SSZTAB2 march 2017 LMG3410R070 , LMG5200

IHS recently reported that “the world market for merchant power supplies rose 7.7 percent year over year to reach $23.5 billion in 2016.” Although the number and ratings of power supplies were not reported, this amounts to a huge amount of energy processed each year. It comes as no surprise that the industry is continuously looking for ways to increase power efficiency and density. Higher efficiency not only saves on electrical bills, but also lowers other operational expenses such as cooling.
Gallium nitride (GaN) enables a new generation of power conversion designs not possible before. These designs allow systems to reach unprecedented levels of power density and efficiency while delivering the reliability and the ruggedness that the power supply engineers expect. GaN-based solutions can be incorporated into power supplies throughout data centers, from the AC mains to the individual points of load (POLs). GaN also enables new architectures such as high-voltage DC distribution systems.
Figure 1 illustrates the major blocks of power supplies in today’s systems.
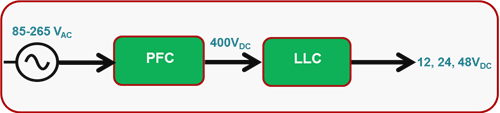 Figure 1 Typical AC/DC Isolated Power
Supply
Figure 1 Typical AC/DC Isolated Power
SupplyElectric utilities require a power-factor-correction (PFC) stage in order to optimize power-grid efficiency. PFC operates as a boost converter, and typically provides a DC output voltage of 380V. This voltage needs to be further stepped down to provide a DC bus supply for the system. Various topologies are used for this stage, but inductor-inductor-capacitor (LLC) and phase-shifted full bridge are commonly used to generate a bus voltage of 12V or 48V. This bus voltage is routed throughout the system, and undergoes multiple conversion steps to power various POLs such as processors, field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), memory and storage.
GaN-based solutions, shown in the figure below, fundamentally change both the architecture and density of the entire power system, from the AC to the processors. Let’s break it down.
- PFC: By enabling a totem-pole topology, GaN devices such as the integrated Texas Instruments LMG3410 reduce the number of active power switches and filter inductors by 50%. A great example of such solution is the new Highly Efficient, 1.6kW High Density GaN Based 1MHz CrM Totem-pole PFC Converter Reference Design. At 252.11 W/in3 of power density, this critical conduction mode [CRM] PFC design operates at 1MHz, as compared to 50 KHz silicon-based solution. This also significantly reduces the size of magnetics while improving overall efficiency to over 99% at 1600W, versus 96% for today’s best-in-class power supplies.
- LLC: The DC/DC stage takes advantage of GaN’s superior switching characteristics to push the resonant converter to over 1MHz. The high frequency reduces the magnetics while improving power density and efficiency. The smaller form factor further enables the emerging high-voltage distribution systems in data centers for 380V-to-48V converters.
- POL DC/DC: GaN devices, such as LMG5200, enable a single step conversion from 48V in order to power processors, memories and other loads directly, reducing component counts on precious printed circuit board (PCB) real estate by as much as 50% while reducing footprints by 75%.
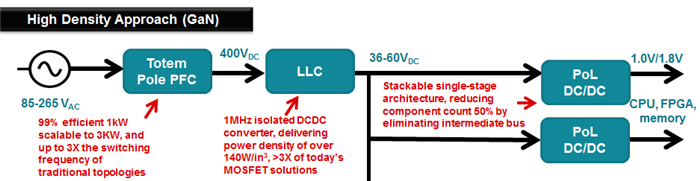
The days of GaN being viewed as a future technology are over. GaN is here now and is enabling designers to do what was once unreachable: design new power systems that are substantially smaller, switch faster and are cooler than ever before.
Discover more about TI GaN solutions TI’s booth (No. 501) at the Applied Power Electronics Conference (APEC), March 4-8 in San Antonio, Texas.
Additional Resources:
- Get started by downloading guides and schematics for these new reference designs: