SSZT200 january 2021 ADC128S102QML-SP , DAC121S101QML-SP , INA901-SP , LMP7704-SP , MSP430FR5969-SP , TMP461-SP

Because satellites on space missions are inaccessible once launched, acquiring accurate telemetry data to monitor the state of health of the satellite sub-systems can help set a baseline to indicate a working system, while fluctuations can indicate failures. Two examples of sensitive components would require accurate monitoring of voltage, temperature and current are the radio-frequency (RF) power amplifiers and thermoelectric coolers. In both applications, performance fluctuates with temperature and radiation effects, and requires adjustments to the applied voltage and current in order to ensure efficient and safe operation. A telemetry circuit monitors critical system power rails and components, gathers performance data (which has value both now and for future satellite designs) and adjusts system settings accordingly.
The most significant blocks of a telemetry circuit (shown in Figure 1) are the analog front end (AFE) that senses the power supply rails and temperature, the main processor that analyzes the data and the output signals needed to adjust different system parameters.
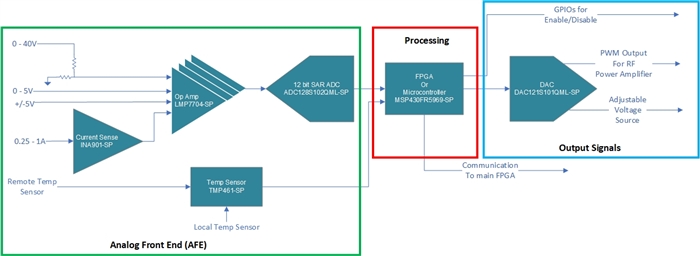 Figure 1 Telemetry circuit block
diagram AFE (green), processing (red), and output signals (blue)
Figure 1 Telemetry circuit block
diagram AFE (green), processing (red), and output signals (blue)AFE voltage, current and temperature sensing
| Accurately monitor temperature, voltage and current in space applications | |
|
Download our reference design, Versatile satellite health monitoring and control platform with <1% accuracy. |
Current sensing can determine faults on any sensitive power rails and flag the main processor of the power rails that need to be shut off to prevent damaging the field-programmable gate array (FPGA) or data converters. The current data collected can help determine whether devices in the system are drawing more current than expected, indicating a possible radiation-induced latch-up. With its wide bandwidth, the INA901-SP current-sense amplifier can provide accurate current measurements to help set a baseline for the power rails, while also reacting quickly in the event of a sudden failure such as a short circuit.
Temperature measurement of devices or the circuit board can help determine if components are working properly. Overheating can be a key indicator of an FPGA or power module being over stressed, reducing the runtime of the device. Other devices like the RF power amplifier are sensitive to temperature fluctuations and requires proper voltage adjustment to counteract the temperature changes. To measure theses temperatures, the TMP461-SP digital-output temperature sensor can provide both local and remote temperature sensing, monitoring the integrated internal temperature diodes of sensitive devices such as FPGAs and high-speed data converters. In addition to the sensing these diodes, the TMP461-SP also includes an internal sensor that can measure the temperature at its location on the board. Placing the device next to other sensitive components, like a RF power amplifier, enables the TMP461-SP to monitor their temperature.
Processing telemetry data: FPGAs vs. MCUs
System recalibration
Conclusion
Additional Resources:
- Watch our video series on how to design the input driver circuitry for a SAR ADC