JAJSCH0D August 2016 – January 2018 TPS25741 , TPS25741A
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 USB Type-C CC Logic (CC1, CC2)
- 8.3.2 9.3.2 VCONN Supply (VCONN, CC1, CC2)
- 8.3.3 USB Power Delivery BMC Transmission (CC1, CC2, VTX)
- 8.3.4 USB Power Delivery BMC Reception (CC1, CC2)
- 8.3.5 Discharging (DSCG, VPWR)
- 8.3.6 Configuring Voltage Capabilities (HIPWR, EN9V, EN12V)
- 8.3.7 Configuring Power Capabilities (PSEL, PCTRL, HIPWR)
- 8.3.8 Gate Drivers
- 8.3.9 Fault Monitoring and Protection
- 8.3.10 Voltage Control (CTL1, CTL2)
- 8.3.11 Sink Attachment Indicator (UFP, DVDD)
- 8.3.12 Accessory Attachment Indicator (AUDIO, DEBUG)
- 8.3.13 Plug Polarity Indication (POL)
- 8.3.14 Power Supplies (VAUX, VDD, VPWR, DVDD)
- 8.3.15 Grounds (AGND, GND)
- 8.3.16 Output Power Supply (DVDD)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RSM|32
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RSM|32
発注情報
9.1.3 Resistor Divider on GD for Programmable Start Up
Figure 44 shows an alternative usage of the GD pin can help protect against shorts on the VBUS pin in the receptacle. A resistor divider is used to minimize the time it takes the GD pin to be pulled low. Consider the situation where the VBUS pin is shorted at startup. At some point, the device closes the NFET switch to supply 5 V to VBUS. At that point, the short pulls down on the voltage seen at the VPWR pin. With the resistor values shown in Figure 44, once the voltage at the VPWR pin reaches 3.95 V the voltage at the GD pin is specified to be below VGD_TH(min). Without the 700-kΩ resistor, the voltage at the VPWR pin would have to reach VGD_TH(min) which takes longer. This comes at the expense of increased leakage current.
 Figure 44. Programmable GD Turn On
Figure 44. Programmable GD Turn On
The GD resistor values can be calculated using the following process. First, calculate the smallest RGD1 that should be used to prevent the internal clamp current from exceeding IGD of 80 µA. For a 20 V advertised voltage, the OVP trip point could be as high as 24 V. Using VGDC(min) = 6.5 V and VOUT = VFOVP20(max) = 24 V, provides Equation 2:
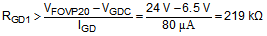
The actual clamping current is less than 80 µA as some current flows into RGD2. Next, RGD2 can be calculated as follows:

where V(VPWR) = V(PWR_TH) falling (max) and V(GD_TH) = V(GD_TH) falling (min).
For this case, VVPWR = VPWR_TH falling (max) and VGD_TH = VGD_TH falling (min).