3.2 FSI Transmitter Module
- 7.4.8.3.3
FSI Receiver Module
- 7.4.8.3.3.1 Initialization
- 7.4.8.3.3.2 FSI_RX Clocking
- 7.4.8.3.3.3 Receiving Frames
- 7.4.8.3.3.4 Ping Frame Watchdog
- 7.4.8.3.3.5 Frame Watchdog
- 7.4.8.3.3.6 Delay Line Control
- 7.4.8.3.3.7 Buffer Management
- 7.4.8.3.3.8 CRC Submodule
- 7.4.8.3.3.9 Using the Zero Bits of the Receiver Tag Registers
- 7.4.8.3.3.10 Conditions in Which the Receiver Must Undergo a Soft Reset
- 7.4.8.3.3.11 FSI_RX Reset
- 7.4.8.3.4 Frame Format
- 7.4.8.3.5 Flush Sequence
- 7.4.8.3.6 Internal Loopback
- 7.4.8.3.7 CRC Generation
- 7.4.8.3.8 ECC Module
- 7.4.8.3.9 FSI Trigger Generation
- 7.4.8.3.10 FSI-SPI Compatibility Mode
- 7.4.8.4 FSI Programing Guide
- 7.4.9
Sigma Delta Filter Module
(SDFM)
- 7.4.9.1 Introduction
- 7.4.9.2 SDFM Integration
- 7.4.9.3 Configuring Device Pins
- 7.4.9.4 Input Qualification
- 7.4.9.5 Input Control Unit
- 7.4.9.6 SDFM Clock Control
- 7.4.9.7 Sinc Filter
- 7.4.9.8 Data (Primary) Filter Unit
- 7.4.9.9 Comparator (Secondary) Filter Unit
- 7.4.9.10 Theoretical SDFM Filter Output
- 7.4.9.11 Interrupt Unit
- 7.4.9.12 SDFM Programming Guide
- 7.4.10 Crossbar (XBAR)
- 7.1
Arm Cortex R5F Subsystem (R5FSS)
- 8 Interprocessor Communication (IPC)
- 9 Memory Controllers
-
10Interrupts
- 10.1 Interrupt Architecture
- 10.2
Interrupt Controllers
- 10.2.1 Vectored Interrupt Manager (VIM)
- 10.2.2 Other Interrupt Controllers
- 10.3 Interrupt Routers
- 10.4 Interrupt Sources
-
11Data Movement Architecture
- 11.1 Overview
- 11.2 Definition of Terms
- 11.3
Enhanced Direct Memory
Access (EDMA)
- 11.3.1 EDMA Module Overview
- 11.3.2 EDMA Integration
- 11.3.3
EDMA Controller Functional Description
- 11.3.3.1 Block Diagram
- 11.3.3.2 Types of EDMA Controller Transfers
- 11.3.3.3
Parameter RAM (PaRAM)
- 11.3.3.3.1 PaRAM
- 11.3.3.3.2
EDMA Channel PaRAM Set Entry Fields
- 11.3.3.3.2.1 Channel Options Parameter (OPT)
- 11.3.3.3.2.2 Channel Source Address (SRC)
- 11.3.3.3.2.3 Channel Destination Address (DST)
- 11.3.3.3.2.4 Count for 1st Dimension (ACNT)
- 11.3.3.3.2.5 Count for 2nd Dimension (BCNT)
- 11.3.3.3.2.6 Count for 3rd Dimension (CCNT)
- 11.3.3.3.2.7 BCNT Reload (BCNTRLD)
- 11.3.3.3.2.8 Source B Index (SBIDX)
- 11.3.3.3.2.9 Destination B Index (DBIDX)
- 11.3.3.3.2.10 Source C Index (SCIDX)
- 11.3.3.3.2.11 Destination C Index (DCIDX)
- 11.3.3.3.2.12 Link Address (LINK)
- 11.3.3.3.3 Null PaRAM Set
- 11.3.3.3.4 Dummy PaRAM Set
- 11.3.3.3.5 Dummy Versus Null Transfer Comparison
- 11.3.3.3.6 Parameter Set Updates
- 11.3.3.3.7 Linking Transfers
- 11.3.3.3.8 Constant Addressing Mode Transfers/Alignment Issues
- 11.3.3.3.9 Element Size
- 11.3.3.4 Initiating a DMA Transfer
- 11.3.3.5 Completion of a DMA Transfer
- 11.3.3.6 Event, Channel, and PaRAM Mapping
- 11.3.3.7 EDMA Channel Controller Regions
- 11.3.3.8 Chaining EDMA Channels
- 11.3.3.9 EDMA Interrupts
- 11.3.3.10 Memory Protection
- 11.3.3.11 Event Queue(s)
- 11.3.3.12 EDMA Transfer Controller (EDMA_TPTC)
- 11.3.3.13 Event Dataflow
- 11.3.3.14 EDMA Controller Prioritization
- 11.3.3.15 Emulation Considerations
- 11.3.4 EDMA Transfer Examples
- 11.3.5 EDMA Debug Checklist and Programming Tips
- 11.3.6 EDMA Event Map
- 12Time Sync
-
13Peripherals
- 13.1
General Connectivity Peripherals
- 13.1.1
General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 13.1.1.1 GPIO Overview
- 13.1.1.2 GPIO Environment
- 13.1.1.3 GPIO Integration
- 13.1.1.4 GPIO Functional Description
- 13.1.2
Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Interface
- 13.1.2.1 I2C Overview
- 13.1.2.2
I2C Environment
- 13.1.2.2.1 I2C Typical Application
- 13.1.2.2.2
I2C Typical Connection Protocol and Data Format
- 13.1.2.2.2.1 I2C Serial Data Formats
- 13.1.2.2.2.2 I2C Data Validity
- 13.1.2.2.2.3 I2C Start and Stop Conditions
- 13.1.2.2.2.4 I2C Addressing
- 13.1.2.2.2.5 I2C Controller Transmitter
- 13.1.2.2.2.6 I2C Controller Receiver
- 13.1.2.2.2.7 I2C Target Transmitter
- 13.1.2.2.2.8 I2C Target Receiver
- 13.1.2.2.2.9 I2C Bus Arbitration
- 13.1.2.2.2.10 I2C Clock Generation and Synchronization
- 13.1.2.3 I2C Integration
- 13.1.2.4 I2C Functional Description
- 13.1.2.5 I2C Programming Guide
- 13.1.3
Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interface (MCSPI)
- 13.1.3.1 MCSPI Overview
- 13.1.3.2 SPI Environment
- 13.1.3.3 SPI Integration
- 13.1.3.4
MCSPI Functional Description
- 13.1.3.4.1 SPI Block Diagram
- 13.1.3.4.2 MCSPI Reset
- 13.1.3.4.3
MCSPI Controller Mode
- 13.1.3.4.3.1 Controller Mode Features
