JAJSCH0D August 2016 – January 2018 TPS25741 , TPS25741A
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 USB Type-C CC Logic (CC1, CC2)
- 8.3.2 9.3.2 VCONN Supply (VCONN, CC1, CC2)
- 8.3.3 USB Power Delivery BMC Transmission (CC1, CC2, VTX)
- 8.3.4 USB Power Delivery BMC Reception (CC1, CC2)
- 8.3.5 Discharging (DSCG, VPWR)
- 8.3.6 Configuring Voltage Capabilities (HIPWR, EN9V, EN12V)
- 8.3.7 Configuring Power Capabilities (PSEL, PCTRL, HIPWR)
- 8.3.8 Gate Drivers
- 8.3.9 Fault Monitoring and Protection
- 8.3.10 Voltage Control (CTL1, CTL2)
- 8.3.11 Sink Attachment Indicator (UFP, DVDD)
- 8.3.12 Accessory Attachment Indicator (AUDIO, DEBUG)
- 8.3.13 Plug Polarity Indication (POL)
- 8.3.14 Power Supplies (VAUX, VDD, VPWR, DVDD)
- 8.3.15 Grounds (AGND, GND)
- 8.3.16 Output Power Supply (DVDD)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RSM|32
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RSM|32
発注情報
8.1 Overview
The TPS25741/TPS25741A and supporting circuits perform the functions required to implement a USB Power Delivery 2.0 Power Delivery as a provider-only and a USB Type-C revision 1.2 source. It uses its CC pins to detect the attachment of a sinking device or upward facing port (UFP) and to determine which of CC1 or CC2 is connected to the CC wire of the cable. It will then communicate over the CC wire in the cable bundle using USB Power Delivery to offer a set of voltages and currents. USB Power Delivery is a technology that utilizes the ubiquitous USB communications and hardware infrastructure to extend the amount of power available to devices from the 7.5 W range for USB BC1.2 to as high as 100 W in a dock. It is a compatible overlay to USB 2.0 and USB 3.0, coexisting with the existing 5 V powered universe of devices by use of adapter cables. Some basic characteristics of this technology relevant to the TPS25741/TPS25741A include:
- Increased power achieved by providing higher current and/or higher voltage.
- New 3 A cable and 5 A connector to support greater than the traditional 1.5 A.
- Cables have controlled voltage drop
- Voltages greater than 5 V are negotiated between Power Delivery partners.
- Standard 5 V is always the default source voltage.
- Voltage and current provisions are negotiated between Power Delivery partners.
- Power Delivery partners negotiate over the CC line to avoid conflict with existing signaling (that is, D+, D-)
- Layered communication protocol defined including PHY, Protocol Layer, Policy Engine, and Device Policy Manager all implemented within the TPS25741/TPS25741A.
- The Type-C connector standard implements pre-powerup signaling to determine:
- Connector orientation
- Source 5-V capability
- Detect through connection of a UFP (upward facing port) to a DFP (downward facing port)
- Detection of when the connected UFP is disconnected. VBUS is unpowered until a through-connection is present
Figure 20, Figure 21, and Figure 22 show typical configurations for the TPS25741/TPS25741A.
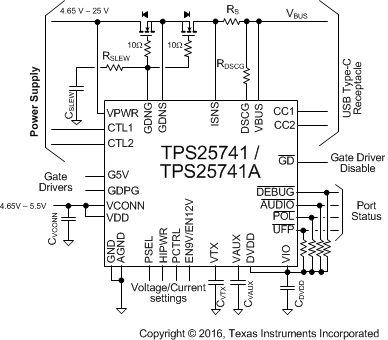 Figure 20. Reference Schematic 1
Figure 20. Reference Schematic 1
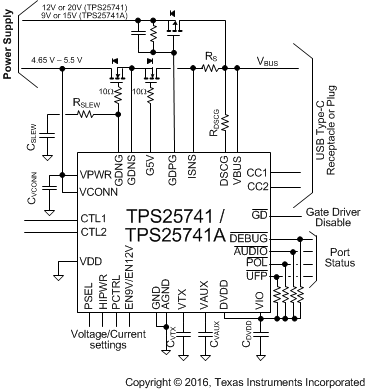 Figure 21. Reference Schematic 2
Figure 21. Reference Schematic 2
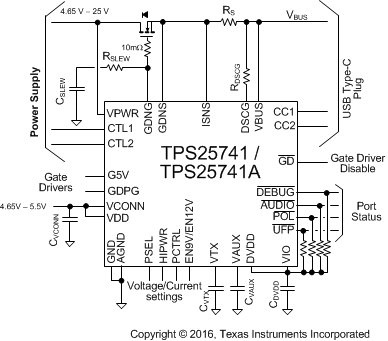 Figure 22. Reference Schematic 3
Figure 22. Reference Schematic 3