SLVS500D DECEMBER 2003 – June 2019 TPS54110
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Information
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Orderable Information
9.2.1.2.2 Input Capacitors
The TPS54110 requires an input decoupling capacitor and, depending on the application, a bulk input capacitor. The minimum value for the decoupling capacitor, C9, is 10 uF. A high quality ceramic type X5R or X7R with a voltage rating greater than the maximum input voltage is recommended. A bulk input capacitor may be needed, especially if the TPS54110 circuit is not located within approximately 2 inches from the input voltage source. The capacitance value is not critical, but the voltage rating must be greater than the maximum input voltage including ripple voltage. The capacitor must filter the input ripple voltage to acceptable levels.
Input ripple voltage can be approximated by Equation 5:
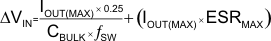
where
- IOUT(MAX) is the maximum load current
- ƒSW is the switching frequency
- CBULK is the bulk capacitor value
- ESRMAX is the maximum series resistance of the bulk capacitor
Worst-case RMS ripple current is approximated by Equation 6:
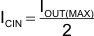
In this case the input ripple voltage is 66 mV with a 10-µF bulk capacitor. Figure 14 shows the measured ripple waveform. The RMS ripple current is 0.75 A. The maximum voltage across the input capacitors is VINMAX + ΔVIN/2. The bypass capacitor and input bulk capacitor are each rated for 6.3 V and a ripple-current capacity of 1.5 A, providing some margin. It is very important that the maximum ratings for voltage and current are not exceeded under any circumstance.