JAJSEQ9E November 2013 – December 2017 TPS56520 , TPS56720 , TPS56920 , TPS56C20
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 List of Devices
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Applications and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 14メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PWP|20
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PWP|20
発注情報
10.2.1.2.1.1 Output Filter Selection
The output filter used with the TPS56X20 is an LC circuit. This LC filter has double pole at:
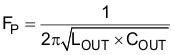
At low frequencies, the overall loop gain is set by the output set-point resistor divider network and the internal gain of the TPS56X20. The low frequency phase is 180 degrees. At the output filter pole frequency, the gain rolls off at a –40 dB per decade rate and the phase drops rapidly. D-CAP2™ introduces a high frequency zero that reduces the gain roll off to –20 dB per decade and increases the phase to 90 degrees one decade above the zero frequency. The inductor and capacitor selected for the output filter must be selected so that the double pole of Equation 4 is located below the high frequency zero but close enough that the phase boost provided be the high frequency zero provides adequate phase margin for a stable circuit. To meet this requirement use the values recommended in Table 5.
Table 5. Recommended Component Values
| Output Voltage (V) | R5 (kΩ) | R6 (kΩ) | C8 (pF)(1) | L1 (µH) | C7 (µF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 14.7 | 22 | DNP | 1.0-2.2 | 44-100 |
| 1.1 | 18.2 | 22 | DNP | 1.0-2.2 | 44-100 |
| 1.2 | 22 | 22 | DNP | 1.0-2.2 | 44-100 |
| 1.5 | 33 | 22 | DNP | 1.0-2.2 | 44-100 |
| 1.8 | 44.2 | 22 | DNP | 1.0-2.2 | 44-100 |
For higher output voltages additional phase boost can be achieved by adding a feed forward capacitor (C6) in parallel with R5.
The inductor peak-to-peak ripple current, peak current and RMS current are calculated using Equation 5, Equation 6 and Equation 7. The inductor saturation current rating must be greater than the calculated peak current and the RMS or heating current rating must be greater than the calculated RMS current. Use 500 kHz for fSW.
Use 500 kHz for fSW. Make sure the chosen inductor is rated for the peak current of Equation 6 and the RMS current of Equation 7.
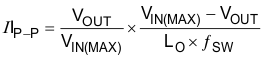
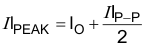
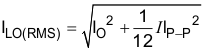
The capacitor value and ESR determines the amount of output voltage ripple. The TPS56X20 is intended for use with ceramic or other low ESR capacitors. Recommended values range from 44µF to 100µF. Use Equation 8 to determine the required RMS current rating for the output capacitor.