-
DC+ Bus Power-Supply Solution Using Bootstrap Charge Pump Technique
DC+ Bus Power-Supply Solution Using Bootstrap Charge Pump Technique
Trademarks
PSpice are registered trademarks of Cadence Design Systems, Inc..
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
1 Background
Fault-detection mechanisms are a necessity in high-power industrial systems such as motor drives and solar inverters, as well as automotive systems including electric vehicle (EV) chargers, traction inverters, onboard chargers and DC/DC converters. DC bus-based overcurrent protection is widely used in electric motor drives. The traditional implementation of overcurrent (OC) fault detection is discrete with a combination of non-isolated multichannel comparators and either optocouplers or digital isolators. To meet the growing needs of fault detection, TI is introducing a new family of basic and reinforced isolated comparators to the TI isolation portfolio. The primary use case is ultra-fast overcurrent, overvoltage, over temperature detection in high-voltage industrial and automotive HEV/EV systems. Its smaller PCB area is particularly suitable for applications with miniaturization and high-power density needs. Compared with traditional solutions, it has significant advantages in CMTI, response time, threshold accuracy, hysteresis, and latching function.
The power supply on DC+ for overcurrent protection can be generating by either adding a transformer or adding an additional secondary winding to an existing transformer. However, technical challenges such as transformer size limitations or the proximity of these transformers to the actual OC implementation will practically limit such a transformer-based implementation.
2 Overcurrent Protection on DC+
Figure 2-1 shows how the OC protection based on the DC+ bus can protect three short-circuit situations: a shoot-through fault of IGBT (blue), DC+ ground fault (red), and phase-to-phase short fault (yellow).
Figure 2-1 DC+ Overcurrent Protection
Adding an isolated comparator such as a single threshold comparator AMC23C11 for OC detection ensures appropriate detection and protection of power circuits from these three conditions. The dual-threshold version (AMC23C14) can achieve both short circuit and overload protection.
As there is no need for a power supply on DC+ other than for an isolated comparator, a simple, low-cost, and low BOM implementation is critical.
3 DC+ Power Supply Solution
Figure 3-1 shows the implementation of a DC+ power supply.
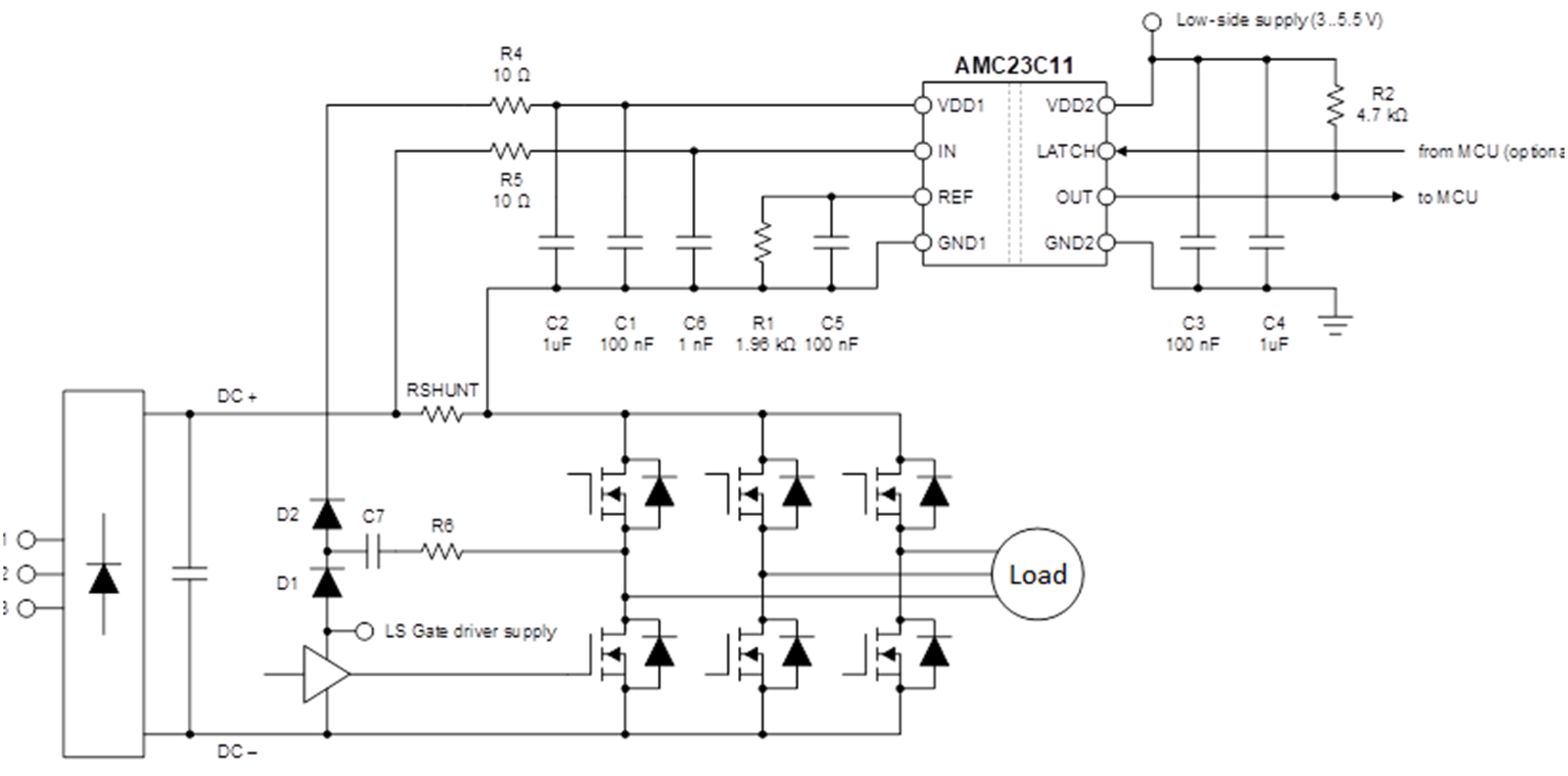
Figure 3-1 DC+ Power Supply Solution
The DC+ power supply solution consists of two parts. The first part is a bootstrap circuit consisting of a high-voltage diode D1, a capacitor C7 and current-limiting resistor R6. C7 is charged by the low-side gate driver power supply. The second part is a charge pump consisting of a high-voltage diode D2, a capacitor C2 and current-limiting resistor R4. When the half bridge starts to operate there are three operating states as follows:
