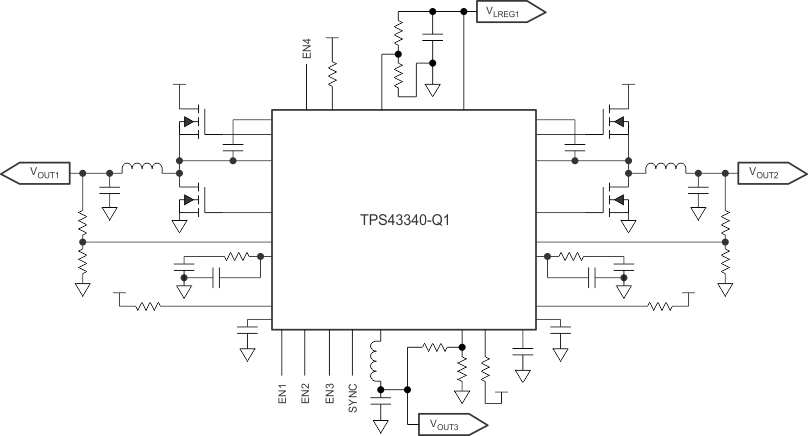
-
TPS43340-Q1 Low-IQ, 30-µA, High-VIN Quad-Output Power Supply
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
TPS43340-Q1 Low-IQ, 30-µA, High-VIN Quad-Output Power Supply
1 Features
- Qualified for Automotive Applications
- AEC-Q100 Test Guidance With the Following Results:
- Device Temperature Grade 1: –40°C to 125°C Ambient Operating Temperature
- Device HBM ESD Classification Level H1C
- Device CDM ESD Classification Level C3B
- Input Range up to 40 V, (Transients up to 60 V)
- Input Voltage Range: 4 V to 40 V
- Transients up to 60 V
- Dual-Output Synchronous Buck Controller
- Peak Gate Drive Current 0.6 A
- Automatic Low-Power Mode Operation
- Low-Power-Mode IQ : 30 µA (One Buck On), 35 µA (Two Bucks On)
- Low Shutdown Current, Ish = 5 μA Typical
- Single Synchronous Buck Regulator Converter BUCK3
- Max Output Current 2 A
- Linear Regulator LREG1
- Separate Enable Inputs (EN1, EN2, EN3, EN4)
- Internal Oscillator, Programmable via External Resistor, 150 kHz to 600 kHz for Switching Frequency fSW_BUCK1,2,3
- Integrated PLL, External Synchronization Frequency: 150 kHz to 600 kHz
- Switch-Mode Regulators Operate With 180° Phase-Shift
- Reset Output for All Output Rails
- Supply and Overvoltage Detection and Shutdown
- Thermally Enhanced PowerPAD™ Package
- 48-Pin HTQFP (PHP)
2 Applications
- Automotive Infotainment, Head Unit, Navigation, Audio and Clusters
- Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS)
- Automotive and Industrial Multi-Rail DC Power Distribution Systems
3 Description
The TPS43340-Q1 is a quad rail power supply featuring two synchronous Buck Controller with 0.6-A gate drive, one synchronous 2-A Buck Converter and a 300-mA LDO with low quiescent current. The device is designed to power the entire system including MCU and DSP straight from the car battery respectively input voltages up to 40 V. The device features integrated short-circuit and overcurrent protection on the gate-drive outputs for the buck regulator controllers and independent current-foldback control for each buck regulator supply during regulator output short to ground. Each output supply incorporates a soft start to ensure that on initial power up these regulated outputs are not in current limit. Implementation of reset delay on power up allows the outputs of Buck1, Buck2, Buck3 and the linear regulator to get to stable regulation. An external capacitor sets the delay to a maximum range of 300 ms. Each power-supply output has adjustable output voltage based on the external resistor-network settings. The device has sequencing control during power up and power down of the output rails, based on the enable-and-disable control or soft start.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| TPS43340-Q1 | HTQFP (48) | 7.00 mm × 7.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
4 Revision History
Changes from D Revision (July 2015) to E Revision
- Update the HBM ESD ratings and added the MM ESD rating back in the ESD Ratings table Go
Changes from C Revision (January 2013) to D Revision
- Added ESD Ratings table, Feature Description section, Device Functional Modes, Application and Implementation section, Power Supply Recommendations section, Layout section, Device and Documentation Support section, and Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information section Go
Changes from B Revision (April 2012) to C Revision
- Added bullets to top of Features listGo
- Appended missing "-Q1" to part numberGo
- Revised first-page schematicGo
- Added a sentence to the EXTSUP pin descriptionGo
- Changed "converter" to "controller" for pin SS2Go
- Deleted thermal characteristics from Recommended Operating Characteistics tableGo
- Added the Thermal Information tableGo
- Multiple changes throughout Electrical Characteristics tableGo
- Appended missing "-Q1" to part numberGo
- Changed the recommended capacitor valueGo
- Added a sentence to the second paragraph of the Gate-Driver Supply sectionGo