- 13.1.3.4.3.2 Controller Transmit-and-Receive Mode (Full Duplex)
- 13.1.3.4.3.3 Controller Transmit-Only Mode (Half Duplex)
- 13.1.3.4.3.4 Controller Receive-Only Mode (Half Duplex)
- 13.1.3.4.3.5 Single-Channel Controller Mode
- 13.1.3.4.3.6 Start-Bit Mode
- 13.1.3.4.3.7 Chip-Select Timing Control
- 13.1.3.4.3.8 Programmable MCSPI Clock (SPICLK)
- 13.1.3.4.4 MCSPI Peripheral Mode
- 13.1.3.4.5 MCSPI 3-Pin or 4-Pin Mode
- 13.1.3.4.6 MCSPI FIFO Buffer Management
- 13.1.3.4.7 MCSPI Interrupts
- 13.1.3.4.8 MCSPI DMA Requests
- 13.1.3.5
MCSPI Programming Guide
- 13.1.3.5.1 MCSPI Global Initialization
- 13.1.3.5.2
MCSPI Operational Mode Configuration
- 13.1.3.5.2.1
MCSPI Operational Modes
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.1 Common Transfer Sequence
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.2 End of Transfer Sequences
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.3 Transmit-and-Receive (Controller and Peripheral)
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.4 Transmit-Only (Controller and Peripheral)
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.5 Controller Normal Receive-Only
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.6 Controller Turbo Receive-Only
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.7 Peripheral Receive-Only
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8
Transfer Procedures With FIFO
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8.1 Common Transfer Sequence in FIFO Mode
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8.2 End of Transfer Sequences in FIFO Mode
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8.3 Transmit-and-Receive With Word Count
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8.4 Transmit-and-Receive Without Word Count
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8.5 Transmit-Only
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8.6 Receive-Only With Word Count
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.8.7 Receive-Only Without Word Count
- 13.1.3.5.2.1.9 Common Transfer Procedures Without FIFO – Polling Method
- 13.1.3.5.2.1
MCSPI Operational Modes
- 13.1.3.5.3 Common Transfer Procedures Without FIFO – Polling Method
- 13.1.4
Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 13.1.4.1 UART Overview
- 13.1.4.2
UART Environment
- 13.1.4.2.1 UART Functional Interfaces
- 13.1.4.2.2 RS-485 Functional Interfaces
- 13.1.4.2.3 IrDA Functional Interfaces
- 13.1.4.2.4 CIR Functional Interfaces
- 13.1.4.3 UART Integration
- 13.1.4.4
UART Functional Description
- 13.1.4.4.1 UART Block Diagram
- 13.1.4.4.2 UART Clock Configuration
- 13.1.4.4.3 UART Software Reset
- 13.1.4.4.4 UART Power Management
- 13.1.4.4.5 UART Interrupt Requests
- 13.1.4.4.6 UART FIFO Management
- 13.1.4.4.7 UART Mode Selection
- 13.1.4.4.8
UART Protocol Formatting
- 13.1.4.4.8.1
UART Mode
- 13.1.4.4.8.1.1 UART Clock Generation: Baud Rate Generation
- 13.1.4.4.8.1.2 Choosing the Appropriate Divisor Value
- 13.1.4.4.8.1.3 Multi-drop Parity Mode with Address Match
- 13.1.4.4.8.1.4 Time-guard
- 13.1.4.4.8.1.5 UART Data Formatting
- 13.1.4.4.8.2 RS-485 Mode
- 13.1.4.4.8.3
IrDA Mode
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.1 IrDA Clock Generation: Baud Generator
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.2 Choosing the Appropriate Divisor Value
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3
IrDA Data Formatting
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.1 IR RX Polarity Control
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.2 IrDA Reception Control
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.3 IR Address Checking
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.4 Frame Closing
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.5 Store and Controlled Transmission
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.6 Error Detection
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.7 Underrun During Transmission
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.8 Overrun During Receive
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.3.9 Status FIFO
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.4 SIR Mode Data Formatting
- 13.1.4.4.8.3.5 MIR and FIR Mode Data Formatting
- 13.1.4.4.8.4 CIR Mode
- 13.1.4.4.8.1
UART Mode
- 13.1.4.5
UART Programming Guide
- 13.1.4.5.1 UART Global Initialization
- 13.1.4.5.2 UART Mode selection
- 13.1.4.5.3 UART Submode selection
- 13.1.4.5.4 UART Load FIFO trigger and DMA mode settings
