-
Space-Grade, 100-krad, Isolated Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) LVDS Circuit SNOAA58 October 2020 DS26F31MQML-SP , DS26F32MQML-SP , SN55LVDS31-SP , SN55LVDS33-SP
Space-Grade, 100-krad, Isolated Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) LVDS Circuit
Design Goals
| Parameter | Design Requirement |
|---|---|
| Maximum Bit Rate | ≥ 100 kbit/s |
| Isolation Voltage | ≥ ±100 V |
| Maximum Cable Length | ≥ 5 m |
| Maximum Total Ionizing Dose | ≥ 100krad (Si) |
| Maximum SEL | ≥ 75MeV-cm2/mg |
Design Description
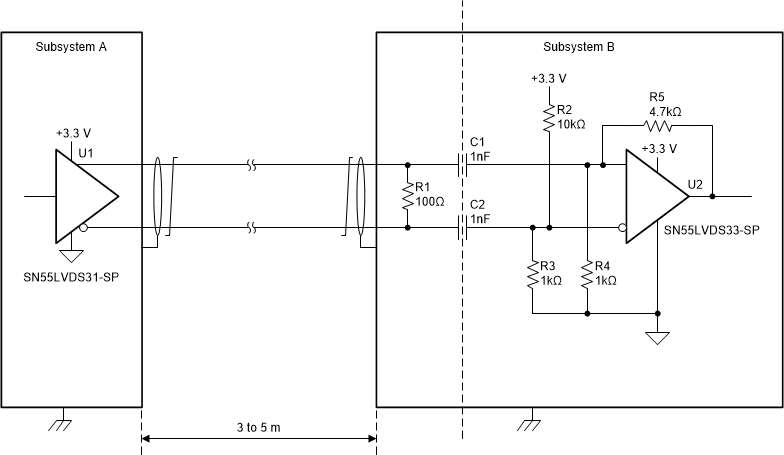
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is commonly used in embedded systems to connect microcontrollers to peripheral devices such as ADCs and DACs. It is often used in spacecraft applications, and sometimes an isolated SPI implementation is necessary to preserve the spacecraft grounding principles or to support DC offsets. The following circuit uses the SN55LVDS31-SP and SN55LVDS33-SP RS-422 driver and receiver devices to implement one channel of an isolated SPI. Isolation is provided by the AC-coupling capacitors, whose voltage rating determines the level of isolation supported.
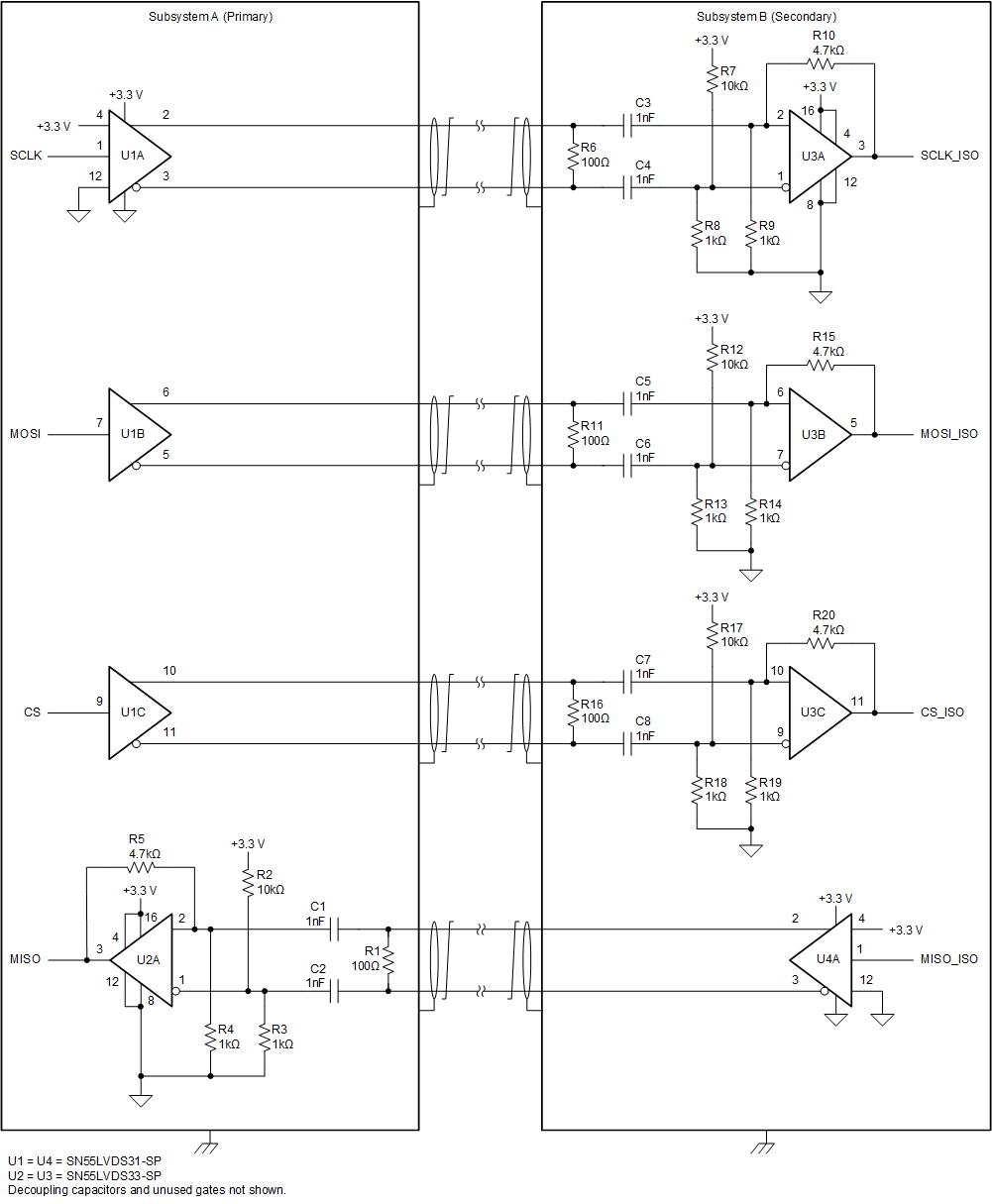
Complete SPI Implementation
The following image is a typical four-signal SPI implementation. The circuit shown uses the SN55LVDS31-SP and SN55LVDS33-SP devices and a 3.3-V supply voltage.