-
LM5168-Q1 and LM5169-Q1Functional Safety FIT Rate, FMD and Pin FMA
LM5168-Q1 and LM5169-Q1Functional Safety FIT Rate, FMD and Pin FMA
Trademarks
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
1 Overview
This document contains information for the LM5168-Q1 and LM5169-Q1 (SO PowerPAD package) to aid in a functional safety system design. Information provided are:
- Functional safety failure in time (FIT) rates of the semiconductor component estimated by the application of industry reliability standards
- Component failure modes and their distribution (FMD) based on the primary function of the device
- Pin failure mode analysis (pin FMA)
Figure 1-1 shows the device functional block diagram for reference.
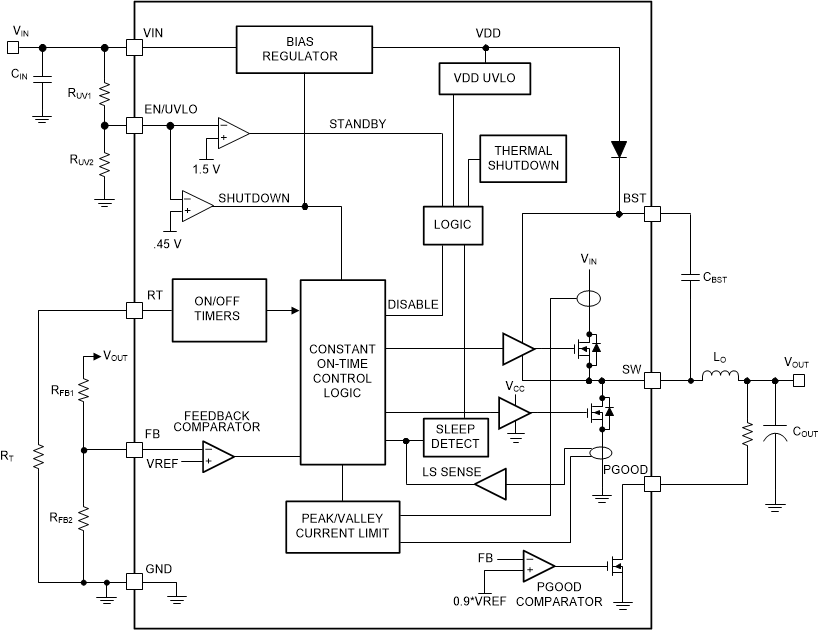 Figure 1-1 Functional Block
Diagram
Figure 1-1 Functional Block
DiagramThe LM5168-Q1 and LM5169-Q1 were developed using a quality-managed development process, but was not developed in accordance with the IEC 61508 or ISO 26262 standards.
2 Functional Safety Failure In Time (FIT) Rates
This section provides functional safety failure in time (FIT) rates for the LM5168-Q1 and LM5169-Q1 based on two different industry-wide used reliability standards:
- Table 2-1 provides FIT rates based on IEC TR 62380 / ISO 26262 part 11
- Table 2-2 provides FIT rates based on the Siemens Norm SN 29500-2
| FIT IEC TR 62380 / ISO 26262 | FIT (Failures Per 109 Hours) |
|---|---|
| Total component FIT rate | 13 |
| Die FIT rate | 5 |
| Package FIT rate | 8 |
The failure rate and mission profile information in Table 2-1 comes from the reliability data handbook IEC TR 62380 / ISO 26262 part 11:
- Mission profile: motor control from table 11
- Power dissipation: 500 mW
- Climate type: world-wide table 8
- Package factor (lambda 3): table 17b
- Substrate material: FR4
- EOS FIT rate assumed: 0 FIT
| Table | Category | Reference FIT Rate | Reference Virtual TJ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | CMOS/BICMOS, ASICs, Analog & Mixed HV > 50 V Supply | 30 FIT | 75°C |
The reference FIT rate and reference virtual TJ (junction temperature) in Table 2-2 come from the Siemens Norm SN 29500-2 tables 1 through 5. Failure rates under operating conditions are calculated from the reference failure rate and virtual junction temperature using conversion information in SN 29500-2 section 4.
3 Failure Mode Distribution (FMD)
The failure mode distribution estimation for the LM5168-Q1 and LM5169-Q1 in Table 3-1 comes from the combination of common failure modes listed in standards such as IEC 61508 and ISO 26262, the ratio of sub-circuit function size and complexity, and from best engineering judgment.
