SSZT482 May 2019 LM4132-Q1 , TPS3703-Q1 , TPS3850-Q1 , TPS3890-Q1
Many safety related automotive systems are required to meet Automotive Safety Integrity Level (ASIL) as defined by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 26262.
It is a common misconception that integrated circuits (ICs) not developed following the ISO 26262 standards cannot be used to achieve functional safety goals. Many automotive OEMs have been able to use the features and reliability of non-ASIL compliant semiconductor devices to develop systems that target ASIL requirements. In this post, it will be demonstrated how both voltage references and supervisors can help you achieve ASIL compliance for your automotive systems.
Voltage References and Supervisors
 Figure 1 System-level Design Assumptions for SEooC Based on ISO 26262
Figure 1 System-level Design Assumptions for SEooC Based on ISO 26262Features and Mechanisms of Voltage Reference and Supervisors
 Figure 2 Window Watchdog Timing Diagram
Figure 2 Window Watchdog Timing DiagramDevice Functional Safety Collateral
Automotive Reference Designs with Functional Safety Considerations
Figure 3 describes how the TPS3703-Q1 detects overvoltage and undervoltage. For potential clocking failures, the TPS3850-Q1 doubles as an overvoltage/under-voltage monitor and window watchdog timer which is illustrated in Figure 2 and Figure 3. It also has the flexibility of changing the watchdog timeout and window ratio and disabling the watchdog timer. In cases where only undervoltage monitoring is necessary, the TPS3890-Q1 can provide accurate voltage monitoring at a very low quiescent current to save system power consumption. Last but not least, the LM4132-Q1 provides precision voltage to reference the ADC for voltage monitoring. With 0.05% initial accuracy and low temperature drifts of 10 ppm/°C, the LM4132-Q1 solves accurate voltage monitoring at a low supply current cost of 60 µA.
 Figure 3 Under-voltage and Over-voltage Window Detector Timing Diagram
Figure 3 Under-voltage and Over-voltage Window Detector Timing DiagramAccommodating the ISO 26262 Standard in the ADAS Power Reference Design
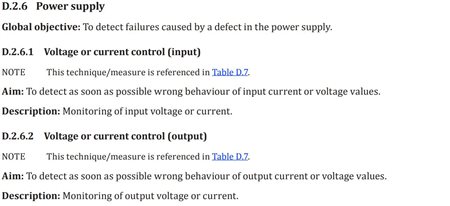
 Figure 4 Safety Mechanism Examples for Power-supply and Watchdog Failures Based on ISO 26262
Figure 4 Safety Mechanism Examples for Power-supply and Watchdog Failures Based on ISO 26262The voltage supervisors and references used in this reference design can provide an additional layer of safety by providing extra diagnostic coverage, safety mechanisms or redundant safety monitoring. The product’s performance and functionality of detecting faults can help achieve functional safety goals in automotive systems. Additionally, TI can provide collateral to improve time-to-market for system integrators.
Additional Resources
- For more information on why watchdog timers are important, read the blog post, “What is a watchdog timer and why is it important?”