- 13.1.4.5.5 UART Protocol, Baud rate and interrupt settings
- 13.1.4.5.6 UART Hardware and Software Flow Control Configuration
- 13.1.4.5.7 IrDA Programming Model
- 13.1.1
General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 13.2
High-speed Serial Interfaces
- 13.2.1
Gigabit Ethernet Switch (CPSW)
- 13.2.1.1 CPSW0 Overview
- 13.2.1.2 CPSW0 Environment
- 13.2.1.3 CPSW Integration
- 13.2.1.4
CPSW0 Functional Description
- 13.2.1.4.1 Functional Block Diagram
- 13.2.1.4.2 CPSW Ports
- 13.2.1.4.3 Clocking
- 13.2.1.4.4 Software IDLE
- 13.2.1.4.5 Interrupt Functionality
- 13.2.1.4.6
CPSW
- 13.2.1.4.6.1
Address Lookup Engine (ALE)
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.1 Error Handling
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.2 Bypass Operations
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.3 OUI Deny or Accept
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.4 Statistics Counting
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.5 Automotive Security Features
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.6 CPSW Switching Solutions
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.7 VLAN Routing and OAM Operations
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.8 Supervisory packets
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9
Address Table Entry
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.1 Free Table Entry
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.2 OUI Unicast Address Table Entry
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.3 Unicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40 == 0)
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.4 Multicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40==1)
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.5 VLAN/Unicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40 == 0)
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.6 VLAN/Multicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40==1)
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.7 Inner VLAN Table Entry
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.8 Outer VLAN Table Entry
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.9 EtherType Table Entry
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.10 IPv4 Table Entry
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.11 IPv6 Table Entry High
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.9.12 IPv6 Table Entry Low
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.10 Multicast Address
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.11 Aging and Auto Aging
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.12 ALE Policing and Classification
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.13 Mirroring
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.14 Trunking
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.15 DSCP
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.16 Packet Forwarding Processes
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.17 VLAN Aware Mode
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.18 VLAN Unaware Mode
- 13.2.1.4.6.1.19 Transmit VLAN Processing
- 13.2.1.4.6.2 Packet Priority Handling
- 13.2.1.4.6.3 CPPI Port Ingress
- 13.2.1.4.6.4 Packet CRC Handling
- 13.2.1.4.6.5 FIFO Memory Control
- 13.2.1.4.6.6 FIFO Transmit Queue Control
- 13.2.1.4.6.7 Rate Limiting (Traffic Shaping)
- 13.2.1.4.6.8
Enhanced Scheduled Traffic (EST – P802.1Qbv/D2.2)
- 13.2.1.4.6.8.1 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Overview
- 13.2.1.4.6.8.2 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Fetch RAM
- 13.2.1.4.6.8.3 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Time Interval
- 13.2.1.4.6.8.4 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Fetch Values
- 13.2.1.4.6.8.5 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Packet Fill
- 13.2.1.4.6.8.6 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Time Stamp
- 13.2.1.4.6.9 Audio Video Bridging
- 13.2.1.4.6.10
Ethernet MAC Sliver
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1
Ethernet MAC Sliver
Overview
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1.1 CRC Insertion
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1.2 MTXER
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1.3 Adaptive Performance Optimization (APO)
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1.4 Inter-Packet-Gap Enforcement