- Added new sentence to Gate-Driver Supply sectionGo
- Replaced the two paragraphs following Figure 15 with three new paragraphsGo
- Modified Equation 2Go
- Changed fSW-Trans-delay to tSW-Trans-delayGo
- Modified Equation 3Go
- Renamed VBUCKx to VOUTxGo
- Added (Farads) to Equation 4Go
- Changed "resistor" to "VOUT3"Go
- Revised Figure 18Go
- Changed "VBAT" to "VIN"Go
- Modified power-dissipation equationsGo
- Buck2 Component Selection, modified Equation 22, Equation 25, Equation 26, and Equation 29, Equation 31Go
- Added Equation 27, Equation 28, Equation 30, and Equation 32Go
- Buck3 Component Selection, modified Equation 34, Equation 36, Equation 37, and Equation 38,Go
- Added Equation 39, Equation 40, Equation 41, and Equation 43Go
- Modified several equations in Summary of Equations tableGo
Changes from A Revision (January 2012) to B Revision
- Changed Feedback input to Supply sense input in Abs Max Ratings table.Go
- Inserted Input voltage for Buck 2 information in the Recommended Operating Conditions table.Go
- Added VIN2SENSE = 4 V to 40 V in Electrical Characteristics table header.Go
- Changed Iq_LPM to Iq, changed LPM quiescent current to Quiescent current, and changed the conditions for EN in the Electrical Characteristics table.Go
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| BOOT1 | 48 | I | A capacitor on this pin acts as the voltage supply for the high-side N-channel MOSFET gate-drive circuitry in buck converter Buck1. When the buck is in a dropout condition, the device automatically reduces the duty cycle of the high-side MOSFET to approximately 95% on every fourth cycle to allow the capacitor to recharge. |
| BOOT2 | 37 | I | A capacitor on this pin acts as the voltage supply for the high-side N-channel MOSFET gate-drive circuitry in buck converter Buck2. When the buck is in a dropout condition, the device automatically reduces the duty cycle of the high-side MOSFET to approximately 95% on every fourth cycle to allow the capacitor to recharge. |
| BOOT3 | 14 | I | A capacitor between BOOT3 and PH3 acts as the voltage supply for the high-side N-channel MOSFET gate-drive circuitry in buck converter Buck3. When the buck is in a dropout condition, the device automatically reduces the duty cycle of the high-side MOSFET to approximately 95% on every fourth cycle to allow the capacitor to recharge. |
| COMP1 | 8 | O | Error amplifier output of Buck1 and compensation node for voltage-loop stability. The voltage at this node sets the target for the peak current through the respective inductor. Clamping this voltage on the upper and lower ends provides current-limit protection for the external MOSFETs. |
| COMP2 | 29 | O | Error amplifier output of Buck2 and compensation node for voltage-loop stability. The voltage at this node sets the target for the peak current through the respective inductor. Clamping this voltage on the upper and lower ends provides current-limit protection for the external MOSFETs. |
| COMP3 | 18 | O | Error amplifier output of Buck3 and compensation node for voltage loop stability. The voltage at this node sets the target for the peak current through the respective inductor. |
| EN1 | 22 | I | Enable input for Buck1. This input has an internal pullup with approximately 0.5 µA of current. |
| EN2 | 21 | I | Enable input for Buck2. This input has an internal pullup with approximately 0.5 µA of current. |
| EN3 | 20 | I | Enable input for Buck3. This input has an internal pullup with approximately 0.5 µA of current. |
| EN4 | 47 | I | Enable input for LREG1 (active-high with an internal pullup current source). An input voltage higher than VIH enables the regulator, whereas an input voltage lower than VIL disables the regulator. This input has an internal pullup with approximately 0.5 µA of current. |
| EXTSUP | 40 | I | One can use EXTSUP to supply the VREG regulator from one of theTPS43340 buck regulator rails to reduce power dissipation in cases where there is an expectation of high VIN. When EXTSUP is open or lower than 4.6 V, VIN powers the regulator. If EXTSUP is unused, leave the pin open without a capacitor installed. |
