TIDUE53I march 2018 – july 2023 TMS320F28P550SG , TMS320F28P550SJ , TMS320F28P559SJ-Q1
- 1
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 6
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
-
3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 3.1 Required Hardware and Software
- 3.2 Testing and Results
- 4Design Files
- 5Trademarks
- 6About the Authors
- 7Revision History
2.3.2 Voltage Sensing
Voltage sensing happens at two points in the inverter signal path to aid in control: before and after the primary output relay. By enabling measurement on both sides of the relay, the control system can lock into the grid voltage and frequency before connecting, thus preventing any mismatch issues.
Both sensing topologies are similar. First, PGND is used as a virtual neutral using a resistor network. On the grid side of the relay, only neutral is used. The high voltage signal is attenuated using a series of large value resistances. An offset of 1.65 V is added to the attenuated neutral point to center the voltage signal in the middle of the input range of the OPA4350, and the attenuated value from the phase voltage is measured. Figure 2-36 shows this sensing arrangement.
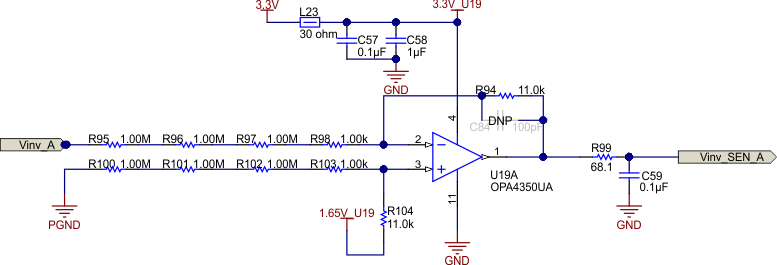 Figure 2-36 High-Voltage Sensing Signal Path
Figure 2-36 High-Voltage Sensing Signal Path