SNVAA16 May 2021 TPS548A28 , TPS548A29 , TPS548B28 , TPS54JA20 , TPS54JB20
2 DC/DC Converters with External Bias
Several DC/DC converters on the market have an additional pin that accepts an externally applied voltage, such as the TPS548A28 and TPS548A29 shown in Table 2-1. An external bias voltage, also called a split-bias rail voltage, above the internal LDO's output voltage will override the internal LDO and enhance the efficiency of the converter by eliminating its power loss. The VCC current will be supplied from the external bias instead of the internal LDO. Figure 2-1 shows an external bias voltage applied to the VCC pin allowing a lower input voltage into the VIN pins. The VCC pin needs to be bypassed with a 2.2 μF ceramic capacitor, CVCC with a 6.3-V or higher rating as shown in Figure 1-1 and Figure 2-1. The external VCC voltage is supplied by a separate DC/DC converter or connected directly from an existing 3.3-V or 5-V voltage source already available on the circuit board.
| Device | Output Current | Internal LDO Voltage | External Bias Voltage Range | Power Stage Voltage Range with External Bias Voltage | Power Stage Voltage Range with Internal LDO Voltage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPS548A28 | 15-A | 3-V | 3.13-V to 5.3-V | 2.7-V to 16-V | 4-V to 16-V |
| TPS548A29 | 15-A | 4.5-V | 4.75-V to 5.3-V | 2.7-V to 16V | 4-V to 16-V |
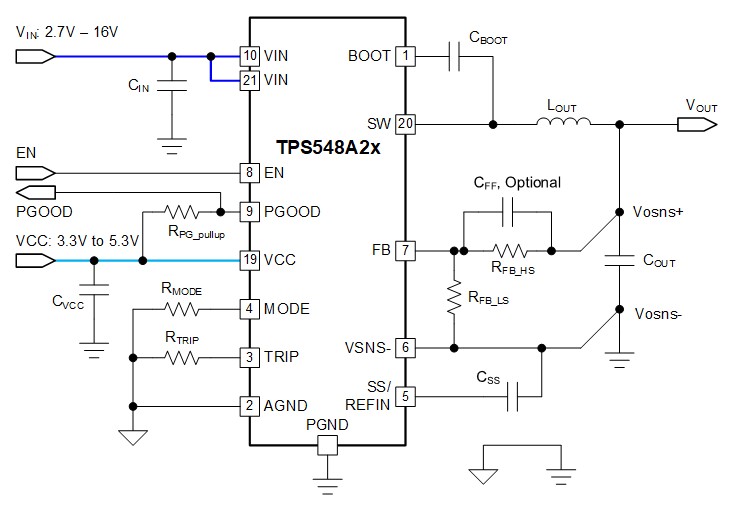 Figure 2-1 Typical DC/DC Converter with Split-Bias Rail Input Voltages
Figure 2-1 Typical DC/DC Converter with Split-Bias Rail Input Voltages