- When the low-side IGBT turns on, C7 is charged by the power supply of the low-side gate driver and D2 is turned off.
- When the high-side IGBT turns on, D2 conducts, C7 charges the isolated comparator and capacitor C2.
- When the low-side IGBT turns on again, C7 is charged by the low-side power supply and C2 continues to supply power to the isolated comparator.
In summary, this charge-pump based bootstrap circuit provides power to the isolated comparators with the help of energy stored in capacitors C7 and C2 during the IGBT switch phases.
3.1 Selection of Charge Pump Capacitor
The selection of the two capacitors, C2 and C7, is important to minimize the ripple on the generated power supply. The following is an example to calculate the capacitor value under extreme conditions. The good news is that the integrated low-dropout (LDO) regulator on the high-side of the AMC23C11 eases the pre-regulation requirements of this power supply. As an example, this design is capable of taking a ripple voltage of 3 V, and other parameters are as follows:
- Half-bridge circuit switching frequency f = 1 kHz
- Duty cycle D = 20%
- Current required for isolated comparator I = 3.3 mA (max)
- Low-side driver supply U_low side = 15 V
Switching frequencies in motor drive systems are typically 1 kHz to 20 kHz. Lower switching frequencies result in larger ripple because of longer discharge times. Increasing the capacitance reduces the ripple but increases the charging time. Assume the switching frequency is 1 kHz and 20% duty cycle in the extreme case. This case means that the isolated comparator is powered only by the capacitor C2 of the charge pump for 80% of a PWM cycle, the minimum capacitance required for C2 under this condition is:
In this design, C2 takes a capacitance of 1 μF and the bootstrap capacitor C7 is also 1 μF. R4 and R6 limit the high currents that may occur during initial power-up. Typical values for this resistor are 5 Ω to 10 Ω. A larger resistance increases the time constant of the RC circuit and prolong the time to reach the minimum supply. When R4 is taken as 10 Ω, the maximum current at initial power-up is 1.36 A:
The two diodes D1 and D2 should be able to withstand the voltage of DC bus. For a motor drive system with a 380 VAC input, the diodes need to have a withstand voltage value ≥ 1200 V, and must have fast reverse recovery characteristics to minimize the recovery charge and thereby ensure the stability of the supply circuit. The circuit can theoretically generate a supply voltage of 13.6 V, which is 15 V minus the voltage drop of the two diodes (0.7 V).