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1.5 Back Off
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1.6 Programmable Transmit Inter-Packet Gap
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1.7 Speed, Duplex and Pause Frame Support Negotiation
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.2 RMII Interface
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.3 RGMII Interface
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.4 Frame Classification
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.5 Receive FIFO Architecture
- 13.2.1.4.6.10.1
Ethernet MAC Sliver
Overview
- 13.2.1.4.6.11 Embedded Memories
- 13.2.1.4.6.12 Memory Error Detection and Correction
- 13.2.1.4.6.13 Ethernet Port Flow Control
- 13.2.1.4.6.14 Energy Efficient Ethernet Support (802.3az)
- 13.2.1.4.6.15 Ethernet Switch Latency
- 13.2.1.4.6.16 MAC Emulation Control
- 13.2.1.4.6.17 MAC Command IDLE
- 13.2.1.4.6.18
CPSW Network Statistics
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1
Rx-only Statistics Descriptions
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.1 Good Rx Frames (Offset = 3A000h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.2 Broadcast Rx Frames (Offset = 3A004h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.3 Multicast Rx Frames (Offset = 3A008h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.4 Pause Rx Frames (Offset = 3A00Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.5 Rx CRC Errors (Offset = 3A010h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.6 Rx Align/Code Errors (Offset = 3A014h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.7 Oversize Rx Frames (Offset = 3A018h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.8 Rx Jabbers (Offset = 3A01Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.9 Undersize (Short) Rx Frames (Offset = 3A020h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.10 Rx Fragments (Offset = 3A024h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.11 RX IPG Error (Offset = 3A05Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.12 ALE Drop (Offset = 3A028h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.13 ALE Overrun Drop (Offset = 3A02Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.14 Rx Octets (Offset = 3A030h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.15 Rx Bottom of FIFO Drop (Offset = 3A084h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.16 Portmask Drop (Offset = 3A088h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.17 Rx Top of FIFO Drop (Offset = 3A08Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.18 ALE Rate Limit Drop (Offset = 3A090h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1.19
ALE VLAN Ingress Check Drop (Offset = 3A094h)
- 2.1.4.6.18.1.19.1 ALE DA=SA Drop (Offset = 3A098h)
- 2.1.4.6.18.1.19.2 Block Address Drop (Offset = 3A09Ch)
- 2.1.4.6.18.1.19.3 ALE Secure Drop (Offset = 3A0A0h)
- 2.1.4.6.18.1.19.4 ALE Authentication Drop (Offset = 3A0A4h)
- 2.1.4.6.18.1.19.5 ALE Unknown Unicast (Offset = 3A0A8h)
- 2.1.4.6.18.1.19.6 ALE Unknown Unicast Bytecount (Offset = 3A0ACh)
- 2.1.4.6.18.1.19.7 ALE Unknown Multicast (Offset = 3A0B0h)
- 2.1.4.6.18.1.19.8 ALE Unknown Multicast Bytecount (Offset = 3A0B4h)
- 2.1.4.6.18.1.19.9 ALE Unknown Broadcast (Offset = 3A0B8h)
- 2.1.4.6.18.1.19.10 ALE Unknown Broadcast Bytecount (Offset = 3A0BCh)
- 2.1.4.6.18.1.19.11 ALE Policer Match (Offset = 3A0C0h)
- 2.1.4.6.18.1.19.12 ALE Policer Match Red (Offset = 3A0C4h)
- 2.1.4.6.18.1.19.13 ALE Policer Match Yellow (Offset = 3A0C8h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2
Tx-only Statistics Descriptions
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.1 Good Tx Frames (Offset = 3A034h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.2 Broadcast Tx Frames (Offset = 3A038h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.3 Multicast Tx Frames (Offset = 3A03Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.4 Pause Tx Frames (Offset = 3A040h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.5 Deferred Tx Frames (Offset = 3A044h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.6 Collisions (Offset = 3A048h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.7 Single Collision Tx Frames (Offset = 3A04Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.8 Multiple Collision Tx Frames (Offset = 3A050h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.9 Excessive Collisions (Offset = 3A054h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.10 Late Collisions (Offset = 3A058h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.11 Carrier Sense Errors (Offset = 3A060h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.12 Tx Octets (Offset = 3A064h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.13 Transmit Priority 0-7 (Offset = 3A180h to 3A1A8h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.14 Transmit Priority 0-7 Drop (Offset = 3A1C0h to 3A1E8)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.15 Tx Memory Protect Errors (Offset = 3A17Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.2.16 Tx CRC Errors
