SBOS392H August 2007 – August 2019 REF3312 , REF3318 , REF3320 , REF3325 , REF3330 , REF3333
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
-
10Applications and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1
REF3312 in a Bipolar Signal-Chain Configuration
- 10.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 10.2.1
REF3312 in a Bipolar Signal-Chain Configuration
- 11Power-Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
10.2.1.2.6 Input Filtering
The MSP430 ADC is configured to run from the 1.1-MHz SMCLK with an oversampling rate (OSR) of 256, yielding a sample rate of roughly 4.3 kHz. The input filter cutoff frequency is set to 1 kHz in order to limit the input signal bandwidth, as shown in Equation 17. R8 is 1 kΩ in order to provide isolation from the capacitive load of the low-pass filter, thereby reducing stability concerns.
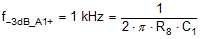
where
Reduce C1 to 150 nF so that it is a standard value.
The A1– input of the delta-sigma (ΔΣ) converter is not buffered, and therefore requires a large capacitor to supply the charge for the internal sampling capacitor. A 47-μF capacitor is selected, resulting in the cutoff frequency illustrated in Equation 18.

In applications that cannot tolerate such a low-frequency cutoff, and therefore a long start-up time, buffer the A1– input with another OPA317 to properly drive the ADC input with a lower-input capacitor.