3.2 Simulation in PSpice for TI
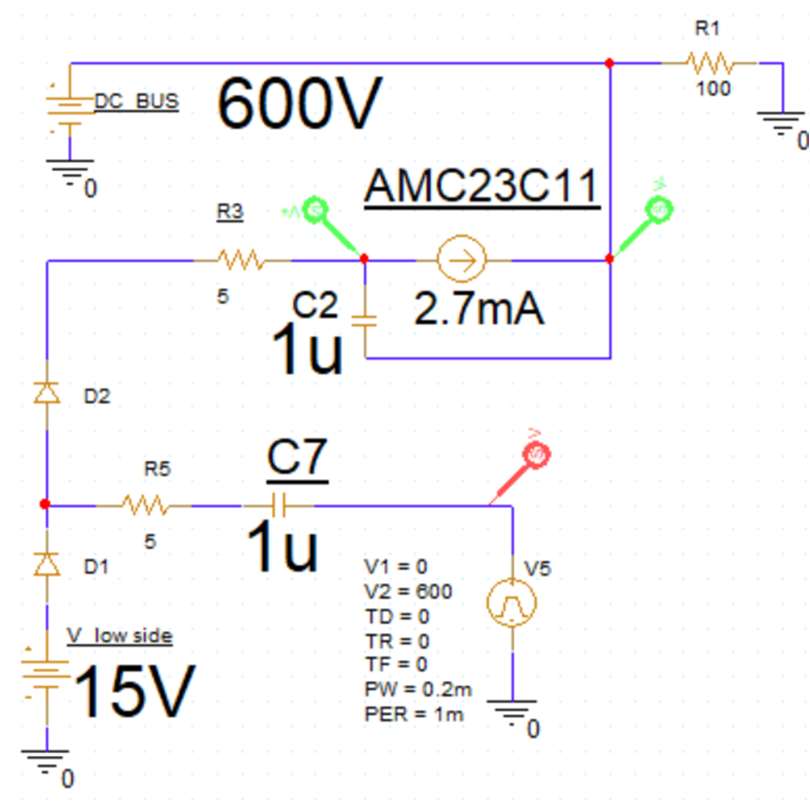
Figure 3-2 Simulation Model
The DC bus in the simulation model is 600 V, a 2.7-mA current source is used to simulate the isolated comparator, the square wave source V5 simulates the switch of the half bridge. The low-side supply is 15 V. Both capacitors, C2 and C7, are 1 μF and the current-limiting resistors R3 and R5 are 5 Ω.
The supply voltage of the isolated comparator (V_DC+) and the half-bridge center point voltage (V_half bridge) are measured at 1-kHz switching frequency and 20% duty cycle as Figure 3-3 shows.