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.3
Rx- and Tx (Shared) Statistics Descriptions
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.3.1 Rx + Tx 64 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A068h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.3.2 Rx + Tx 65–127 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A06Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.3.3 Rx + Tx 128–255 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A070h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.3.4 Rx + Tx 256–511 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A074h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.3.5 Rx + Tx 512–1023 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A078h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.3.6 Rx + Tx 1024_Up Octet Frames (Offset = 3A07Ch)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.3.7 Net Octets (Offset = 3A080h)
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.4 1765
- 13.2.1.4.6.18.1
Rx-only Statistics Descriptions
- 13.2.1.4.6.1
Address Lookup Engine (ALE)
- 13.2.1.4.7
Common Platform Time Sync (CPTS)
- 13.2.1.4.7.1 CPTS Architecture
- 13.2.1.4.7.2 CPTS Initialization
- 13.2.1.4.7.3 32-bit Time Stamp Value
- 13.2.1.4.7.4 64-bit Time Stamp Value
- 13.2.1.4.7.5 64-Bit Timestamp Nudge
- 13.2.1.4.7.6 64-bit Timestamp PPM
- 13.2.1.4.7.7 Event FIFO
- 13.2.1.4.7.8 Timestamp Compare Output
- 13.2.1.4.7.9 Timestamp Sync Output
- 13.2.1.4.7.10 Timestamp GENFn Output
- 13.2.1.4.7.11 Timestamp ESTFn
- 13.2.1.4.7.12 Time Sync Events
- 13.2.1.4.7.13 Timestamp Compare Event
- 13.2.1.4.7.14 Host Transmit Event
- 13.2.1.4.7.15 CPTS Interrupt Handling
- 13.2.1.4.8 CPDMA Host Interface
- 13.2.1.4.9 CPPI Checksum Offload
- 13.2.1.4.10 Egress Packet Operations
- 13.2.1.4.11 MII Management Interface (MDIO)
- 13.2.1.5 CPSW0 Programming Guide
- 13.2.1
Gigabit Ethernet Switch (CPSW)
- 13.3
Memory Interfaces
- 13.3.1
General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 13.3.1.1 GPMC Overview
- 13.3.1.2 GPMC Environment
- 13.3.1.3 GPMC Integration
- 13.3.1.4
GPMC Functional Description
- 13.3.1.4.1 GPMC Block Diagram
- 13.3.1.4.2 GPMC Clock Configuration
- 13.3.1.4.3 GPMC Power Management
- 13.3.1.4.4 GPMC Interrupt Requests
- 13.3.1.4.5 GPMC Interconnect Port Interface
- 13.3.1.4.6 GPMC Address and Data Bus
- 13.3.1.4.7
GPMC Address Decoder and Chip-Select Configuration
- 13.3.1.4.7.1 Chip-Select Base Address and Region Size
- 13.3.1.4.7.2 Access Protocol
- 13.3.1.4.7.3
External Signals
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1
WAIT Pin Monitoring Control
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1.1 Wait Monitoring During Asynchronous Read Access
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1.2 Wait Monitoring During Asynchronous Write Access
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1.3 Wait Monitoring During Synchronous Read Access
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1.4 Wait Monitoring During Synchronous Write Access
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1.5 Wait With NAND Device
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1.6 Idle Cycle Control Between Successive Accesses
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1.7 Slow Device Support (TIMEPARAGRANULARITY Parameter)
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.2 DIR Pin
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.3 Reset
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.4 Write Protect Signal (nWP)
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.5 Byte Enable (nBE1/nBE0)
- 13.3.1.4.7.3.1
WAIT Pin Monitoring Control
- 13.3.1.4.7.4 Error Handling
- 13.3.1.4.8
GPMC Timing Setting
- 13.3.1.4.8.1 Read Cycle Time and Write Cycle Time (RDCYCLETIME / WRCYCLETIME)