The failure modes listed in this section reflect random failure events and do not include failures resulting from misuse or overstress.
| Die Failure Modes | Failure Mode Distribution (%) |
|---|---|
| No SW Output | 45 |
| SW output not in specification - voltage or timing | 45 |
| SW driver stuck on | 5 |
| PGOOD false trip or fails to trip | 5 |
The FMD in Table 3-1 excludes short-circuit faults across the isolation barrier. Faults for short circuits across the isolation barrier can be excluded according to ISO 61800-5-2:2016 if the following requirements are fulfilled:
- The signal isolation component is OVC III according to IEC 61800-5-1. If a safety-separated extra low voltage (SELV) or protective extra low voltage (PELV) power supply is used, pollution degree 2 / OVC II applies. All requirements of IEC 61800-5-1:2007, 4.3.6 apply.
- Measures are taken to ensure that an internal failure of the signal isolation component cannot result in excessive temperature of its insulating material.
Apply creepage and clearance requirements according to the specific equipment isolation standards of an application. Care must be taken to maintain the creepage and clearance distance of a board design to ensure that the mounting pads of the isolator on the printed-circuit board do not reduce this distance.
4 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
This section provides a failure mode analysis (FMA) for the pins of the LM5168-Q1 and LM5169-Q1. The failure modes covered in this document include the typical pin-by-pin failure scenarios:
- Pin short-circuited to ground (see Table 4-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 4-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 4-4)
- Pin short-circuited to supply (see Table 4-5)
Table 4-2 through Table 4-5 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 4-1.
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality. |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality. |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation. |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance. |
Figure 4-1 shows the LM5168-Q1 and LM5169-Q1 pin diagram. For a detailed description of the device pins, see the Pin Configuration and Functions section in the LM5168-Q1 and LM5169-Q1 data sheet.
 Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram
Figure 4-1 Pin DiagramFollowing are the assumptions of use and the device configuration assumed for the pin FMA in this section:
- Device used within the Recommended Operating Conditions and the Absolute Maximum Ratings found in the LM5169-Q1/LM5168-Q1 0.65-A/0.3-A, 120-V, Step-Down Converter with Fly-Buck™ Converter Capability Data Sheet
- Configuration as shown in the Example Application Circuit found in the LM5169-Q1/LM5168-Q1 0.65-A/0.3-A, 120-V, Step-Down Converter with Fly-Buck™ Converter Capability Data Sheet.
- Valid for an ambient temperature of 25ºC.
- Faults applied after device start-up is complete.
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| GND | 1 | Normal operation | D |
| VIN | 2 | Input supply shorted to ground. No output voltage | B |
| EN/UVLO | 3 | No output voltage. Loss of EN/UVLO functionality | B |
| RT | 4 | No or low output voltage | B |
| FB | 5 | Output voltage increases to near input voltage level. Possible damage to load | B |
| PGOOD | 6 | Normal operation. Loss of PGOOD function | B |
| BST | 7 | No output voltage. Possible device damage | A |
| SW | 8 | No output voltage. Possible device damage | A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| GND | 1 | No output voltage | B |
| VIN | 2 | No output voltage | B |
| EN/UVLO | 3 | No output voltage. Loss of EN/UVLO functionality | B |
| RT | 4 | Output voltage out of regulation. Possible damage to load | B |
| FB | 5 | Output voltage out of regulation. Possible damage to load | B |
| PGOOD | 6 | Normal operation. Loss of PGOOD function | B |
| BST | 7 | No output voltage | B |
| SW | 8 | No output voltage | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GND | 1 | 2, VIN | No output voltage. Input supply shorted to ground. | B |
| VIN | 2 | 3, EN/UVLO | Normal operation. Loss of EN/UVLO functionality | B |
| EN/UVLO | 3 | 4, RT | No output voltage. Possible device damage | A |
| FB | 5 | 6, PGOOD | Output voltage out of regulation. Possible damage to load | B |
| PGOOD | 6 | 7, BST | No output voltage | B |
| BST | 7 | 8, SW | No output voltage | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| GND | 1 | Input supply shorted. No output voltage | B |
| VIN | 2 | Normal operation | D |
| EN/UVLO | 3 | Normal operation. EN/UVLO functionality lost | B |
| RT | 4 | No output voltage. Device damage | A |
| FB | 5 | No output voltage. Device damage | A |
| PGOOD | 6 | Loss of PGOOD functionality. Possible device damage | A |
| BST | 7 | No output voltage. Device damage | A |
| SW | 8 | Output voltage at level of input voltage. Damage to load. Possible device damage | A |