JAJSLH2 March 2021 TPS62810M , TPS62811M , TPS62812M , TPS62813M
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RWY|9
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RWY|9
発注情報
9.3.2 COMP/FSET
This pin lets the user set two different parameters independently:
- Internal compensation settings for the control loop
- The switching frequency in PWM mode from 1.8 MHz to 4 MHz
A resistor from COMP/FSET to GND changes the compensation and switching frequency. The change in compensation allows the user to adapt the device to different values of output capacitance. The resistor must be placed close to the pin to keep the parasitic capacitance on the pin to a minimum. The compensation setting is sampled when the converter starts up, so a change in the resistor during operation only has an effect on the switching frequency, but not on the compensation.
To save external components, the pin can also be directly tied to VIN or GND to set a pre-defined switching frequency or compensation. Do not leave the pin floating.
The switching frequency has to be selected based on the input voltage and the output voltage to meet the specifications for the minimum on time and minimum off time.
For example: VIN = 5 V, VOUT = 1 V --> duty cycle (DC) = 1 V / 5 V = 0.2
- with ton = DC × T --> ton,min = 1 / fs,max × DC
- --> fs,max = 1 / ton,min × DC = 1 / 0.075 µs × 0.2 = 2.67 MHz
The compensation range has to be chosen based on the minimum capacitance used. The capacitance can be increased from the minimum value as given in Table 9-1 and Table 9-2, up to a maximum of 470 µF in all of the three compensation ranges. If the capacitance of an output changes during operation, for example, when load switches are used to connect or disconnect parts of the circuitry, the compensation must be chosen for the minimum capacitance on the output. With large output capacitance, the compensation must be done based on that large capacitance to get the best load transient response. Compensating for large output capacitance, but placing less capacitance on the output, can lead to instability.
The switching frequency for the different compensation settings is determined by the following equations.
For compensation (comp) setting 1:
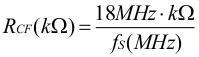
For compensation (comp) setting 2:
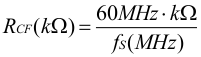
For compensation (comp) setting 3:
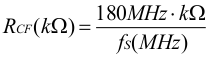
| COMPENSATION | RCF | SWITCHING FREQUENCY | MINIMUM OUTPUT CAPACITANCE FOR VOUT < 1 V | MINIMUM OUTPUT CAPACITANCE FOR 1 V ≤ VOUT < 3.3 V | MINIMUM OUTPUT CAPACITANCE FOR VOUT ≥ 3.3 V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for the smallest output capacitance (comp setting 1) | 10 kΩ ... 4.5 kΩ | 1.8 MHz (10 kΩ) ... 4 MHz (4.5 kΩ) according to Equation 1 | 53 µF | 32 µF | 27 µF |
| for medium output capacitance (comp setting 2) | 33 kΩ ... 15 kΩ | 1.8 MHz (33 kΩ) ... 4 MHz (15 kΩ) according to Equation 2 | 100 µF | 60 µF | 50 µF |
| for large output capacitance (comp setting 3) | 100 kΩ ... 45 kΩ | 1.8 MHz (100 kΩ) ... 4 MHz (45 kΩ) according to Equation 3 | 200 µF | 120 µF | 100 µF |
| for the smallest output capacitance (comp setting 1) | tied to GND | internally fixed 2.25 MHz | 53 µF | 32 µF | 27 µF |
| for large output capacitance (comp setting 3) | tied to VIN | internally fixed 2.25 MHz | 200 µF | 120 µF | 100 µF |
| COMPENSATION | RCF | SWITCHING FREQUENCY | MINIMUM OUTPUT CAPACITANCE FOR VOUT < 1 V | MINIMUM OUTPUT CAPACITANCE FOR 1 V ≤ VOUT < 3.3 V | MINIMUM OUTPUT CAPACITANCE FOR VOUT ≥ 3.3 V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for the smallest output capacitance (comp setting 1) | 10 kΩ ... 4.5 kΩ | 1.8 MHz (10 kΩ) ... 4 MHz (4.5 kΩ) according to Equation 1 | 30 µF | 18 µF | 15 µF |
| for medium output capacitance (comp setting 2) | 33 kΩ ... 15 kΩ | 1.8 MHz (33 kΩ) ... 4 MHz (15 kΩ) according to Equation 2 | 60 µF | 36 µF | 30 µF |
| for large output capacitance (comp setting 3) | 100 kΩ ... 45 kΩ | 1.8MHz (100 kΩ) ...4 MHz (45 kΩ) according to Equation 3 | 130 µF | 80 µF | 68 µF |
| for the smallest output capacitance (comp setting 1) | tied to GND | internally fixed 2.25 MHz | 30 µF | 18 µF | 15 µF |
| for large output capacitance (comp setting 3) | tied to VIN | internally fixed 2.25 MHz | 130 µF | 80 µF | 68 µF |
Refer to Section 10.1.3.2 for further details on the required output capacitance required depending on the output voltage.
A too-high resistor value for RCF is decoded as "tied to VIN". A value below the lowest range is decoded as "tied to GND". The minimum output capacitance in Table 9-1 and Table 9-2 is for capacitors close to the output of the device. If the capacitance is distributed, a lower compensation setting can be required. All values are effective capacitance including, but not limited to:
- All tolerances
- Aging
- DC bias effect