| GL1 | 3 | O | External low-side N-channel MOSFET gate drive for buck regulator Buck1. The output provides high peak currents to drive capacitive loads. VREG provides the voltage swing on this pin. |
| GL2 | 34 | O | External low-side N-channel MOSFET for buck regulator This output can drive Buck2. The output provides high peak currents to drive capacitive loads. VREG provides the voltage swing on this pin. |
| GND | 26 | O | Analog ground reference |
| GPULL | 39 | O | Gate-driver output to implement the reverse-battery protection by an external PMOS. See the Application Information section for more details. |
| GU1 | 1 | O | External high-side N-channel MOSFET gate drive for buck regulator Buck1. The output provides high peak currents to drive capacitive loads. The gate-drive reference is a floating-ground reference provided by PH1 and has a voltage swing provided by BOOT1. |
| GU2 | 36 | O | This output can drive an external high-side N-channel MOSFET for buck regulator Buck2. The output provides high peak currents to drive capacitive loads. The gate-drive reference is a floating-ground reference provided by PH2 and has a voltage swing provided by BOOT2. |
| LREG1 | 46 | O | Linear regulator output. Decouple with a low-ESR ceramic output capacitor in the range of 1 µF to 47 µF connected from this terminal to ground. |
| PGND1 | 4 | O | Power ground connection for the GL1 driver. Connect to the source of the low-side N-channel MOSFET of Buck1. |
| PGND2 | 33 | O | Power ground connection to the source of the low-side N-channel MOSFETs of Buck2 |
| PGND3 | 12 | O | Buck3 power ground |
| PH1 | 2 | O | Switching terminal of buck regulator Buck1, providing a floating ground reference for the high-side MOSFET gate-driver circuitry and used to sense current reversal in the inductor when discontinuous-mode operation is desirable. |
| PH2 | 35 | O | Switching terminal of buck regulator Buck2, providing a floating ground reference for the high-side MOSFET gate-driver circuitry and used to sense current reversal in the inductor when discontinuous-mode operation is desirable. |
| PH3 | 13 | O | Switching terminal of buck converter Buck3. Also provides a floating ground reference for the high-side MOSFET gate-driver circuitry |
| Rdelay | 24 | O | The capacitor at the Rdelay pin sets the power-good delay interval used to de-glitch the outputs of the power-good comparators. Leaving this pin open sets the power-good delay to an internal default value of 20 μs, typical. |
| RST1 | 9 | O | Open-drain power-good output for Buck1, with a 50-kΩ pullup resistor to S2. An internal power-good comparator monitors the voltage at the feedback pin and pulls this output low when the output voltage falls by RSTxth1 of the set value. |
| RST2 | 28 | O | Open-drain power-good output for Buck2 with a 50 kΩ pullup resistor to S4. An internal power-good comparator monitors the voltage at the feedback pin and pulls this output low when the output voltage falls by RSTxth1 of the set value. |
| RST3 | 16 | O | Open-drain power-good output for Buck3. An internal power-good comparator monitors the voltage at the feedback pin and pulls this output low when the output voltage falls by RSTxth1 of the set value. |
| RST4 | 44 | O | Open-drain power-good indicator pin for LREG1, with a 50-kΩ pullup resistor to LREG1. An internal power-good comparator monitors the voltage at the feedback pin and pulls this output low when the output voltage falls by RSTxth1 of the set value. |
| RT | 25 | O | Connecting a resistor to analog ground on this pin sets the operating switching frequency of the buck controllers and converter. Shorting this pin to ground or leaving it open defaults operation to 400 kHz for the buck controllers and the converter. |