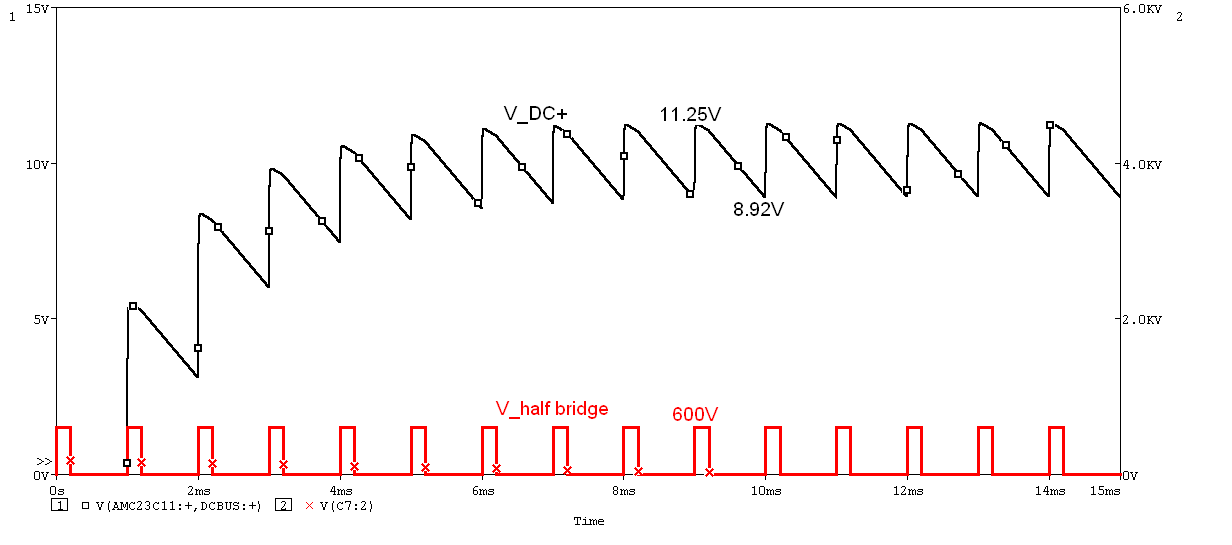
Figure 3-3 1 kHz, 20% Duty Cycle Power Supply
In Figure 3-3, the power supply is stabilized between 11.25 V and 8.92 V after a few PWM cycles, that is, there is a ripple of 2.33 V. Since the half-bridge circuit turns on the upper IGBT first in the first cycle, the isolated comparator is not powered until one cycle later, that is, the system is not protected from power-up short-circuit in the first cycle. An optimized solution to minimize risk is provided in Section 4.
Keeping the same switching frequency and duty cycle, increase the C2 and C7 simultaneous capacitance value from 1 μF to 30 μF gradually. This method reveals that the supply voltage gradually increases and gets closer to the ideal value (13.6 V), and the power supply ripple also decreases.
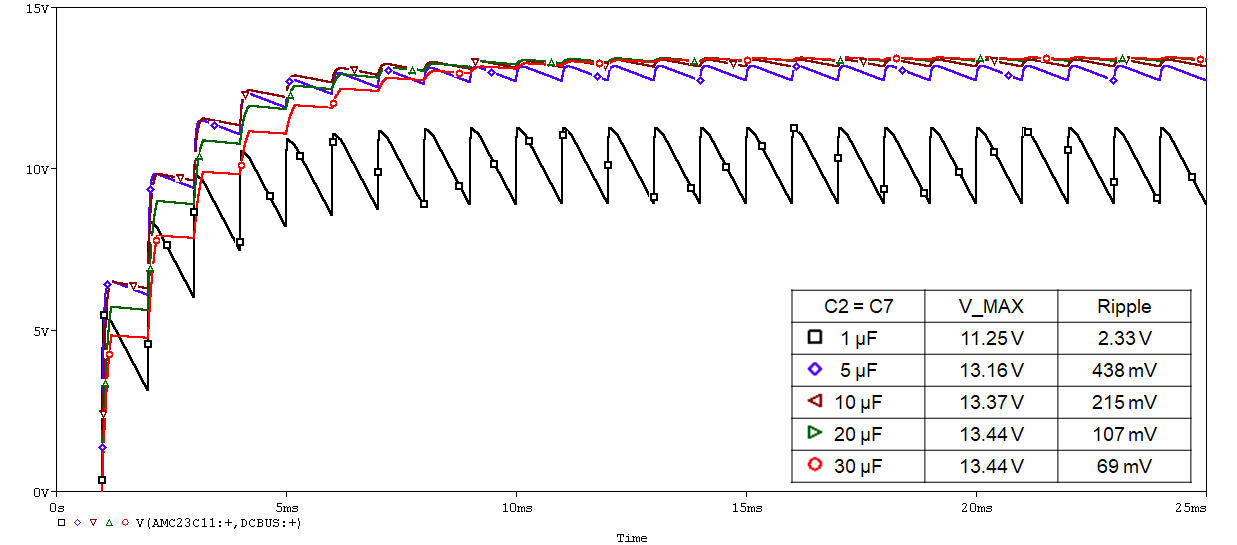
Figure 3-4 Increase Capacitor Value From 1 μF to 30 μF
In Figure 3-4, V_MAX is the maximum voltage value that can be achieved with a stable supply. Therefore, controlling the capacitance of the two capacitors above 5 μF to obtain a more stable supply voltage is recommended. But a capacitance value that is too large will also increase the charging time.