TIDUE90 July 2018
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- Design Images
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3Hardware, Software, Test Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design Files
- 5Software Files
- 6Related Documentation
- 7About the Author
3.2.1.2 Continuous Water Spray Test
Test Setup
The test setup is similar to the continuous water flow test in Section 3.2.1.1. The difference is a spray nozzle added on the plastic water tube to provide a continuous water spray on the touch sensor area (see Figure 20).
 Figure 20. Continuous Water Spray Test Setup
Figure 20. Continuous Water Spray Test Setup Test Procedures
The test procedures are the same as the continuous water flow testing (see Section 3.2.1.1).
Test Result
Figure 21 shows the sensor measurement count result. The result is similar to the continuous water flow test result (see Section 3.2.1.1). The difference is that when the continuous water spray is applied on the touch sensor area, the measurement count is not as consistent as the continuous water flow test case. This is because the spray water does not contact the touch sensor area consistently. The "negative touch" behavior is still present, which means that the spray water causes the measurement result to go in the opposite direction of a touch event. Therefore, there is no false touch detection. While the continuous water spray is applied on the touch sensor area, each touch event still causes a distinguishable count increase for the touched button. Based on this test result and by using the dominant button lock algorithm (see Section 3.1.2), the system can reliably operate when exposed to continuous water spray, with no false touch detections and with accurate detection of a button touch.
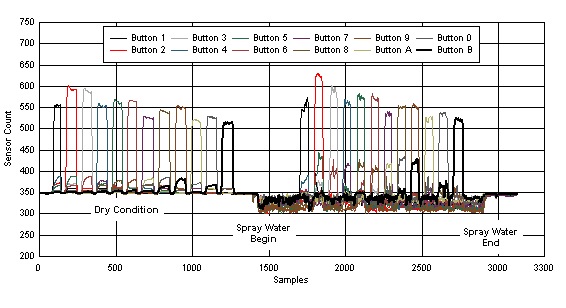 Figure 21. Sensor Count Result With Continuous Water Spray (Well Grounded Power Supply)
Figure 21. Sensor Count Result With Continuous Water Spray (Well Grounded Power Supply)