- 13.3.1.4.8.2 nCS: Chip-Select Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (CSONTIME / CSRDOFFTIME / CSWROFFTIME / CSEXTRADELAY)
- 13.3.1.4.8.3 nADV/ALE: Address Valid/Address Latch Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (ADVONTIME / ADVRDOFFTIME / ADVWROFFTIME / ADVEXTRADELAY/ADVAADMUXONTIME/ADVAADMUXRDOFFTIME/ADVAADMUXWROFFTIME)
- 13.3.1.4.8.4 nOE/nRE: Output Enable/Read Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (OEONTIME / OEOFFTIME / OEEXTRADELAY / OEAADMUXONTIME / OEAADMUXOFFTIME)
- 13.3.1.4.8.5 nWE: Write Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (WEONTIME / WEOFFTIME / WEEXTRADELAY)
- 13.3.1.4.8.6 GPMC_CLKOUT
- 13.3.1.4.8.7 GPMC Output Clock and Control Signals Setup and Hold
- 13.3.1.4.8.8 Access Time (RDACCESSTIME / WRACCESSTIME)
- 13.3.1.4.8.9 Page Burst Access Time (PAGEBURSTACCESSTIME)
- 13.3.1.4.8.10 Bus Keeping Support
- 13.3.1.4.9
GPMC NOR Access Description
- 13.3.1.4.9.1 Asynchronous Access Description
- 13.3.1.4.9.2 Synchronous Access Description
- 13.3.1.4.9.3
Asynchronous and Synchronous Accesses in non-multiplexed Mode
- 13.3.1.4.9.3.1 Asynchronous Single-Read Operation on non-multiplexed Device
- 13.3.1.4.9.3.2 Asynchronous Single-Write Operation on non-multiplexed Device
- 13.3.1.4.9.3.3 Asynchronous Multiple (Page Mode) Read Operation on non-multiplexed Device
- 13.3.1.4.9.3.4 Synchronous Operations on a non-multiplexed Device
- 13.3.1.4.9.4 Page and Burst Support
- 13.3.1.4.9.5 System Burst vs External Device Burst Support
- 13.3.1.4.10 GPMC pSRAM Access Specificities
- 13.3.1.4.11
GPMC NAND Access Description
- 13.3.1.4.11.1
NAND Memory Device in Byte or 16-bit Word Stream Mode
- 13.3.1.4.11.1.1 Chip-Select Configuration for NAND Interfacing in Byte or Word Stream Mode
- 13.3.1.4.11.1.2 NAND Device Command and Address Phase Control
- 13.3.1.4.11.1.3 Command Latch Cycle
- 13.3.1.4.11.1.4 Address Latch Cycle
- 13.3.1.4.11.1.5 NAND Device Data Read and Write Phase Control in Stream Mode
- 13.3.1.4.11.1.6 NAND Device General Chip-Select Timing Control Requirement
- 13.3.1.4.11.1.7 Read and Write Access Size Adaptation
- 13.3.1.4.11.2 NAND Device-Ready Pin
- 13.3.1.4.11.3
ECC Calculator
- 13.3.1.4.11.3.1 Hamming Code
- 13.3.1.4.11.3.2
BCH Code
- 13.3.1.4.11.3.2.1 Requirements
- 13.3.1.4.11.3.2.2
Memory Mapping of BCH Codeword
- 3.1.4.11.3.2.2.1 Memory Mapping of Data Message
- 3.1.4.11.3.2.2.2 Memory-Mapping of the ECC
- 3.1.4.11.3.2.2.3
Wrapping Modes
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.1 Manual Mode (0x0)
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.2 Mode 0x1
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.3 Mode 0xA (10)
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.4 Mode 0x2
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.5 Mode 0x3
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.6 Mode 0x7
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.7 Mode 0x8
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.8 Mode 0x4
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.9 Mode 0x9
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.10 Mode 0x5
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.11 Mode 0xB (11)
- 1.4.11.3.2.2.3.12 Mode 0x6
- 13.3.1.4.11.3.2.3 Supported NAND Page Mappings and ECC Schemes
- 13.3.1.4.11.4
Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine
- 13.3.1.4.11.4.1 General Facts About the Engine Configuration
- 13.3.1.4.11.4.2 Prefetch Mode
- 13.3.1.4.11.4.3 FIFO Control in Prefetch Mode
- 13.3.1.4.11.4.4 Write-Posting Mode
- 13.3.1.4.11.4.5 FIFO Control in Write-Posting Mode
- 13.3.1.4.11.4.6 Optimizing NAND Access Using the Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine
- 13.3.1.4.11.4.7 Interleaved Accesses Between Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine and Other Chip-Selects
- 13.3.1.4.11.1
NAND Memory Device in Byte or 16-bit Word Stream Mode
- 13.3.1.4.12 GPMC Memory Regions
- 13.3.1.4.13 GPMC Use Cases and Tips
- 13.3.1.5 GPMC Basic Programming Model
- 13.3.2 Error Location Module (ELM)
- 13.3.3
Multimedia Card (MMC)
- 13.3.3.1 Introduction
- 13.3.3.2 Integration
- 13.3.3.3
Functional Description
- 13.3.3.3.1 MMC/SD/SDIO Functional Modes
- 13.3.3.3.2 Resets
- 13.3.3.3.3 Power Management
- 13.3.3.3.4 Interrupt Requests
- 13.3.3.3.5 DMA Modes
- 13.3.3.3.6 Mode Selection
- 13.3.3.3.7 Buffer Management
- 13.3.3.3.8 Transfer Process
- 13.3.3.3.9 Transfer or Command Status and Error Reporting
- 13.3.3.3.10 Transfer Stop
- 13.3.3.3.11 Output Signals Generation