| S1 | 6 | I | High-impedance differential-voltage inputs from the current-sense element (sense resistor or inductor DCR) for the buck controller. For details, see the Functional Description section. |
| S2 | 5 | I | |
| S3 | 31 | I | |
| S4 | 32 | I | |
| SLEW | 19 | I | Slew rate (dV/dt) selector of the internal high-side switching MOSFET for Buck3. For details, see the Application Information section. |
| SS1 | 10 | O | Soft-start or tracking input for buck controller Buck1. The buck controller regulates the VSENSE1 voltage to the lower of 0.8 V or the SS1 pin voltage. An internal pullup current source of 1 μA is present at the pin, and use of an appropriate capacitor connected here can set the soft-start ramp duration. Alternatively, use of a resistor divider from another supply can provide a tracking input to this pin. |
| SS2 | 27 | O | Soft-start or tracking input for buck controller Buck2. The buck controller regulates the VSENSE2 voltage to the lower of 0.8 V or the SS2 pin voltage. An internal pullup current source of 1 μA is present at the pin, and use of an appropriate capacitor connected here can set the soft-start ramp interval. Alternatively, use of a resistor divider from another supply can provide a tracking input to this pin. |
| SS3 | 15 | O | Soft-start or tracking input for buck converter Buck3. The buck converter regulates the VSENSE3 voltage to the lower of 0.8 V or the SS3 pin voltage. An internal pullup current source of 1 μA is present at the pin, and an appropriate capacitor connected here can set the soft-start ramp duration. Alternatively, use of a resistor divider from another supply can provide a tracking input to this pin. |
| SYNC | 23 | I | PLL synchronization, low-power mode-control pin. If an external clock is present on this pin, the device detects it and the internal PLL locks on to the external clock. This overrides the internal oscillator frequency. The device can synchronize to frequencies from 150 kHz to 600 kHz. For details, see the Application Information section. |
| VIN | 41 | I | Main Input pin. This is the buck controller and buck converter input pin. Additionally, it powers the internal control circuits of the device. Connect a bypass capacitor to filter noise between this pin and signal ground. |
| VIN2SENSE | 43 | I | Supply-voltage sense input for the current mode of Buck2. Connect to the drain of the high-side-FET of Buck2. Cascading Buck1 as the supply for the Buck2 configuration does not support LPM on Buck2. |
| VLR1 | 42 | I | The VLR1 terminal is the input voltage source for the linear regulator supply. This pin requires an input capacitor to ground to filter any noise present on the line. |
| VREG | 38 | O | This pin requires an external capacitor to provide a regulated supply for the gate drivers of the buck controllers and converter. The regulator can obtain power either from VIN or EXTSUP. This pin has current limit-protection; do not use it to drive any other loads. |
| VSENSE1 | 7 | I | Feedback voltage pin for Buck1. For details, see the Application Information section. |
| VSENSE2 | 30 | I | Feedback voltage pin for Buck2. The buck controller regulates the feedback voltage to the internal reference of 0.8 V. A suitable resistor divider network between the buck output and the feedback pin sets the desired output voltage. |
| VSENSE3 | 17 | I | Feedback voltage pin for Buck3. The buck controller regulates the feedback voltage to the internal reference of 0.8 V. A suitable resistor divider network between the buck output and the feedback pin sets the desired output voltage. |
| VSENSE4 | 45 | I | Feedback voltage pin for linear regulator LREG1. LREG1 regulates the feedback voltage to the internal reference. A suitable resistor divider network between the LDO output and the feedback pin sets the desired output voltage. See the LREG1 parameters and the Application Information section. |
| VSUP | 11 | I | Power supply for the Buck3 regulator. Provide good decoupling to PGND3 with a ceramic capacitor close to the pins. |