SLVSA06K October 2009 – January 2022 DRV8824
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHD|28
- PWP|28
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.2 Current Regulation
The current through the motor windings is regulated by a fixed-frequency PWM current regulation, or current chopping. When an H-bridge is enabled, current rises through the winding at a rate dependent on the DC voltage and inductance of the winding. After the current hits the current chopping threshold, the bridge disables the current until the beginning of the next PWM cycle.
In stepping motors, current regulation is used to vary the current in the two windings in a semi-sinusoidal fashion to provide smooth motion.
The PWM chopping current is set by a comparator which compares the voltage across a current sense resistor connected to the xISEN pins, multiplied by a factor of 5, with a reference voltage. The reference voltage is input from the xVREF pins.
The full-scale (100%) chopping current is calculated in Equation 1.
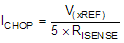
Example:
If a 0.5-Ω sense resistor is used and the xVREF pin is 3.3 V, the full-scale (100%) chopping current will be 3.3 V / (5 × 0.5 Ω) = 1.32 A.
The reference voltage is scaled by an internal DAC that allows fractional stepping of a bipolar stepper motor, as described in Section 7.3.5.