- 13.3.3.3.12 CE-ATA Command Completion Disable Management
- 13.3.3.3.13 Test Registers
- 13.3.3.3.14 MMC/SD/SDIO Hardware Status Features
- 13.3.3.4 Low-Level Programming Models
- 13.3.4 Quad Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI)
- 13.3.1
General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 13.4
Industrial and Control Interfaces
- 13.4.1
Modular Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 13.4.1.1 MCAN Overview
- 13.4.1.2 MCAN Environment
- 13.4.1.3 MCAN Integration
- 13.4.1.4
MCAN Functional Description
- 13.4.1.4.1 Module Clocking Requirements
- 13.4.1.4.2 Interrupt and DMA Requests
- 13.4.1.4.3
Operating Modes
- 13.4.1.4.3.1 Software Initialization
- 13.4.1.4.3.2 Normal Operation
- 13.4.1.4.3.3 CAN FD Operation
- 13.4.1.4.3.4 Transmitter Delay Compensation
- 13.4.1.4.3.5 Restricted Operation Mode
- 13.4.1.4.3.6 Bus Monitoring Mode
- 13.4.1.4.3.7 Disabled Automatic Retransmission (DAR) Mode
- 13.4.1.4.3.8 Power Down (Sleep Mode)
- 13.4.1.4.3.9 Test Modes
- 13.4.1.4.4 Timestamp Generation
- 13.4.1.4.5 Timeout Counter
- 13.4.1.4.6 ECC Support
- 13.4.1.4.7 Rx Handling
- 13.4.1.4.8 Tx Handling
- 13.4.1.4.9 FIFO Acknowledge Handling
- 13.4.1.4.10 Message RAM
- 13.4.1.5 MCAN Programming Guide
- 13.4.2
Local Interconnect Network (LIN)
- 13.4.2.1 LIN Overview
- 2161
- 13.4.2.2 LIN Integration
- 13.4.2.3 Serial Communications Interface Module
- 13.4.2.4
Local Interconnect Network Module
- 13.4.2.4.1
LIN Communication Formats
- 13.4.2.4.1.1 LIN Standards
- 13.4.2.4.1.2 Message Frame
- 13.4.2.4.1.3 Synchronizer
- 13.4.2.4.1.4 Baud Rate
- 13.4.2.4.1.5 Header Generation
- 13.4.2.4.1.6 Extended Frames Handling
- 13.4.2.4.1.7 Timeout Control
- 13.4.2.4.1.8 TXRX Error Detector (TED)
- 13.4.2.4.1.9 Message Filtering and Validation
- 13.4.2.4.1.10 Receive Buffers
- 13.4.2.4.1.11 Transmit Buffers
- 13.4.2.4.2 LIN Interrupts
- 13.4.2.4.3 Servicing LIN Interrupts
- 13.4.2.4.4 LIN DMA Interface
- 13.4.2.4.5 LIN Configurations
- 13.4.2.4.1
LIN Communication Formats
- 13.4.2.5 Low-Power Mode
- 13.4.2.6 Emulation Mode
- 13.4.2.7 LIN Programming Guide
- 13.4.1
Modular Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 13.5 Timer Modules
- 13.6
Internal Diagnostics Modules
- 13.6.1 Dual Clock Comparator (DCC)
- 13.6.2 ECC Aggregator
- 13.6.3
Error Signaling Module (ESM)
- 13.6.3.1 ESM Overview
- 13.6.3.2 ESM Features
- 13.6.3.3 ESM Integration
- 13.6.3.4 ESM Functional Description
- 13.6.4
Memory Cyclic Redundancy Check (MCRC) Controller
- 13.6.4.1 MCRC Overview
- 13.6.4.2 MCRC Integration
- 13.6.4.3
MCRC Functional Description
- 13.6.4.3.1 MCRC Block Diagram
- 13.6.4.3.2 MCRC General Operation
- 13.6.4.3.3 MCRC Modes of Operation
- 13.6.4.3.4 PSA Signature Register
- 13.6.4.3.5 PSA Sector Signature Register
- 13.6.4.3.6 CRC Value Register
- 13.6.4.3.7 Raw Data Register
- 13.6.4.3.8 Example DMA Controller Setup
- 13.6.4.3.9 Pattern Count Register
- 13.6.4.3.10 Sector Count Register/Current Sector Register
- 13.6.4.3.11 Interrupts
- 13.6.4.3.12 Power Down Mode
- 13.6.4.3.13 Emulation
- 13.6.4.4 MCRC Programming Examples
- 13.6.5
Self-Test Controller (STC)
- 13.6.5.1 STC Overview
- 13.6.5.2 Block Diagram
- 13.6.5.3
Module Description
- 13.6.5.3.1 ROM Interface
- 13.6.5.3.2 FSM and Sequence Control
- 13.6.5.3.3 Register Block
- 13.6.5.3.4 VBUSP Interface
- 13.6.5.3.5 STC Flow
- 13.6.5.3.6 Programming Sequence
- 13.6.5.3.7
ROM Organization
- 13.6.5.3.7.1 TR_T: Transition Delay Methodology Type
- 13.6.5.3.7.2 FT: Fault Model for the BIST Run
- 13.6.5.3.7.3 SEG_ID[1:0]
- 13.6.5.3.7.4 Pattern Count ( patt_count[9:0] )
- 13.6.5.3.7.5 MISR_GOLDEN[895:0]: Golden Signature Data Bits
- 13.6.5.3.7.6 LP_MISR_GOLDEN[895:0]: Low Power Mode Golden Signature Data Bits
- 13.6.5.3.7.7 INV_MISR_GOLDEN[895:0]: Inverse Mode Golden Signature Data Bits
- 13.6.5.3.7.8 LP_INV_MISR_GOLDEN[895:0]: Low Power Inverse Mode Golden Signature Data Bits
- 13.6.5.3.7.9 Pn_SDm[7:0] (n - no. of patterns, m - scan chain length): OP-MISR Scan Data
- 13.6.6 Programmable Built-In Self-Test (PBIST) Module
- 13.1
General Connectivity Peripherals
-
14On-Chip Debug
- 14.1
On-Chip Debug
- 14.1.1 On-Chip Debug Overview
- 14.1.2 On-Chip Debug Features
- 14.1.3 On-Chip Debug Functional Description
- 14.1.4 Arm Debug Links
- 14.1
On-Chip Debug
- Revision History
7.4.10 Crossbar (XBAR)
The crossbars (referred to as XBAR throughout this chapter) provide flexibility to connect device inputs, outputs, and internal resources in a variety of configurations.
