-
DP83TG720x-Q1Functional Safety FIT Rate, FMD and Pin FMA SFFS030 October 2024 DP83TC812R-Q1 , DP83TG720S-Q1
-
DP83TG720x-Q1Functional Safety FIT Rate, FMD and Pin FMA
DP83TG720x-Q1
Functional Safety FIT Rate, FMD and Pin
FMA
Trademarks
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
1 Overview
This document contains information for the DP83TG720S-Q1 and DP83TG720R-Q1 to aid in a functional safety system design. Information provided are:
- Functional safety failure in time (FIT) rates of the semiconductor component estimated by the application of industry reliability standards
- Component failure modes and their distribution (FMD) based on the primary function of the device
- Pin failure mode analysis (pin FMA)
Figure 1-1 shows the device functional block diagram for reference.
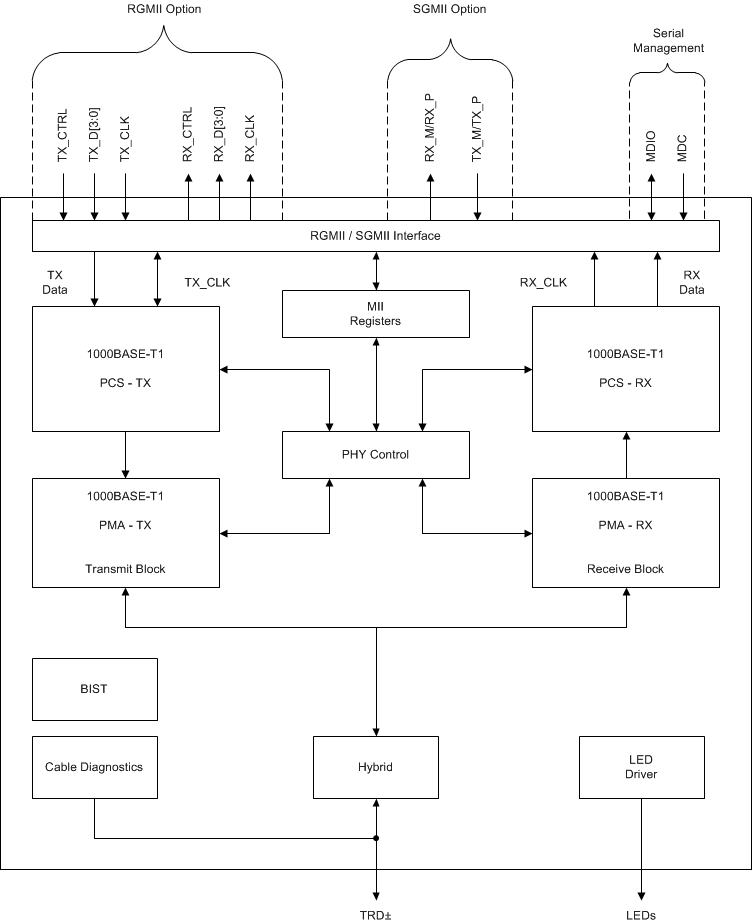 Figure 1-1 Functional Block
Diagram
Figure 1-1 Functional Block
DiagramThe DP83TG720S-Q1 and DP83TG720R-Q1 were developed using a quality-managed development process, but were not developed in accordance with the IEC 61508 or ISO 26262 standards.
2 Functional Safety Failure In Time (FIT) Rates
This section provides functional safety failure in time (FIT) rates for the DP83TG720S-Q1 and DP83TG720R-Q1 based on two different industry-wide used reliability standards:
- Table 2-1 provides FIT rates based on IEC TR 62380 / ISO 26262 part 11
- Table 2-2 provides FIT rates based on the Siemens Norm SN 29500-2
| FIT IEC TR 62380 / ISO 26262 | FIT (Failures Per 109 Hours) |
|---|---|
| Total component FIT rate | 26 |
| Die FIT rate | 3 |
| Package FIT rate | 23 |
The failure rate and mission profile information in Table 2-1 comes from the reliability data handbook IEC TR 62380 / ISO 26262 part 11:
- Mission profile: Motor control from table 11
- Power dissipation: 590mW
- Climate type: World-wide Table 8
- Package factor (lambda 3): Table 17b
- Substrate material: FR4
- EOS FIT rate assumed: 0 FIT
| Table | Category | Reference FIT Rate | Reference Virtual TJ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | CMOS, BICMOS Digital, analog or mixed | 70 FIT | 70°C |
The reference FIT rate and reference virtual TJ (junction temperature) in Table 2-2 come from the Siemens Norm SN 29500-2 tables 1 through 5. Failure rates under operating conditions are calculated from the reference failure rate and virtual junction temperature using conversion information in SN 29500-2 section 4.
3 Failure Mode Distribution (FMD)
The failure mode distribution estimation for the DP83TG720S-Q1 and DP83TG720R-Q1 in Table 3-1 comes from the combination of common failure modes listed in standards such as IEC 61508 and ISO 26262, the ratio of sub-circuit function size and complexity, and from best engineering judgment.
The failure modes listed in this section reflect random failure events and do not include failures resulting from misuse or overstress.
| Die Failure Modes | Failure Mode Distribution (%) |
|---|---|
| Fault in MDI transmitter causes IEEE specification compliance issues | 6 |
| Fault in MDI transmitter causes high RF emissions | 3 |
| Fault in MDI receiver causes poor link quality and poor link loss | 5 |
| Fault in internal power circuits causes poor link quality and higher power consumption | 7 |
| Fault in internal clock circuits cause IEEE compliance issues and poor link quality | 5 |
| Fault in GPIO causes higher RF emissions | 5 |
| Fault in GPIO causes RGMII, JEDEC, and data sheet specification violation | 4 |
| Fault in ESD on MDI makes IEC ESD performance lower than 8KV | 3 |
| Fault in ESD on GPIOs makes CDM performance lower than 2KV | 2 |
| Digital core has stuck or transient faults that cause link-up or PCS faults | 60 |