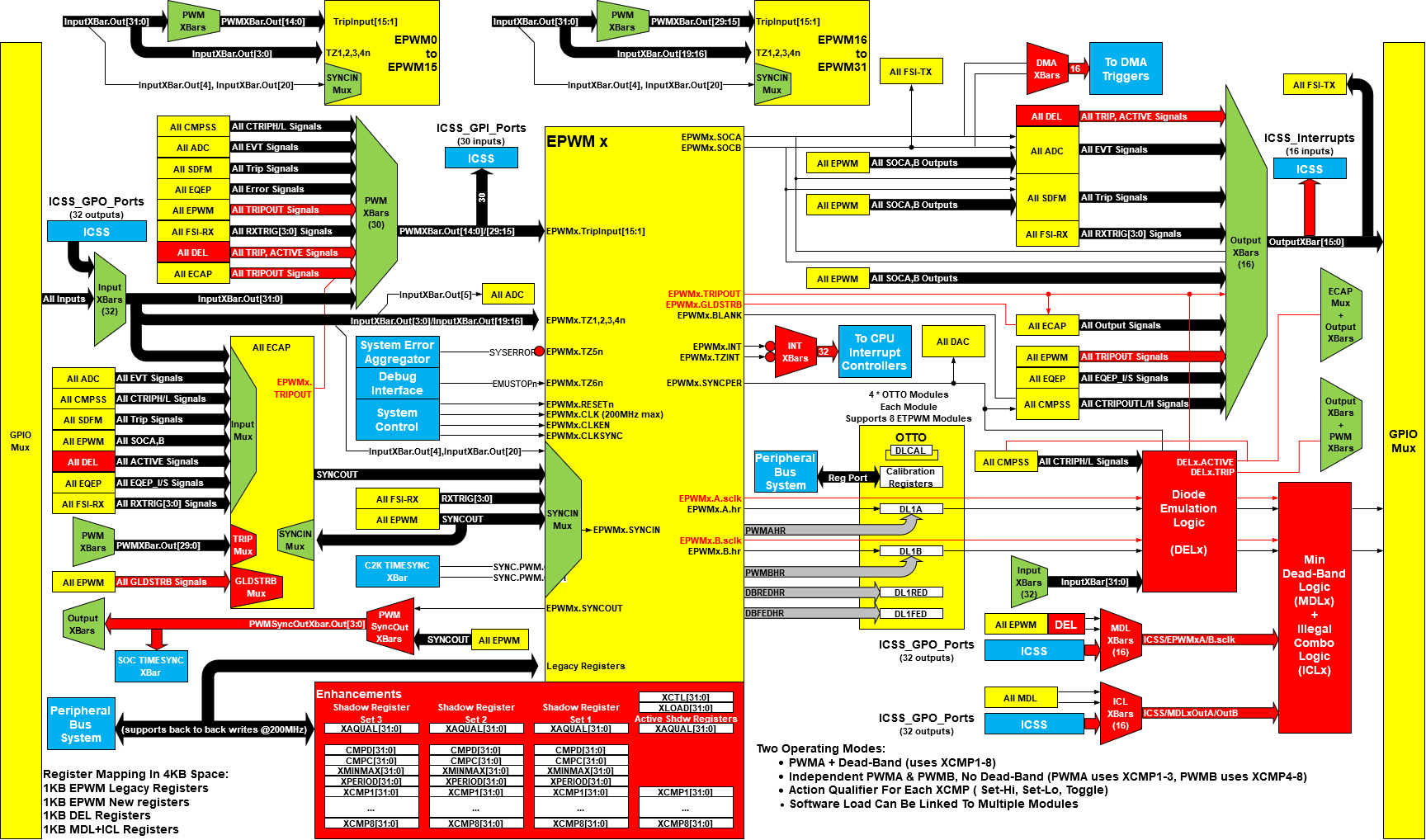 Figure 7-339 CONTROLSS XBAR Diagram
Figure 7-339 CONTROLSS XBAR DiagramThe real time control subsystem contains a total of eight XBARs:
- INPUT XBAR
- PWM XBAR
- MDL XBAR
- ICL XBAR
- INT XBAR
- DMA XBAR
- OUTPUT XBAR
- PWM SyncOut XBAR
Each of the XBARs is named according to signal destination it routes its inputs. For example, the INPUT XBAR brings external signals "in" to the device. The OUTPUT XBAR takes internal signals "out" of the device to a GPIO. The PWM XBAR takes the signal to the trip inputs of the PWM. Similarly, the Diode Emulation logic synchronous values are routed to the Min Dead-Band logic (MDL) and Illegal Combo logic (ICL) of the PWMs via the MDL XBAR and the ICL XBAR respectively. The INT XBAR routes the large quantity of real-time CONTROLSS interrupts efficiently to the SoC interrupt controller. The DMA XBARs route DMA requests from the real-time CONTROLSS to the SOC EDMA module. Both the INT XBAR and DMA XBAR limit the number of interrupt and DMA requests going from CONTROLSS to the SOC. The PWMSYNCOUTXBAR routes all the PWM synchronous outputs to SoC TIMESYNC logic and to the OUTPUT XBAR.
Further details about each of these XBARs can be found in the following sections.